β-Amyloid (Aβ) oligomers impair brain-derived neurotrophic factor retrograde trafficking by down-regulating ubiquitin C-terminal hydrolase, UCH-L1
- PMID: 23599427
- PMCID: PMC3675626
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M113.463711
β-Amyloid (Aβ) oligomers impair brain-derived neurotrophic factor retrograde trafficking by down-regulating ubiquitin C-terminal hydrolase, UCH-L1
Abstract
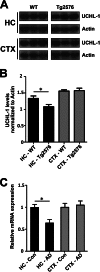
We previously found that BDNF-dependent retrograde trafficking is impaired in AD transgenic mouse neurons. Utilizing a novel microfluidic culture chamber, we demonstrate that Aβ oligomers compromise BDNF-mediated retrograde transport by impairing endosomal vesicle velocities, resulting in impaired downstream signaling driven by BDNF/TrkB, including ERK5 activation, and CREB-dependent gene regulation. Our data suggest that a key mechanism mediating the deficit involves ubiquitin C-terminal hydrolase L1 (UCH-L1), a deubiquitinating enzyme that functions to regulate cellular ubiquitin. Aβ-induced deficits in BDNF trafficking and signaling are mimicked by LDN (an inhibitor of UCH-L1) and can be reversed by increasing cellular UCH-L1 levels, demonstrated here using a transducible TAT-UCH-L1 strategy. Finally, our data reveal that UCH-L1 mRNA levels are decreased in the hippocampi of AD brains. Taken together, our data implicate that UCH-L1 is important for regulating neurotrophin receptor sorting to signaling endosomes and supporting retrograde transport. Further, our results support the idea that in AD, Aβ may down-regulate UCH-L1 in the AD brain, which in turn impairs BDNF/TrkB-mediated retrograde signaling, compromising synaptic plasticity and neuronal survival.
Keywords: Alzheimer Disease; Amyloid; BDNF; Microfluidic Device; Trafficking; Ubiquitin.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Ubiquitin C-Terminal Hydrolase L1 (UCH-L1) Promotes Hippocampus-Dependent Memory via Its Deubiquitinating Effect on TrkB.J Neurosci. 2017 Jun 21;37(25):5978-5995. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3148-16.2017. Epub 2017 May 12. J Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28500221 Free PMC article.
-
β-Amyloid impairs axonal BDNF retrograde trafficking.Neurobiol Aging. 2011 May;32(5):821-33. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2009.05.012. Epub 2009 Jun 21. Neurobiol Aging. 2011. PMID: 19540623 Free PMC article.
-
IL-1β impairs retrograde flow of BDNF signaling by attenuating endosome trafficking.J Neuroinflammation. 2017 Feb 2;14(1):29. doi: 10.1186/s12974-017-0803-z. J Neuroinflammation. 2017. PMID: 28153028 Free PMC article.
-
The functions of UCH-L1 and its relation to neurodegenerative diseases.Neurochem Int. 2007 Jul-Sep;51(2-4):105-11. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2007.05.007. Epub 2007 May 24. Neurochem Int. 2007. PMID: 17586089 Review.
-
Ubiquitin C-terminal hydrolase L1 (UCH-L1): structure, distribution and roles in brain function and dysfunction.Biochem J. 2016 Aug 15;473(16):2453-62. doi: 10.1042/BCJ20160082. Biochem J. 2016. PMID: 27515257 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF) Preserves the Functional Integrity of Neural Networks in the β-Amyloidopathy Model in vitro.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020 Jul 8;8:582. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.00582. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 32733889 Free PMC article.
-
The Amyloid-β Oligomer Hypothesis: Beginning of the Third Decade.J Alzheimers Dis. 2018;64(s1):S567-S610. doi: 10.3233/JAD-179941. J Alzheimers Dis. 2018. PMID: 29843241 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multi-compartment Microfluidic Device Geometry and Covalently Bound Poly-D-Lysine Influence Neuronal Maturation.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2019 May 7;7:84. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2019.00084. eCollection 2019. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2019. PMID: 31134192 Free PMC article.
-
Delta-secretase-cleaved Tau antagonizes TrkB neurotrophic signalings, mediating Alzheimer's disease pathologies.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019 Apr 30;116(18):9094-9102. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1901348116. Epub 2019 Apr 19. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019. PMID: 31004063 Free PMC article.
-
The Ubiquitin-Proteasome System: Potential Therapeutic Targets for Alzheimer's Disease and Spinal Cord Injury.Front Mol Neurosci. 2016 Jan 26;9:4. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2016.00004. eCollection 2016. Front Mol Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 26858599 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Näslund J., Haroutunian V., Mohs R., Davis K. L., Davies P., Greengard P., Buxbaum J. D. (2000) Correlation between elevated levels of amyloid β-peptide in the brain and cognitive decline. JAMA 283, 1571–1577 - PubMed
-
- McLean C. A., Cherny R. A., Fraser F. W., Fuller S. J., Smith M. J., Beyreuther K., Bush A. I., Masters C. L. (1999) Soluble pool of Aβ amyloid as a determinant of severity of neurodegeneration in Alzheimer's disease. Ann. Neurol. 46, 860–866 - PubMed
-
- Walsh D. M., Klyubin I., Fadeeva J. V., Cullen W. K., Anwyl R., Wolfe M. S., Rowan M. J., Selkoe D. J. (2002) Naturally secreted oligomers of amyloid β protein potently inhibit hippocampal long-term potentiation in vivo. Nature 416, 535–539 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

