Repression of myoblast proliferation and fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 promoter activity by KLF10 protein
- PMID: 23569208
- PMCID: PMC3650423
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M113.457648
Repression of myoblast proliferation and fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 promoter activity by KLF10 protein
Abstract
Background: FGFR1 gene expression regulates myoblast proliferation and differentiation, and its expression is controlled by Krüppel-like transcription factors.
Results: KLF10 interacts with the FGFR1 promoter, repressing its activity and cell proliferation.
Conclusion: KLF10 represses FGFR1 promoter activity and thereby myoblast proliferation.
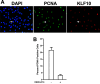
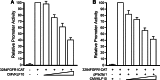
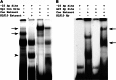
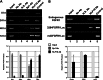
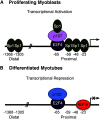
Significance: A model of transcriptional control of chicken FGFR1 gene regulation during myogenesis is presented. Skeletal muscle development is controlled by regulation of myoblast proliferation and differentiation into muscle fibers. Growth factors such as fibroblast growth factors (FGFs) and their receptors (FGFRs) regulate cell proliferation and differentiation in numerous tissues, including skeletal muscle. Transcriptional regulation of FGFR1 gene expression is developmentally regulated by the Sp1 transcription factor, a member of the Krüppel-like factor (KLF) family of transcriptional regulators. Here, we show that another KLF transcription factor, KLF10, also regulates myoblast proliferation and FGFR1 promoter activity. Expression of KLF10 reduced myoblast proliferation by 86%. KLF10 expression also significantly reduced FGFR1 promoter activity in myoblasts and Sp1-mediated FGFR1 promoter activity in Drosophila SL2 cells. Southwestern blot, electromobility shift, and chromatin immunoprecipitation assays demonstrated that KLF10 bound to the proximal Sp factor binding site of the FGFR1 promoter and reduced Sp1 complex formation with the FGFR1 promoter at that site. These results indicate that KLF10 is an effective repressor of myoblast proliferation and represses FGFR1 promoter activity in these cells via an Sp1 binding site.
Keywords: Cell Proliferation; DNA Transcription; Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor (FGFR); Gene Regulation; Myogenesis.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Bimodal, reciprocal regulation of fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 promoter activity by BTEB1/KLF9 during myogenesis.Mol Biol Cell. 2010 Aug 1;21(15):2780-7. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E10-04-0290. Epub 2010 Jun 16. Mol Biol Cell. 2010. PMID: 20554758 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic transcriptional regulatory complexes, including E2F4, p107, p130, and Sp1, control fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 gene expression during myogenesis.J Biol Chem. 2005 Jun 3;280(22):21284-94. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M410744200. Epub 2005 Apr 4. J Biol Chem. 2005. PMID: 15811856
-
Two distal Sp1-binding cis-elements regulate fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 (FGFR1) gene expression in myoblasts.Gene. 2001 May 30;270(1-2):171-80. doi: 10.1016/s0378-1119(01)00478-4. Gene. 2001. PMID: 11404014
-
Klf10 and Klf11 as mediators of TGF-beta superfamily signaling.Cell Tissue Res. 2012 Jan;347(1):65-72. doi: 10.1007/s00441-011-1186-6. Epub 2011 May 17. Cell Tissue Res. 2012. PMID: 21574058 Review.
-
Functional role of KLF10 in multiple disease processes.Biofactors. 2010 Jan-Feb;36(1):8-18. doi: 10.1002/biof.67. Biofactors. 2010. PMID: 20087894 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Key Genes Regulating Skeletal Muscle Development and Growth in Farm Animals.Animals (Basel). 2021 Mar 16;11(3):835. doi: 10.3390/ani11030835. Animals (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33809500 Free PMC article. Review.
-
miR-21-5p Regulates the Proliferation and Differentiation of Skeletal Muscle Satellite Cells by Targeting KLF3 in Chicken.Genes (Basel). 2021 May 26;12(6):814. doi: 10.3390/genes12060814. Genes (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34073601 Free PMC article.
-
The transcriptional regulator KLF15 is necessary for myoblast differentiation and muscle regeneration by activating FKBP5.J Biol Chem. 2023 Oct;299(10):105226. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2023.105226. Epub 2023 Sep 4. J Biol Chem. 2023. PMID: 37673339 Free PMC article.
-
Gene co-expression network analysis provides novel insights into myostatin regulation at three different mouse developmental timepoints.PLoS One. 2015 Feb 19;10(2):e0117607. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0117607. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25695797 Free PMC article.
-
Krüpple-like factors in cardiomyopathy: emerging player and therapeutic opportunities.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2024 Mar 7;11:1342173. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2024.1342173. eCollection 2024. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2024. PMID: 38516000 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Stockdale F. E., Holtzer H. (1961) DNA synthesis and myogenesis. Exp. Cell Res. 24, 508–520 - PubMed
-
- Gospodarowicz D., Weseman J., Moran J. (1975) Presence in brain of a mitogenic agent promoting proliferation of myoblasts in low density culture. Nature 256, 216–219 - PubMed
-
- Kardami E., Spector D., Strohman R. C. (1985) Select muscle and nerve extracts contain an activity which stimulates myoblast proliferation and which is distinct from transferrin. Dev. Biol. 112, 353–358 - PubMed
-
- Wanaka A., Milbrandt J., Johnson E. M. (1991) Expression of FGF receptor gene in rat development. Development 111, 455–468 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

