Human cytomegalovirus pUL97 regulates the viral major immediate early promoter by phosphorylation-mediated disruption of histone deacetylase 1 binding
- PMID: 23616659
- PMCID: PMC3700266
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.02825-12
Human cytomegalovirus pUL97 regulates the viral major immediate early promoter by phosphorylation-mediated disruption of histone deacetylase 1 binding
Abstract
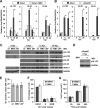
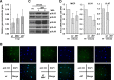
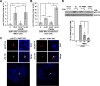
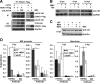
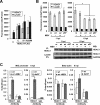
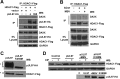
Human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) is a common agent of congenital infection and causes severe disease in immunocompromised patients. Current approved therapies focus on inhibiting viral DNA replication. The HCMV kinase pUL97 contributes to multiple stages of viral infection including DNA replication, controlling the cell cycle, and virion maturation. Our studies demonstrate that pUL97 also functions by influencing immediate early (IE) gene expression during the initial stages of infection. Inhibition of kinase activity using the antiviral compound maribavir or deletion of the UL97 gene resulted in decreased expression of viral immediate early genes during infection. Expression of pUL97 was sufficient to transactivate IE1 gene expression from the viral genome, which was dependent on viral kinase activity. We observed that pUL97 associates with histone deacetylase 1 (HDAC1). HDAC1 is a transcriptional corepressor that acts to silence expression of viral genes. We observed that inhibition or deletion of pUL97 kinase resulted in increased HDAC1 and decreased histone H3 lysine 9 acetylation associating with the viral major immediate early (MIE) promoter. IE expression during pUL97 inhibition or deletion was rescued following inhibition of deacetylase activity. HDAC1 associates with chromatin by protein-protein interactions. Expression of active but not inactive pUL97 kinase decreased HDAC1 interaction with the transcriptional repressor protein DAXX. Finally, using mass spectrometry, we found that HDAC1 is uniquely phosphorylated upon expression of pUL97. Our results support the conclusion that HCMV pUL97 kinase regulates viral immediate early gene expression by phosphorylation-mediated disruption of HDAC1 binding to the MIE promoter.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Antagonistic Relationship between Human Cytomegalovirus pUL27 and pUL97 Activities during Infection.J Virol. 2015 Oct;89(20):10230-46. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00986-15. Epub 2015 Jul 29. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 26223645 Free PMC article.
-
Human cytomegalovirus UL29/28 protein interacts with components of the NuRD complex which promote accumulation of immediate-early RNA.PLoS Pathog. 2010 Jun 24;6(6):e1000965. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1000965. PLoS Pathog. 2010. PMID: 20585571 Free PMC article.
-
Differential properties of cytomegalovirus pUL97 kinase isoforms affect viral replication and maribavir susceptibility.J Virol. 2014 May;88(9):4776-85. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00192-14. Epub 2014 Feb 12. J Virol. 2014. PMID: 24522923 Free PMC article.
-
The Cytomegalovirus Protein Kinase pUL97:Host Interactions, Regulatory Mechanisms and Antiviral Drug Targeting.Microorganisms. 2020 Apr 4;8(4):515. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms8040515. Microorganisms. 2020. PMID: 32260430 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical development of letermovir and maribavir: Overview of human cytomegalovirus drug resistance.Antiviral Res. 2019 Mar;163:91-105. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2019.01.011. Epub 2019 Jan 25. Antiviral Res. 2019. PMID: 30690043 Review.
Cited by
-
A conserved gammaherpesvirus protein kinase targets histone deacetylases 1 and 2 to facilitate viral replication in primary macrophages.J Virol. 2013 Jul;87(13):7314-25. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02713-12. Epub 2013 Apr 24. J Virol. 2013. PMID: 23616648 Free PMC article.
-
Human Cytomegalovirus Compromises Development of Cerebral Organoids.J Virol. 2019 Aug 13;93(17):e00957-19. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00957-19. Print 2019 Sep 1. J Virol. 2019. PMID: 31217239 Free PMC article.
-
Bright and Early: Inhibiting Human Cytomegalovirus by Targeting Major Immediate-Early Gene Expression or Protein Function.Viruses. 2020 Jan 16;12(1):110. doi: 10.3390/v12010110. Viruses. 2020. PMID: 31963209 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Insights into the Transcriptome of Human Cytomegalovirus: A Comprehensive Review.Viruses. 2023 Aug 8;15(8):1703. doi: 10.3390/v15081703. Viruses. 2023. PMID: 37632045 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human cytomegalovirus UL97 phosphorylates the viral nuclear egress complex.J Virol. 2015 Jan;89(1):523-34. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02426-14. Epub 2014 Oct 22. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 25339763 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mocarski E, Pass TSRF. 2007. Cytomegaloviruses, p 2702–2772 In Knipe DM, Howley PM, Griffin DE, Lamb RA, Martin MA, Roizman B, Straus SE. (ed), Fields virology, 5th ed Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia, PA
-
- Littler E, Stuart AD, Chee MS. 1992. Human cytomegalovirus UL97 open reading frame encodes a protein that phosphorylates the antiviral nucleoside analogue ganciclovir. Nature 358:160–162 - PubMed
-
- Sullivan V, Talarico CL, Stanat SC, Davis M, Coen DM, Biron KK. 1992. A protein kinase homologue controls phosphorylation of ganciclovir in human cytomegalovirus-infected cells. Nature 359:85. - PubMed
-
- van Zeijl M, Fairhurst J, Baum EZ, Sun L, Jones TR. 1997. The human cytomegalovirus UL97 protein is phosphorylated and a component of virions. Virology 231:72–80 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

