Danger signalling during cancer cell death: origins, plasticity and regulation
- PMID: 23686135
- PMCID: PMC3858605
- DOI: 10.1038/cdd.2013.48
Danger signalling during cancer cell death: origins, plasticity and regulation
Abstract
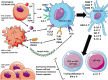
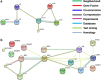
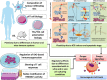
Accumulating data indicates that following anti-cancer treatments, cancer cell death can be perceived as immunogenic or tolerogenic by the immune system. The former is made possible due to the ability of certain anti-cancer modalities to induce immunogenic cell death (ICD) that is associated with the emission of damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs), which assist in unlocking a sequence of events leading to the development of anti-tumour immunity. In response to ICD inducers, activation of endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress has been identified to be indispensable to confer the immunogenic character of cancer cell death, due to its ability to coordinate the danger signalling pathways responsible for the trafficking of vital DAMPs and subsequent anti-cancer immune responses. However, in recent times, certain processes apart from ER stress have emerged (e.g., autophagy and possibly viral response-like signature), which have the ability to influence danger signalling. In this review, we discuss the molecular nature, emerging plasticity in the danger signalling mechanisms and immunological impact of known DAMPs in the context of immunogenic cancer cell death. We also discuss key effector mechanisms modulating the interface between dying cancer cells and the immune cells, which we believe are crucial for the therapeutic relevance of ICD in the context of human cancers, and also discuss the influence of experimental conditions and animal models on these.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The PERKs of damage-associated molecular patterns mediating cancer immunogenicity: From sensor to the plasma membrane and beyond.Semin Cancer Biol. 2015 Aug;33:74-85. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2015.03.010. Epub 2015 Apr 13. Semin Cancer Biol. 2015. PMID: 25882379 Review.
-
Cancer immunogenicity, danger signals, and DAMPs: what, when, and how?Biofactors. 2013 Jul-Aug;39(4):355-67. doi: 10.1002/biof.1125. Epub 2013 Jul 31. Biofactors. 2013. PMID: 23900966 Review.
-
Inducers of immunogenic cancer cell death.Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2013 Aug;24(4):319-33. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2013.01.005. Epub 2013 Feb 5. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2013. PMID: 23391812 Review.
-
Stress-induced cellular responses in immunogenic cell death: Implications for cancer immunotherapy.Biochem Pharmacol. 2018 Jul;153:12-23. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2018.02.006. Epub 2018 Feb 10. Biochem Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29438676 Review.
-
Cell death and immunity in cancer: From danger signals to mimicry of pathogen defense responses.Immunol Rev. 2017 Nov;280(1):126-148. doi: 10.1111/imr.12574. Immunol Rev. 2017. PMID: 29027218 Review.
Cited by
-
Honokiol confers immunogenicity by dictating calreticulin exposure, activating ER stress and inhibiting epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition.Mol Oncol. 2015 Apr;9(4):834-49. doi: 10.1016/j.molonc.2014.12.009. Epub 2015 Jan 6. Mol Oncol. 2015. PMID: 25619450 Free PMC article.
-
Neutrophil: A Cell with Many Roles in Inflammation or Several Cell Types?Front Physiol. 2018 Feb 20;9:113. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2018.00113. eCollection 2018. Front Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29515456 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Trial Watch: Chemotherapy with immunogenic cell death inducers.Oncoimmunology. 2014 Jan 1;3(1):e27878. doi: 10.4161/onci.27878. Epub 2014 Mar 1. Oncoimmunology. 2014. PMID: 24800173 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploiting the Immunogenic Potential of Cancer Cells for Improved Dendritic Cell Vaccines.Front Immunol. 2016 Jan 14;6:663. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2015.00663. eCollection 2015. Front Immunol. 2016. PMID: 26834740 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Feto-Maternal Trafficking of Exosomes in Murine Pregnancy Models.Front Pharmacol. 2016 Nov 15;7:432. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2016.00432. eCollection 2016. Front Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27895585 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Krysko DV, Garg AD, Kaczmarek A, Krysko O, Agostinis P, Vandenabeele P. Immunogenic cell death and DAMPs in cancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 2012;12:860–875. - PubMed
-
- Kroemer G, Galluzzi L, Kepp O, Zitvogel L. Immunogenic cell death in cancer therapy. Annu Rev Immunol. 2012;31:51–72. - PubMed
-
- Gregory CD, Pound JD. Cell death in the neighbourhood: direct microenvironmental effects of apoptosis in normal and neoplastic tissues. J Pathol. 2010;223:177–194. - PubMed
-
- Garg AD, Nowis D, Golab J, Vandenabeele P, Krysko DV, Agostinis P. Immunogenic cell death, DAMPs and anticancer therapeutics: an emerging amalgamation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010;1805:53–71. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

