Profiling epidermal growth factor receptor and heregulin receptor 3 heteromerization using receptor tyrosine kinase heteromer investigation technology
- PMID: 23700486
- PMCID: PMC3659105
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0064672
Profiling epidermal growth factor receptor and heregulin receptor 3 heteromerization using receptor tyrosine kinase heteromer investigation technology
Abstract
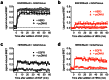
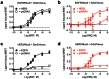
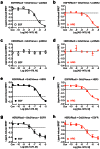
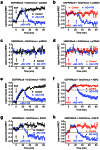
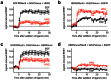
Heteromerization can play an important role in regulating the activation and/or signal transduction of most forms of receptors, including receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs). The study of receptor heteromerization has evolved extensively with the emergence of resonance energy transfer based approaches such as bioluminescence resonance energy transfer (BRET). Here, we report an adaptation of our Receptor-Heteromer Investigation Technology (Receptor-HIT) that has recently been published as the G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) Heteromer Identification Technology (GPCR-HIT). We now demonstrate the utility of this approach for investigating RTK heteromerization by examining the functional interaction between the epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptor (EGFR; also known as erbB1/HER1) and heregulin (HRG) receptor 3 (HER3; also known as erbB3) in live HEK293FT cells using recruitment of growth factor receptor-bound protein 2 (Grb2) to the activated receptors. We found that EGFR and HER3 heteromerize specifically as demonstrated by HRG inducing a BRET signal between EGFR/Rluc8 and Grb2/Venus only when HER3 was co-expressed. Similarly, EGF stimulation promoted a specific BRET signal between HER3/Rluc8 and Grb2/Venus only when EGFR was co-expressed. Both EGF and HRG effects on Grb2 interaction are dose-dependent, and specifically blocked by EGFR inhibitor AG-1478. Furthermore, truncation of HER3 to remove the putative Grb2 binding sites appears to abolish EGF-induced Grb2 recruitment to the EGFR-HER3 heteromer. Our results support the concept that EGFR interacts with Grb2 in both constitutive and EGF-dependent manners and this interaction is independent of HER3 co-expression. In contrast, HER3-Grb2 interaction requires the heteromerization between EGFR and HER3. These findings clearly indicate the importance of EGFR-HER3 heteromerization in HER3-mediated Grb2-dependent signaling pathways and supports the central role of HER3 in the diversity and regulation of HER family functioning.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
BRET-based assay to monitor EGFR transactivation by the AT1R reveals Gq/11 protein-independent activation and AT1R-EGFR complexes.Biochem Pharmacol. 2018 Dec;158:232-242. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2018.10.017. Epub 2018 Oct 19. Biochem Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 30347205 Free PMC article.
-
Epidermal growth factor receptor, c-erbB2 and c-erbB3 receptor interaction, and related cell cycle kinetics of SK-BR-3 and BT474 breast carcinoma cells.Cytometry. 2001 Aug 1;44(4):338-48. doi: 10.1002/1097-0320(20010801)44:4<338::aid-cyto1125>3.0.co;2-v. Cytometry. 2001. PMID: 11500850
-
Quantification and kinetic analysis of Grb2-EGFR interaction on micro-patterned surfaces for the characterization of EGFR-modulating substances.PLoS One. 2014 Mar 21;9(3):e92151. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0092151. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24658383 Free PMC article.
-
ErbB Receptors and Cancer.Methods Mol Biol. 2017;1652:3-35. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-7219-7_1. Methods Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 28791631 Review.
-
Internalization of the epidermal growth factor receptor: role in signalling.Biochem Soc Trans. 2001 Aug;29(Pt 4):480-4. doi: 10.1042/bst0290480. Biochem Soc Trans. 2001. PMID: 11498013 Review.
Cited by
-
Differential Effects of Camel Milk on Insulin Receptor Signaling - Toward Understanding the Insulin-Like Properties of Camel Milk.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2016 Jan 27;7:4. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2016.00004. eCollection 2016. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2016. PMID: 26858689 Free PMC article.
-
Biophysical Detection of Diversity and Bias in GPCR Function.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2014 Mar 5;5:26. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2014.00026. eCollection 2014. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2014. PMID: 24634666 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Quantifying the Interaction between EGFR Dimers and Grb2 in Live Cells.Biophys J. 2017 Sep 19;113(6):1353-1364. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2017.06.029. Epub 2017 Jul 19. Biophys J. 2017. PMID: 28734476 Free PMC article.
-
HER-3 targeting alters the dimerization pattern of ErbB protein family members in breast carcinomas.Oncotarget. 2016 Feb 2;7(5):5576-97. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.6762. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 26716646 Free PMC article.
-
Investigation of Receptor Heteromers Using NanoBRET Ligand Binding.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jan 22;22(3):1082. doi: 10.3390/ijms22031082. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33499147 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kamath S, Buolamwini JK (2006) Targeting EGFR and HER-2 receptor tyrosine kinases for cancer drug discovery and development. Med Res Rev 26: 569–594. - PubMed
-
- Yarden Y, Sliwkowski MX (2001) Untangling the ErbB signalling network. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2: 127–137. - PubMed
-
- Hynes NE, MacDonald G (2009) ErbB receptors and signaling pathways in cancer. Curr Opin Cell Biol 21: 177–184. - PubMed
-
- Linggi B, Carpenter G (2006) ErbB receptors: new insights on mechanisms and biology. Trends Cell Biol 16: 649–656. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

