LAMP1/CD107a is required for efficient perforin delivery to lytic granules and NK-cell cytotoxicity
- PMID: 23632890
- PMCID: PMC3674668
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2012-08-453738
LAMP1/CD107a is required for efficient perforin delivery to lytic granules and NK-cell cytotoxicity
Abstract
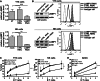
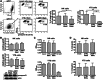
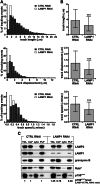
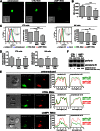
Secretory lysosomes of natural killer (NK) cells, containing perforin and granzymes, are indispensable for NK-cell cytotoxicity because their release results in the induction of target-cell apoptosis. Lysosome-associated membrane protein (LAMP) 1/CD107a is used as a marker for NK-cell degranulation, but its role in NK-cell biology is unknown. We show that LAMP1 silencing causes inhibition of NK-cell cytotoxicity, as LAMP1 RNA interference (RNAi) cells fail to deliver granzyme B to target cells. Reduction of LAMP1 expression affects the movement of lytic granules and results in decreased levels of perforin, but not granzyme B, in the granules. In LAMP1 RNAi cells, more perforin is retained outside of lysosomal compartments in trans-Golgi network-derived transport vesicles. Disruption of expression of LAMP1 binding partner, adaptor protein 1 (AP-1) sorting complex, also causes retention of perforin in the transport vesicles and inhibits cytotoxicity, indicating that the interaction between AP-1 sorting complex and LAMP1 on the surface of the transport vesicles is important for perforin trafficking to lytic granules. We conclude that the decreased level of perforin in lytic granules of LAMP1-deficient cells, combined with disturbed motility of the lytic granules, leads to the inability to deliver apoptosis-inducing granzyme B to target cells and to inhibition of NK-cell cytotoxicity.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Natural Killer Cell Group 7 Sequence in Cytotoxic Cells Optimizes Exocytosis of Lytic Granules Essential for the Perforin-Dependent, but Not Fas Ligand-Dependent, Cytolytic Pathway.Immunohorizons. 2021 Apr 28;5(4):234-245. doi: 10.4049/immunohorizons.2100029. Immunohorizons. 2021. PMID: 33911019
-
Fas Ligand localizes to intraluminal vesicles within NK cell cytolytic granules and is enriched at the immune synapse.Immun Inflamm Dis. 2018 Jun;6(2):312-321. doi: 10.1002/iid3.219. Epub 2018 Apr 11. Immun Inflamm Dis. 2018. PMID: 29642281 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanistic peculiarities of activation-induced mobilization of cytotoxic effector proteins in human T cells.Int Immunol. 2018 Apr 25;30(5):215-228. doi: 10.1093/intimm/dxy007. Int Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29373679
-
Lytic granules, secretory lysosomes and disease.Curr Opin Immunol. 2003 Oct;15(5):516-21. doi: 10.1016/s0952-7915(03)00113-4. Curr Opin Immunol. 2003. PMID: 14499259 Review.
-
TRP Channels as Interior Designers: Remodeling the Endolysosomal Compartment in Natural Killer Cells.Front Immunol. 2020 Apr 28;11:753. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.00753. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32411146 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Polymicrobial sepsis influences NK-cell-mediated immunity by diminishing NK-cell-intrinsic receptor-mediated effector responses to viral ligands or infections.PLoS Pathog. 2018 Oct 31;14(10):e1007405. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1007405. eCollection 2018 Oct. PLoS Pathog. 2018. PMID: 30379932 Free PMC article.
-
Human natural killer cells mediate adaptive immunity to viral antigens.Sci Immunol. 2019 May 10;4(35):eaat8116. doi: 10.1126/sciimmunol.aat8116. Sci Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31076527 Free PMC article.
-
Annexins-Coordinators of Cholesterol Homeostasis in Endocytic Pathways.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 May 12;19(5):1444. doi: 10.3390/ijms19051444. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29757220 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Potential Role of Fc-Receptor Functions in the Development of a Universal Influenza Vaccine.Vaccines (Basel). 2018 May 17;6(2):27. doi: 10.3390/vaccines6020027. Vaccines (Basel). 2018. PMID: 29772781 Free PMC article.
-
CD8+ T Cell Biology in Cytokine Storm Syndromes.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2024;1448:129-144. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-59815-9_10. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2024. PMID: 39117812 Review.
References
-
- Vivier E, Tomasello E, Baratin M, Walzer T, Ugolini S. Functions of natural killer cells. Nat Immunol. 2008;9(5):503-510. - PubMed
-
- Voskoboinik I, Smyth MJ, Trapani JA. Perforin-mediated target-cell death and immune homeostasis. Nat Rev Immunol. 2006;6(12):940–952. - PubMed
-
- Pipkin ME, Lieberman J. Delivering the kiss of death: progress on understanding how perforin works. Curr Opin Immunol. 2007;19(3):301–308. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

