DNAshape: a method for the high-throughput prediction of DNA structural features on a genomic scale
- PMID: 23703209
- PMCID: PMC3692085
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkt437
DNAshape: a method for the high-throughput prediction of DNA structural features on a genomic scale
Abstract
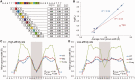
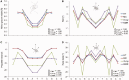
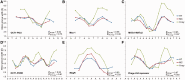
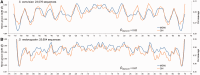
We present a method and web server for predicting DNA structural features in a high-throughput (HT) manner for massive sequence data. This approach provides the framework for the integration of DNA sequence and shape analyses in genome-wide studies. The HT methodology uses a sliding-window approach to mine DNA structural information obtained from Monte Carlo simulations. It requires only nucleotide sequence as input and instantly predicts multiple structural features of DNA (minor groove width, roll, propeller twist and helix twist). The results of rigorous validations of the HT predictions based on DNA structures solved by X-ray crystallography and NMR spectroscopy, hydroxyl radical cleavage data, statistical analysis and cross-validation, and molecular dynamics simulations provide strong confidence in this approach. The DNAshape web server is freely available at http://rohslab.cmb.usc.edu/DNAshape/.
Figures
Similar articles
-
GBshape: a genome browser database for DNA shape annotations.Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Jan;43(Database issue):D103-9. doi: 10.1093/nar/gku977. Epub 2014 Oct 17. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015. PMID: 25326329 Free PMC article.
-
Deep DNAshape webserver: prediction and real-time visualization of DNA shape considering extended k-mers.Nucleic Acids Res. 2024 Jul 5;52(W1):W7-W12. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkae433. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024. PMID: 38801070 Free PMC article.
-
Systematic prediction of DNA shape changes due to CpG methylation explains epigenetic effects on protein-DNA binding.Epigenetics Chromatin. 2018 Feb 6;11(1):6. doi: 10.1186/s13072-018-0174-4. Epigenetics Chromatin. 2018. PMID: 29409522 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide prediction of minor-groove electrostatic potential enables biophysical modeling of protein-DNA binding.Nucleic Acids Res. 2017 Dec 1;45(21):12565-12576. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx915. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017. PMID: 29040720 Free PMC article.
-
Predicting conformational ensembles and genome-wide transcription factor binding sites from DNA sequences.Sci Rep. 2017 Jun 22;7(1):4071. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-03199-6. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28642456 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
High-resolution profiling of Drosophila replication start sites reveals a DNA shape and chromatin signature of metazoan origins.Cell Rep. 2015 May 5;11(5):821-34. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2015.03.070. Epub 2015 Apr 23. Cell Rep. 2015. PMID: 25921534 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative modeling of gene expression using DNA shape features of binding sites.Nucleic Acids Res. 2016 Jul 27;44(13):e120. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw446. Epub 2016 Jun 1. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016. PMID: 27257066 Free PMC article.
-
Computational challenges in modeling gene regulatory events.Transcription. 2016 Oct 19;7(5):188-195. doi: 10.1080/21541264.2016.1204491. Epub 2016 Jul 8. Transcription. 2016. PMID: 27390891 Free PMC article.
-
How motif environment influences transcription factor search dynamics: Finding a needle in a haystack.Bioessays. 2016 Jul;38(7):605-12. doi: 10.1002/bies.201600005. Epub 2016 May 19. Bioessays. 2016. PMID: 27192961 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Satb1 integrates DNA binding site geometry and torsional stress to differentially target nucleosome-dense regions.Nat Commun. 2019 Jul 19;10(1):3221. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-11118-8. Nat Commun. 2019. PMID: 31324780 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

