Probing the structure and dynamics of confined water in AOT reverse micelles
- PMID: 23687916
- PMCID: PMC3709849
- DOI: 10.1021/jp402270e
Probing the structure and dynamics of confined water in AOT reverse micelles
Abstract
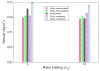
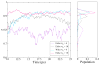
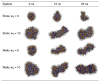
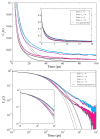
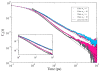
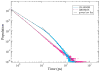
Reverse micelles are attractive nanoscale systems used for the confinement of molecules in studies of structure and chemical reactions, including protein folding, and aggregation. The simulation of reverse micelles, in which a water "pool" is separated from a nonpolar bulk phase by a surfactant layer, poses significant challenges to empirical force fields due to the diversity of interactions between nonpolar, polar, and charged groups. We have explored the dependence of system density, reverse micelle structure, and water configurational relaxation times as a function of reverse micelle composition, including water:surfactant ratio, absolute number of water molecules, and force field using molecular dynamics simulations. The resulting structures and dynamics are found to depend more on the force field used than on varying interpretations of the water:surfactant ratio in terms of absolute size of the reverse micelle. Substantial deviations from spherical reverse micelle geometries are observed in all unrestrained simulations. Rotational anisotropy decay times and water residence times show a strong dependence on force field and water model used, but power-law relaxation in time is observed independent of the force field. Our results suggest the need for further experimental study of reverse micelles that can provide insight into the distribution and dynamics of shape fluctuations in these complex systems.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Exploring the role of hydration and confinement in the aggregation of amyloidogenic peptides Aβ(16-22) and Sup35(7-13) in AOT reverse micelles.J Chem Phys. 2014 Dec 14;141(22):22D530. doi: 10.1063/1.4902550. J Chem Phys. 2014. PMID: 25494801 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Charge and Solvation in the Structure and Dynamics of Alanine-Rich Peptide AKA2 in AOT Reverse Micelles.J Phys Chem B. 2015 Jul 23;119(29):9084-90. doi: 10.1021/jp508813n. Epub 2014 Nov 6. J Phys Chem B. 2015. PMID: 25337983 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamics of water at the interface in reverse micelles: measurements of spectral diffusion with two-dimensional infrared vibrational echoes.J Phys Chem B. 2011 Oct 13;115(40):11658-70. doi: 10.1021/jp206903k. Epub 2011 Sep 22. J Phys Chem B. 2011. PMID: 21899355
-
Geometry and nanolength scales versus interface interactions: water dynamics in AOT lamellar structures and reverse micelles.J Am Chem Soc. 2009 Jun 17;131(23):8318-28. doi: 10.1021/ja901950b. J Am Chem Soc. 2009. PMID: 19449867
-
Integrating cellular and molecular structures and dynamics into whole-cell models.Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2022 Aug;75:102392. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2022.102392. Epub 2022 May 24. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2022. PMID: 35623188 Review.
Cited by
-
Confinement Effects on Reorientation Dynamics of Water Confined within Graphite Nanoslits.J Phys Chem B. 2024 Oct 3;128(39):9525-9535. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcb.4c03898. Epub 2024 Sep 22. J Phys Chem B. 2024. PMID: 39307993 Free PMC article.
-
Mutual Relationships of Nanoconfined Hexoses: Impacts on Hydrodynamic Radius and Anomeric Ratios.Langmuir. 2024 Oct 8;40(40):20918-20926. doi: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.4c01826. Epub 2024 Sep 22. Langmuir. 2024. PMID: 39306762 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Different States of Solubilized Water on Solvation Dynamics and Rotational Relaxation of Coumarin 490 in Reverse Micelles of Gemini Surfactants, Water/12-s-12.2Br- (s = 5, 6, 8)/n-Propanol/Cyclohexane.ACS Omega. 2020 Mar 17;5(12):6738-6753. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.0c00035. eCollection 2020 Mar 31. ACS Omega. 2020. PMID: 32258909 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Dynamics Simulations of Amyloid β-Peptide (1-42): Tetramer Formation and Membrane Interactions.Biophys J. 2016 Sep 6;111(5):937-49. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2016.08.001. Biophys J. 2016. PMID: 27602722 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the role of hydration and confinement in the aggregation of amyloidogenic peptides Aβ(16-22) and Sup35(7-13) in AOT reverse micelles.J Chem Phys. 2014 Dec 14;141(22):22D530. doi: 10.1063/1.4902550. J Chem Phys. 2014. PMID: 25494801 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hoar T, Schulman J. Transparent Water-in-Oil Dispersions: The Oleopathic Hydro-Micelle. Nature. 1943;152:102–103.
-
- Levinger NE. Water in Confinement. Science. 2002;298:1722–1723. - PubMed
-
- Thompson KF, Gierasch LM. Conformation of a Peptide Solubilizate in a Reversed Micelle Water Pool. J Am Chem Soc. 1984;106:3648–3652.
-
- Mukherjee S, Chowdhury P, Gai F. Tuning the Cooperativity of the Helix-Coil Transition by Aqueous Reverse Micelles. J Phys Chem B. 2006;110:11615–11619. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

