The conserved SKN-1/Nrf2 stress response pathway regulates synaptic function in Caenorhabditis elegans
- PMID: 23555279
- PMCID: PMC3605294
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1003354
The conserved SKN-1/Nrf2 stress response pathway regulates synaptic function in Caenorhabditis elegans
Abstract
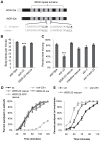
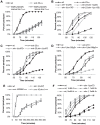
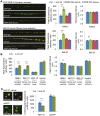
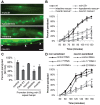
The Nrf family of transcription factors plays a critical role in mediating adaptive responses to cellular stress and defends against neurodegeneration, aging, and cancer. Here, we report a novel role for the Caenorhabditis elegans Nrf homolog SKN-1 in regulating synaptic transmission at neuromuscular junctions (NMJs). Activation of SKN-1, either by acute pharmacological treatment with the mitochondrial toxin sodium arsenite or by mutations that cause constitutive SKN-1 activation, results in defects in neuromuscular function. Additionally, elimination of the conserved WD40 repeat protein WDR-23, a principal negative regulator of SKN-1, results in impaired locomotion and synaptic vesicle and neuropeptide release from cholinergic motor axons. Mutations that abolish skn-1 activity restore normal neuromuscular function to wdr-23 mutants and animals treated with toxin. We show that negative regulation of SKN-1 by WDR-23 in the intestine, but not at neuromuscular junctions, is necessary and sufficient for proper neuromuscular function. WDR-23 isoforms differentially localize to the outer membranes of mitochondria and to nuclei, and the effects of WDR-23 on neuromuscular function are dependent on its interaction with cullin E3 ubiquitin ligase. Finally, whole-transcriptome RNA sequencing of wdr-23 mutants reveals an increase in the expression of known SKN-1/Nrf2-regulated stress-response genes, as well as neurotransmission genes not previously implicated in SKN-1/Nrf2 responses. Together, our results indicate that SKN-1/Nrf2 activation may be a mechanism through which cellular stress, detected in one tissue, affects cellular function of a distal tissue through endocrine signaling. These results provide insight into how SKN-1/Nrf2 might protect the nervous system from damage in response to oxidative stress.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The WD40 repeat protein WDR-23 functions with the CUL4/DDB1 ubiquitin ligase to regulate nuclear abundance and activity of SKN-1 in Caenorhabditis elegans.Mol Cell Biol. 2009 May;29(10):2704-15. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01811-08. Epub 2009 Mar 9. Mol Cell Biol. 2009. PMID: 19273594 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of skn-1/wdr-23 phenotypes in Caenorhabditis elegans; pleiotrophy, aging, glutathione, and interactions with other longevity pathways.Mech Ageing Dev. 2015 Jul;149:88-98. doi: 10.1016/j.mad.2015.06.001. Epub 2015 Jun 6. Mech Ageing Dev. 2015. PMID: 26056713
-
Direct interaction between the WD40 repeat protein WDR-23 and SKN-1/Nrf inhibits binding to target DNA.Mol Cell Biol. 2014 Aug;34(16):3156-67. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00114-14. Epub 2014 Jun 9. Mol Cell Biol. 2014. Retraction in: Mol Cell Biol. 2015 Sep;35(18):3255. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00658-15 PMID: 24912676 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
SKN-1/Nrf, stress responses, and aging in Caenorhabditis elegans.Free Radic Biol Med. 2015 Nov;88(Pt B):290-301. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2015.06.008. Epub 2015 Aug 5. Free Radic Biol Med. 2015. PMID: 26232625 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gap junctions: historical discoveries and new findings in the Caenorhabditiselegans nervous system.Biol Open. 2020 Sep 3;9(8):bio053983. doi: 10.1242/bio.053983. Biol Open. 2020. PMID: 32883654 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Lipid-mediated regulation of SKN-1/Nrf in response to germ cell absence.Elife. 2015 Aug 24;4:e07836. doi: 10.7554/eLife.07836. Elife. 2015. PMID: 26196144 Free PMC article.
-
The Skp1 Homologs SKR-1/2 Are Required for the Caenorhabditis elegans SKN-1 Antioxidant/Detoxification Response Independently of p38 MAPK.PLoS Genet. 2016 Oct 24;12(10):e1006361. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1006361. eCollection 2016 Oct. PLoS Genet. 2016. PMID: 27776126 Free PMC article.
-
Wnt Secretion Is Regulated by the Tetraspan Protein HIC-1 through Its Interaction with Neurabin/NAB-1.Cell Rep. 2018 Nov 13;25(7):1856-1871.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2018.10.053. Cell Rep. 2018. PMID: 30428353 Free PMC article.
-
Comparing the Effects of Ferulic Acid and Sugarcane Aqueous Extract in In Vitro and In Vivo Neurotoxic Models.Neurotox Res. 2018 Oct;34(3):640-648. doi: 10.1007/s12640-018-9926-y. Epub 2018 Jun 15. Neurotox Res. 2018. PMID: 29949107
-
Comparative analysis of the molecular and physiological consequences of constitutive SKN-1 activation.Geroscience. 2023 Dec;45(6):3359-3370. doi: 10.1007/s11357-023-00937-9. Epub 2023 Sep 26. Geroscience. 2023. PMID: 37751046 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

