The CAMKK2-AMPK kinase pathway mediates the synaptotoxic effects of Aβ oligomers through Tau phosphorylation
- PMID: 23583109
- PMCID: PMC3784324
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2013.02.003
The CAMKK2-AMPK kinase pathway mediates the synaptotoxic effects of Aβ oligomers through Tau phosphorylation
Abstract
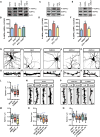
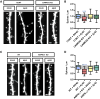
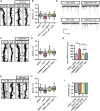
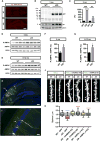
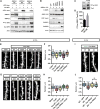
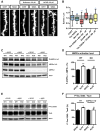
Amyloid-β 1-42 (Aβ42) oligomers are synaptotoxic for excitatory cortical and hippocampal neurons and might play a role in early stages of Alzheimer's disease (AD) progression. Recent results suggested that Aβ42 oligomers trigger activation of AMP-activated kinase (AMPK), and its activation is increased in the brain of patients with AD. We show that increased intracellular calcium [Ca²⁺](i) induced by NMDA receptor activation or membrane depolarization activates AMPK in a CAMKK2-dependent manner. CAMKK2 or AMPK overactivation is sufficient to induce dendritic spine loss. Conversely, inhibiting their activity protects hippocampal neurons against synaptotoxic effects of Aβ42 oligomers in vitro and against the loss of dendritic spines observed in the human APP(SWE,IND)-expressing transgenic mouse model in vivo. AMPK phosphorylates Tau on KxGS motif S262, and expression of Tau S262A inhibits the synaptotoxic effects of Aβ42 oligomers. Our results identify a CAMKK2-AMPK-Tau pathway as a critical mediator of the synaptotoxic effects of Aβ42 oligomers.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
microRNA-9 attenuates amyloidβ-induced synaptotoxicity by targeting calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase kinase 2.Mol Med Rep. 2014 May;9(5):1917-22. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2014.2013. Epub 2014 Mar 6. Mol Med Rep. 2014. PMID: 24603903
-
Intracellular amyloid β oligomers impair organelle transport and induce dendritic spine loss in primary neurons.Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2015 Aug 21;3:51. doi: 10.1186/s40478-015-0230-2. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2015. PMID: 26293809 Free PMC article.
-
Beta-amyloid oligomers induce phosphorylation of tau and inactivation of insulin receptor substrate via c-Jun N-terminal kinase signaling: suppression by omega-3 fatty acids and curcumin.J Neurosci. 2009 Jul 15;29(28):9078-89. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1071-09.2009. J Neurosci. 2009. PMID: 19605645 Free PMC article.
-
The role of CaMKK2 in Golgi-associated vesicle trafficking.Biochem Soc Trans. 2023 Feb 27;51(1):331-342. doi: 10.1042/BST20220833. Biochem Soc Trans. 2023. PMID: 36815702 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Ca(2+)/Calmodulin/CaMKK2 Axis: Nature's Metabolic CaMshaft.Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2016 Oct;27(10):706-718. doi: 10.1016/j.tem.2016.06.001. Epub 2016 Jul 20. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2016. PMID: 27449752 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Metformin Attenuates Aβ Pathology Mediated Through Levamisole Sensitive Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors in a C. elegans Model of Alzheimer's Disease.Mol Neurobiol. 2017 Sep;54(7):5427-5439. doi: 10.1007/s12035-016-0085-y. Epub 2016 Sep 5. Mol Neurobiol. 2017. PMID: 27596506
-
DNA vaccines targeting amyloid-β oligomer ameliorate cognitive deficits of aged APP/PS1/tau triple-transgenic mouse models of Alzheimer's disease.Neural Regen Res. 2022 Oct;17(10):2305-2310. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.337054. Neural Regen Res. 2022. PMID: 35259854 Free PMC article.
-
Aβ42 oligomers trigger synaptic loss through CAMKK2-AMPK-dependent effectors coordinating mitochondrial fission and mitophagy.Nat Commun. 2022 Aug 1;13(1):4444. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-32130-5. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 35915085 Free PMC article.
-
Pre-symptomatic activation of antioxidant responses and alterations in glucose and pyruvate metabolism in Niemann-Pick Type C1-deficient murine brain.PLoS One. 2013 Dec 18;8(12):e82685. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0082685. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24367541 Free PMC article.
-
Association of antidiabetic medication use, cognitive decline, and risk of cognitive impairment in older people with type 2 diabetes: Results from the population-based Mayo Clinic Study of Aging.Int J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2018 Aug;33(8):1114-1120. doi: 10.1002/gps.4900. Epub 2018 Jun 5. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2018. PMID: 29873112 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alessi DR, Sakamoto K, Bayascas JR. LKB1-dependent signaling pathways. Annu Rev Biochem. 2006;75:137–163. - PubMed
-
- Anderson KA, Ribar TJ, Lin F, Noeldner PK, Green MF, Muehlbauer MJ, Witters LA, Kemp BE, Means AR. Hypothalamic CaMKK2 contributes to the regulation of energy balance. Cell Metab. 2008;7:377–388. - PubMed
-
- Barnes AP, Lilley BN, Pan YA, Plummer LJ, Powell AW, Raines AN, Sanes JR, Polleux F. LKB1 and SAD kinases define a pathway required for the polarization of cortical neurons. Cell. 2007;129:549–563. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

