The Subread aligner: fast, accurate and scalable read mapping by seed-and-vote
- PMID: 23558742
- PMCID: PMC3664803
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkt214
The Subread aligner: fast, accurate and scalable read mapping by seed-and-vote
Abstract
Read alignment is an ongoing challenge for the analysis of data from sequencing technologies. This article proposes an elegantly simple multi-seed strategy, called seed-and-vote, for mapping reads to a reference genome. The new strategy chooses the mapped genomic location for the read directly from the seeds. It uses a relatively large number of short seeds (called subreads) extracted from each read and allows all the seeds to vote on the optimal location. When the read length is <160 bp, overlapping subreads are used. More conventional alignment algorithms are then used to fill in detailed mismatch and indel information between the subreads that make up the winning voting block. The strategy is fast because the overall genomic location has already been chosen before the detailed alignment is done. It is sensitive because no individual subread is required to map exactly, nor are individual subreads constrained to map close by other subreads. It is accurate because the final location must be supported by several different subreads. The strategy extends easily to find exon junctions, by locating reads that contain sets of subreads mapping to different exons of the same gene. It scales up efficiently for longer reads.
Figures
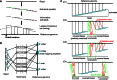
 ) of the two mapped regions in the reference is equal to the size (L) of the read region that is spanned by the subreads that vote for the best two mapping locations, the determined splicing points will be recorded in the putative exon–exon junction table. Anchor locations of each read in the genome and in the read are also recorded, which gives the mapping location to which the read is best mapped and the location of the leftmost base of the set of extracted subreads that vote for that location, respectively. Anchor locations will be used for retrieving putative splicing points and for the validation performed by the second scan. The first scan is applied to all the reads, and two tables are produced on completion. These two tables include chromosomal locations of putative splicing points found for each exon–exon junction and anchor information for each read, respectively. The input to the second scan includes these two tables and also the read data. For each read, the second scan uses its anchor location to search for the putative splicing points falling within the read from the junction table output from the first scan and then examines all mapping possibilities (including mapping the read as an exonic read) to eventually determine how the read should be mapped. The similarity between the read sequence and the mapped regions when it is mapped as a junction read has to be greater than that from being mapped as an exonic read (i.e.
) of the two mapped regions in the reference is equal to the size (L) of the read region that is spanned by the subreads that vote for the best two mapping locations, the determined splicing points will be recorded in the putative exon–exon junction table. Anchor locations of each read in the genome and in the read are also recorded, which gives the mapping location to which the read is best mapped and the location of the leftmost base of the set of extracted subreads that vote for that location, respectively. Anchor locations will be used for retrieving putative splicing points and for the validation performed by the second scan. The first scan is applied to all the reads, and two tables are produced on completion. These two tables include chromosomal locations of putative splicing points found for each exon–exon junction and anchor information for each read, respectively. The input to the second scan includes these two tables and also the read data. For each read, the second scan uses its anchor location to search for the putative splicing points falling within the read from the junction table output from the first scan and then examines all mapping possibilities (including mapping the read as an exonic read) to eventually determine how the read should be mapped. The similarity between the read sequence and the mapped regions when it is mapped as a junction read has to be greater than that from being mapped as an exonic read (i.e.  ), if it is called a junction read. The cyan dashed line indicates the mapping location of the first base or the last base of the read when it is assumed that the read does not contain junctions. Putative splicing points are removed from the final results if they are found to not have any supporting reads after the second scan is completed. The final output from this two-scan procedure is a table of validated exon–exon junctions with the number of supporting reads included, and also the complete mapping results for each read including CIGAR strings, which describes how each base in each read is mapped.
), if it is called a junction read. The cyan dashed line indicates the mapping location of the first base or the last base of the read when it is assumed that the read does not contain junctions. Putative splicing points are removed from the final results if they are found to not have any supporting reads after the second scan is completed. The final output from this two-scan procedure is a table of validated exon–exon junctions with the number of supporting reads included, and also the complete mapping results for each read including CIGAR strings, which describes how each base in each read is mapped.
Similar articles
-
A fast read alignment method based on seed-and-vote for next generation sequencing.BMC Bioinformatics. 2016 Dec 23;17(Suppl 17):466. doi: 10.1186/s12859-016-1329-6. BMC Bioinformatics. 2016. PMID: 28155631 Free PMC article.
-
Ψ-RA: a parallel sparse index for genomic read alignment.BMC Genomics. 2011;12 Suppl 2(Suppl 2):S7. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-12-S2-S7. Epub 2011 Jul 27. BMC Genomics. 2011. PMID: 21989248 Free PMC article.
-
Fast and accurate read alignment for resequencing.Bioinformatics. 2012 Sep 15;28(18):2366-73. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bts450. Epub 2012 Jul 18. Bioinformatics. 2012. PMID: 22811546 Free PMC article.
-
SRPRISM (Single Read Paired Read Indel Substitution Minimizer): an efficient aligner for assemblies with explicit guarantees.Gigascience. 2020 Apr 1;9(4):giaa023. doi: 10.1093/gigascience/giaa023. Gigascience. 2020. PMID: 32315028 Free PMC article.
-
Alignment of Next-Generation Sequencing Reads.Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet. 2015;16:133-51. doi: 10.1146/annurev-genom-090413-025358. Epub 2015 May 4. Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet. 2015. PMID: 25939052 Review.
Cited by
-
Pre-mitotic genome re-organisation bookends the B cell differentiation process.Nat Commun. 2021 Feb 26;12(1):1344. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-21536-2. Nat Commun. 2021. PMID: 33637722 Free PMC article.
-
Widespread premature transcription termination of Arabidopsis thaliana NLR genes by the spen protein FPA.Elife. 2021 Apr 27;10:e65537. doi: 10.7554/eLife.65537. Elife. 2021. PMID: 33904405 Free PMC article.
-
Sperm acrosome overgrowth and infertility in mice lacking chromosome 18 pachytene piRNA.PLoS Genet. 2021 Apr 8;17(4):e1009485. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1009485. eCollection 2021 Apr. PLoS Genet. 2021. PMID: 33831001 Free PMC article.
-
Single-cell transcriptional changes associated with drug tolerance and response to combination therapies in cancer.Nat Commun. 2021 Mar 12;12(1):1628. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-21884-z. Nat Commun. 2021. PMID: 33712615 Free PMC article.
-
pLxIS-containing domains are biochemically flexible regulators of interferons and metabolism.Mol Cell. 2024 Jul 11;84(13):2436-2454.e10. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2024.05.030. Epub 2024 Jun 25. Mol Cell. 2024. PMID: 38925114
References
-
- Marco-Sola S, Sammeth M, Guig R, Ribeca P. The GEM mapper: fast, accurate and versatile alignment by filtration. Nat. Methods. 2012;9:1185–1188. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

