Neuroprotectin/protectin D1 protects against neuropathic pain in mice after nerve trauma
- PMID: 23686636
- PMCID: PMC3791159
- DOI: 10.1002/ana.23928
Neuroprotectin/protectin D1 protects against neuropathic pain in mice after nerve trauma
Abstract
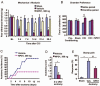
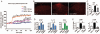
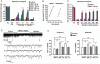
Prevalence of neuropathic pain is high after major surgery. However, effective treatment for preventing neuropathic pain is lacking. Here we report that perisurgical treatment of neuroprotectin D1/protectin D1 (NPD1/PD1), derived from docosahexaenoic acid, prevents nerve injury-induced mechanical allodynia and ongoing pain in mice. Intrathecal post-treatment of NPD1/PD1 also effectively reduces established neuropathic pain and produces no apparent signs of analgesic tolerance. Mechanistically, NPD1/PD1 treatment blocks nerve injury-induced long-term potentiation, glial reaction, and inflammatory responses, and reverses synaptic plasticity in the spinal cord. Thus, NPD1/PD1 and related mimetics might serve as a new class of analgesics for preventing and treating neuropathic pain.
Copyright © 2013 American Neurological Association.
Figures
Similar articles
-
NPD1 Relieves Neuropathic Pain and Accelerates the Recovery of Motor Function After Peripheral Nerve Injury.Pain Res Manag. 2024 Oct 30;2024:1109287. doi: 10.1155/2024/1109287. eCollection 2024. Pain Res Manag. 2024. PMID: 39512892 Free PMC article.
-
Resolving TRPV1- and TNF-α-mediated spinal cord synaptic plasticity and inflammatory pain with neuroprotectin D1.J Neurosci. 2011 Oct 19;31(42):15072-85. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2443-11.2011. J Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 22016541 Free PMC article.
-
The role of keratinocyte-derived chemokine (KC) on hyperalgesia caused by peripheral nerve injury in mice.Neuropharmacology. 2014 Apr;79:17-27. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2013.10.026. Epub 2013 Nov 1. Neuropharmacology. 2014. PMID: 24184386
-
Neuropathic Pain: Sensory Nerve Injury or Motor Nerve Injury?Adv Exp Med Biol. 2016;904:59-75. doi: 10.1007/978-94-017-7537-3_5. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2016. PMID: 26900063 Review.
-
Microglial regulation of neuropathic pain.J Pharmacol Sci. 2013;121(2):89-94. doi: 10.1254/jphs.12r14cp. Epub 2013 Jan 22. J Pharmacol Sci. 2013. PMID: 23337437 Review.
Cited by
-
Optogenetic Activation of Peripheral Somatosensory Neurons in Transgenic Mice as a Neuropathic Pain Model for Assessing the Therapeutic Efficacy of Analgesics.ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2023 Dec 13;7(1):236-248. doi: 10.1021/acsptsci.3c00254. eCollection 2024 Jan 12. ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2023. PMID: 38230281 Free PMC article.
-
GPR37 regulates macrophage phagocytosis and resolution of inflammatory pain.J Clin Invest. 2018 Aug 1;128(8):3568-3582. doi: 10.1172/JCI99888. Epub 2018 Jul 16. J Clin Invest. 2018. PMID: 30010619 Free PMC article.
-
Ratio of Omega-6/Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids Associated With Somatic and Depressive Symptoms in People With Painful Temporomandibular Disorder and Irritable Bowel Syndrome.J Pain. 2022 Oct;23(10):1737-1748. doi: 10.1016/j.jpain.2022.04.006. Epub 2022 Apr 25. J Pain. 2022. PMID: 35477107 Free PMC article.
-
Dietary alteration of n-3 and n-6 fatty acids for headache reduction in adults with migraine: randomized controlled trial.BMJ. 2021 Jun 30;374:n1448. doi: 10.1136/bmj.n1448. BMJ. 2021. PMID: 34526307 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Spinal CCL2 Promotes Central Sensitization, Long-Term Potentiation, and Inflammatory Pain via CCR2: Further Insights into Molecular, Synaptic, and Cellular Mechanisms.Neurosci Bull. 2018 Feb;34(1):13-21. doi: 10.1007/s12264-017-0106-5. Epub 2017 Mar 6. Neurosci Bull. 2018. PMID: 28265898 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hong S, Gronert K, Devchand PR, et al. Novel docosatrienes and 17S-resolvins generated from docosahexaenoic acid in murine brain, human blood, and glial cells. Autacoids in anti-inflammation. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:14677–14687. - PubMed
-
- Marcheselli VL, Hong S, Lukiw WJ, et al. Novel docosanoids inhibit brain ischemiareperfusion-mediated leukocyte infiltration and pro-inflammatory gene expression. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:43807–43817. - PubMed
-
- Serhan CN, Gotlinger K, Hong S, et al. Anti-inflammatory actions of neuroprotectin D1/protectin D1 and its natural stereoisomers: assignments of dihydroxy-containing docosatrienes. J Immunol. 2006;176:1848–1859. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

