Advanced proteomic analyses yield a deep catalog of ubiquitylation targets in Arabidopsis
- PMID: 23667124
- PMCID: PMC3694690
- DOI: 10.1105/tpc.112.108613
Advanced proteomic analyses yield a deep catalog of ubiquitylation targets in Arabidopsis
Abstract
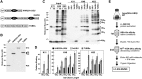
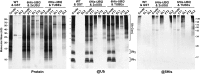
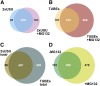
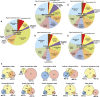
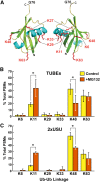
The posttranslational addition of ubiquitin (Ub) profoundly controls the half-life, interactions, and/or trafficking of numerous intracellular proteins. Using stringent two-step affinity methods to purify Ub-protein conjugates followed by high-sensitivity mass spectrometry, we identified almost 950 ubiquitylation substrates in whole Arabidopsis thaliana seedlings. The list includes key factors regulating a wide range of biological processes, including metabolism, cellular transport, signal transduction, transcription, RNA biology, translation, and proteolysis. The ubiquitylation state of more than half of the targets increased after treating seedlings with the proteasome inhibitor MG132 (carbobenzoxy-Leu-Leu-Leu-al), strongly suggesting that Ub addition commits many to degradation by the 26S proteasome. Ub-attachment sites were resolved for a number of targets, including six of the seven Lys residues on Ub itself with a Lys-48>Lys-63>Lys-11>>>Lys-33/Lys-29/Lys-6 preference. However, little sequence consensus was detected among conjugation sites, indicating that the local environment has little influence on global ubiquitylation. Intriguingly, the level of Lys-11-linked Ub polymers increased substantially upon MG132 treatment, revealing that they might be important signals for proteasomal breakdown. Taken together, this proteomic analysis illustrates the breadth of plant processes affected by ubiquitylation and provides a deep data set of individual targets from which to explore the roles of Ub in various physiological and developmental pathways.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Ubiquitylome analysis reveals a central role for the ubiquitin-proteasome system in plant innate immunity.Plant Physiol. 2021 Apr 23;185(4):1943-1965. doi: 10.1093/plphys/kiab011. Plant Physiol. 2021. PMID: 33793954 Free PMC article.
-
Ubiquitin-Mediated Proteasomal Degradation of Oleosins is Involved in Oil Body Mobilization During Post-Germinative Seedling Growth in Arabidopsis.Plant Cell Physiol. 2015 Jul;56(7):1374-87. doi: 10.1093/pcp/pcv056. Epub 2015 Apr 22. Plant Cell Physiol. 2015. PMID: 25907570
-
Mass Spectrometric Analyses Reveal a Central Role for Ubiquitylation in Remodeling the Arabidopsis Proteome during Photomorphogenesis.Mol Plant. 2017 Jun 5;10(6):846-865. doi: 10.1016/j.molp.2017.04.008. Epub 2017 Apr 28. Mol Plant. 2017. PMID: 28461270 Free PMC article.
-
Ubiquitylation of ABA Receptors and Protein Phosphatase 2C Coreceptors to Modulate ABA Signaling and Stress Response.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jul 1;22(13):7103. doi: 10.3390/ijms22137103. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34281157 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The complexity of recognition of ubiquitinated substrates by the 26S proteasome.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014 Jan;1843(1):86-96. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2013.07.007. Epub 2013 Jul 18. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014. PMID: 23872423 Review.
Cited by
-
Autophagic Degradation of the 26S Proteasome Is Mediated by the Dual ATG8/Ubiquitin Receptor RPN10 in Arabidopsis.Mol Cell. 2015 Jun 18;58(6):1053-66. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2015.04.023. Epub 2015 May 21. Mol Cell. 2015. PMID: 26004230 Free PMC article.
-
Advanced Cataloging of Lysine-63 Polyubiquitin Networks by Genomic, Interactome, and Sensor-Based Proteomic Analyses.Plant Cell. 2020 Jan;32(1):123-138. doi: 10.1105/tpc.19.00568. Epub 2019 Nov 11. Plant Cell. 2020. PMID: 31712406 Free PMC article.
-
Advanced Proteomic Approaches to Elucidate Somatic Embryogenesis.Front Plant Sci. 2018 Nov 20;9:1658. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2018.01658. eCollection 2018. Front Plant Sci. 2018. PMID: 30524454 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The E3 Ligase GmPUB21 Negatively Regulates Drought and Salinity Stress Response in Soybean.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jun 21;23(13):6893. doi: 10.3390/ijms23136893. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35805901 Free PMC article.
-
The Ubiquitin Conjugating Enzyme: An Important Ubiquitin Transfer Platform in Ubiquitin-Proteasome System.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Apr 21;21(8):2894. doi: 10.3390/ijms21082894. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32326224 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Baunsgaard L., Fuglsang A.T., Jahn T., Korthout H.A., de Boer A.H., Palmgren M.G. (1998). The 14-3-3 proteins associate with the plant plasma membrane H(+)-ATPase to generate a fusicoccin binding complex and a fusicoccin responsive system. Plant J. 13: 661–671 - PubMed
-
- Book A.J., Smalle J., Lee K.H., Yang P., Walker J.M., Casper S., Holmes J.H., Russo L.A., Buzzinotti Z.W., Jenik P.D., Vierstra R.D. (2009). The RPN5 subunit of the 26S proteasome is essential for gametogenesis, sporophyte development, and complex assembly in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 21: 460–478 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chevalier D., Walker J.C. (2005). Functional genomics of protein kinases in plants. Brief. Funct. Genomics Proteomics 3: 362–371 - PubMed
-
- Colaert N., Helsens K., Martens L., Vandekerckhove J., Gevaert K. (2009). Improved visualization of protein consensus sequences by iceLogo. Nat. Methods 6: 786–787 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

