Trypanosoma cruzi trans-sialidase initiates a program independent of the transcription factors RORγt and Ahr that leads to IL-17 production by activated B cells
- PMID: 23563688
- PMCID: PMC3631452
- DOI: 10.1038/ni.2569
Trypanosoma cruzi trans-sialidase initiates a program independent of the transcription factors RORγt and Ahr that leads to IL-17 production by activated B cells
Abstract
Here we identified B cells as a major source of rapid, innate-like production of interleukin 17 (IL-17) in vivo in response to infection with Trypanosoma cruzi. IL-17(+) B cells had a plasmablast phenotype, outnumbered cells of the TH17 subset of helper T cells and were required for an optimal response to this pathogen. With both mouse and human primary B cells, we found that exposure to parasite-derived trans-sialidase in vitro was sufficient to trigger modification of the cell-surface mucin CD45, which led to signaling dependent on the kinase Btk and production of IL-17A or IL-17F via a transcriptional program independent of the transcription factors RORγt and Ahr. Our combined data suggest that the generation of IL-17(+) B cells may be a previously unappreciated feature of innate immune responses required for pathogen control or IL-17-mediated autoimmunity.
Figures

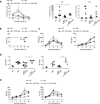
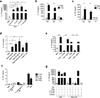
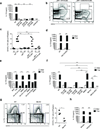
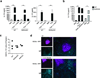
Comment in
-
IL-17-producing B cells combat parasites.Nat Immunol. 2013 May;14(5):419-21. doi: 10.1038/ni.2593. Nat Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23598388 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Trypanosoma cruzi trans-sialidase potentiates T cell activation through antigen-presenting cells: role of IL-6 and Bruton's tyrosine kinase.Eur J Immunol. 2001 May;31(5):1503-12. doi: 10.1002/1521-4141(200105)31:5<1503::AID-IMMU1503>3.0.CO;2-W. Eur J Immunol. 2001. PMID: 11465107
-
IL-17-producing B cells combat parasites.Nat Immunol. 2013 May;14(5):419-21. doi: 10.1038/ni.2593. Nat Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23598388 No abstract available.
-
GLK-IKKβ signaling induces dimerization and translocation of the AhR-RORγt complex in IL-17A induction and autoimmune disease.Sci Adv. 2018 Sep 12;4(9):eaat5401. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aat5401. eCollection 2018 Sep. Sci Adv. 2018. PMID: 30214937 Free PMC article.
-
Parasite-host glycan interactions during Trypanosoma cruzi infection: trans-Sialidase rides the show.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2020 May 1;1866(5):165692. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2020.165692. Epub 2020 Jan 20. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2020. PMID: 31972227 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Theft and Reception of Host Cell's Sialic Acid: Dynamics of Trypanosoma Cruzi Trans-sialidases and Mucin-Like Molecules on Chagas' Disease Immunomodulation.Front Immunol. 2019 Feb 6;10:164. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00164. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 30787935 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Signal transducer and activator of transcription 1 (STAT-1) plays a critical role in control of Trypanosoma cruzi infection.Immunology. 2015 Jun;145(2):225-31. doi: 10.1111/imm.12438. Immunology. 2015. PMID: 25545325 Free PMC article.
-
Costimulatory Effects of an Immunodominant Parasite Antigen Paradoxically Prevent Induction of Optimal CD8 T Cell Protective Immunity.PLoS Pathog. 2016 Sep 19;12(9):e1005896. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1005896. eCollection 2016 Sep. PLoS Pathog. 2016. PMID: 27642757 Free PMC article.
-
Host-parasite dynamics in Chagas disease from systemic to hyper-local scales.Parasite Immunol. 2021 Feb;43(2):e12786. doi: 10.1111/pim.12786. Epub 2020 Sep 24. Parasite Immunol. 2021. PMID: 32799361 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Guidelines for the use of flow cytometry and cell sorting in immunological studies (second edition).Eur J Immunol. 2019 Oct;49(10):1457-1973. doi: 10.1002/eji.201970107. Eur J Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31633216 Free PMC article.
-
IL-17RA-Signaling Modulates CD8+ T Cell Survival and Exhaustion During Trypanosoma cruzi Infection.Front Immunol. 2018 Oct 11;9:2347. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02347. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30364284 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Korn T, Bettelli E, Oukka M, Kuchroo VK. IL-17 and Th17 Cells. Annu Rev Immunol. 2009;27:485–517. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 HL075453/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R56 AI084457/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- K12HD043376/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD037091/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI084457/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- 5T32AR007108/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI075589/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R56 AI071163/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI071163/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI071163/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- HD037091/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- HL075453/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K12 HD043376/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- AI084457/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AR007108/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- AI 075589/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

