Molecular mechanisms underlying RB protein function
- PMID: 23594950
- PMCID: PMC4754300
- DOI: 10.1038/nrm3567
Molecular mechanisms underlying RB protein function
Abstract
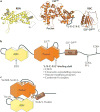
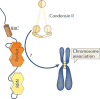
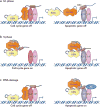
Inactivation of the RB protein is one of the most fundamental events in cancer. Coming to a molecular understanding of its function in normal cells and how it impedes cancer development has been challenging. Historically, the ability of RB to regulate the cell cycle placed it in a central role in proliferative control, and research focused on RB regulation of the E2F family of transcription factors. Remarkably, several recent studies have found additional tumour-suppressor functions of RB, including alternative roles in the cell cycle, maintenance of genome stability and apoptosis. These advances and new structural studies are combining to define the multifunctionality of RB.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
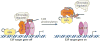

Similar articles
-
RB: mitotic implications of a tumour suppressor.Nat Rev Cancer. 2012 Feb 9;12(3):220-6. doi: 10.1038/nrc3216. Nat Rev Cancer. 2012. PMID: 22318235 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rb family-independent activating E2F increases genome stability, promotes homologous recombination, and decreases non-homologous end joining.Mech Dev. 2020 Jun;162:103607. doi: 10.1016/j.mod.2020.103607. Epub 2020 Mar 23. Mech Dev. 2020. PMID: 32217105 Free PMC article.
-
The Retinoblastoma (RB) Tumor Suppressor: Pushing Back against Genome Instability on Multiple Fronts.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Aug 16;18(8):1776. doi: 10.3390/ijms18081776. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28812991 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging roles of E2Fs in cancer: an exit from cell cycle control.Nat Rev Cancer. 2009 Nov;9(11):785-97. doi: 10.1038/nrc2696. Nat Rev Cancer. 2009. PMID: 19851314 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rb inactivation promotes genomic instability by uncoupling cell cycle progression from mitotic control.Nature. 2004 Aug 12;430(7001):797-802. doi: 10.1038/nature02820. Nature. 2004. PMID: 15306814
Cited by
-
Inhibition of Rb Phosphorylation Leads to mTORC2-Mediated Activation of Akt.Mol Cell. 2016 Jun 16;62(6):929-942. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2016.04.023. Epub 2016 May 26. Mol Cell. 2016. PMID: 27237051 Free PMC article.
-
p53 positively regulates the proliferation of hepatic progenitor cells promoted by laminin-521.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022 Aug 31;7(1):290. doi: 10.1038/s41392-022-01107-7. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022. PMID: 36042225 Free PMC article.
-
High-throughput functional annotation of natural products by integrated activity profiling.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022 Dec 6;119(49):e2208458119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2208458119. Epub 2022 Nov 30. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022. PMID: 36449542 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting Notch signaling as a novel therapy for retinoblastoma.Oncotarget. 2016 Oct 25;7(43):70028-70044. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.12142. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27661116 Free PMC article.
-
Origin of Cancer: Cell work is the Key to Understanding Cancer Initiation and Progression.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Mar 1;10:787995. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.787995. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35300431 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Friend SH, et al. A human DNA segment with properties of the gene that predisposes to retinoblastoma and osteosarcoma. Nature. 1986;323:643–646. - PubMed
-
- Classon M, Harlow E. The retinoblastoma tumour suppressor in development and cancer. Nature Rev Cancer. 2002;2:910–917. - PubMed
-
- Sherr CJ, McCormick F. The RB and p53 pathways in cancer. Cancer Cell. 2002;2:103–112. - PubMed
-
- van den Heuvel S, Dyson NJ. Conserved functions of the pRB and E2F families. Nature Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2008;9:713–724. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

