TGF-β signalling and reactive oxygen species drive fibrosis and matrix remodelling in myxomatous mitral valves
- PMID: 23554457
- PMCID: PMC3687751
- DOI: 10.1093/cvr/cvt083
TGF-β signalling and reactive oxygen species drive fibrosis and matrix remodelling in myxomatous mitral valves
Abstract
Aims: Myxomatous mitral valve disease (MMVD) is associated with leaflet thickening, fibrosis, matrix remodelling, and leaflet prolapse. Molecular mechanisms contributing to MMVD, however, remain poorly understood. We tested the hypothesis that increased transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) signalling and reactive oxygen species (ROS) are major contributors to pro-fibrotic gene expression in human and mouse mitral valves.
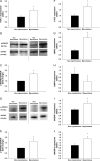
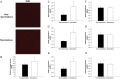
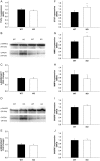
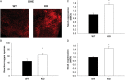
Methods and results: Using qRT-PCR, we found that increased expression of TGF-β1 in mitral valves from humans with MMVD (n = 24) was associated with increased expression of connective tissue growth factor (CTGF) and matrix metalloproteinase 2 (MMP2). Increased levels of phospho-SMAD2/3 (western blotting) and expression of SMAD-specific E3 ubiquitin-protein ligases (SMURF) 1 and 2 (qRT-PCR) suggested that TGF-β1 signalling occurred through canonical signalling cascades. Oxidative stress (dihydroethidium staining) was increased in human MMVD tissue and associated with increases in NAD(P)H oxidase catalytic subunits (Nox) 2 and 4, occurring despite increases in superoxide dismutase 1 (SOD1). In mitral valves from SOD1-deficient mice, expression of CTGF, MMP2, Nox2, and Nox4 was significantly increased, suggesting that ROS can independently activate pro-fibrotic and matrix remodelling gene expression patterns. Furthermore, treatment of mouse mitral valve interstitial cells with cell permeable antioxidants attenuated TGF-β1-induced pro-fibrotic and matrix remodelling gene expression in vitro.
Conclusion: Activation of canonical TGF-β signalling is a major contributor to fibrosis and matrix remodelling in MMVD, and is amplified by increases in oxidative stress. Treatments aimed at reducing TGF-β activation and oxidative stress in early MMVD may slow progression of MMVD.
Keywords: Antioxidants; Cardiovascular surgery; Mitral valve; Regurgitation; Valves.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Nonbiased Molecular Screening Identifies Novel Molecular Regulators of Fibrogenic and Proliferative Signaling in Myxomatous Mitral Valve Disease.Circ Cardiovasc Genet. 2015 Jun;8(3):516-28. doi: 10.1161/CIRCGENETICS.114.000921. Epub 2015 Mar 26. Circ Cardiovasc Genet. 2015. PMID: 25814644 Free PMC article.
-
Induction of renal fibrotic genes by TGF-β1 requires EGFR activation, p53 and reactive oxygen species.Cell Signal. 2013 Nov;25(11):2198-209. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2013.07.007. Epub 2013 Jul 18. Cell Signal. 2013. PMID: 23872073
-
NADPH oxidase 4 contributes to connective tissue growth factor expression through Smad3-dependent signaling pathway.Free Radic Biol Med. 2016 May;94:174-84. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2016.02.031. Epub 2016 Mar 3. Free Radic Biol Med. 2016. PMID: 26945889
-
Activation of Nrf2/AREs-mediated antioxidant signalling, and suppression of profibrotic TGF-β1/Smad3 pathway: a promising therapeutic strategy for hepatic fibrosis - A review.Life Sci. 2020 Sep 1;256:117909. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2020.117909. Epub 2020 Jun 5. Life Sci. 2020. PMID: 32512009 Review.
-
Emerging pathogenic mechanisms in human myxomatous mitral valve: lessons from past and novel data.Cardiovasc Pathol. 2013 Jul-Aug;22(4):245-50. doi: 10.1016/j.carpath.2012.11.001. Epub 2012 Dec 21. Cardiovasc Pathol. 2013. PMID: 23261354 Review.
Cited by
-
Immune-mediated pathology in Duchenne muscular dystrophy.Sci Transl Med. 2015 Aug 5;7(299):299rv4. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aaa7322. Sci Transl Med. 2015. PMID: 26246170 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sirtuin 3 is essential for hypertension-induced cardiac fibrosis via mediating pericyte transition.J Cell Mol Med. 2020 Jul;24(14):8057-8068. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.15437. Epub 2020 May 28. J Cell Mol Med. 2020. PMID: 32463172 Free PMC article.
-
Myofiber-specific inhibition of TGFβ signaling protects skeletal muscle from injury and dystrophic disease in mice.Hum Mol Genet. 2014 Dec 20;23(25):6903-15. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddu413. Epub 2014 Aug 8. Hum Mol Genet. 2014. PMID: 25106553 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Patients Affected by Mitral Valve Prolapse with Severe Regurgitation: A Multivariable Regression Model.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2017;2017:6838921. doi: 10.1155/2017/6838921. Epub 2017 Feb 2. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2017. PMID: 28261377 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Transcriptomic Profiling and Gene Expression for Myxomatous Mitral Valve Disease in the Dog and Human.Vet Sci. 2017 Jul 17;4(3):34. doi: 10.3390/vetsci4030034. Vet Sci. 2017. PMID: 29056693 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Freed LA, Levy D, Levine RA, Larson MG, Evans JC, Fuller DL, et al. Prevalence and clinical outcome of mitral-valve prolapse. N Engl J Med. 1999;341:1–7. doi:10.1056/NEJM199907013410101. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Freed LA, Benjamin EJ, Levy D, Larson MG, Evans JC, Fuller DL, et al. Mitral valve prolapse in the general population: the benign nature of echocardiographic features in the Framingham Heart Study. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2002;40:1298–1304. doi:10.1016/S0735-1097(02)02161-7. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Li C, Gotlieb AI. Transforming growth factor-beta regulates the growth of valve interstitial cells in vitro. Am J Pathol. 2011;179:1746–1755. doi:10.1016/j.ajpath.2011.06.007. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Desmouliere A, Geinoz A, Gabbiani F, Gabbiani G. Transforming growth factor-beta 1 induces alpha-smooth muscle actin expression in granulation tissue myofibroblasts and in quiescent and growing cultured fibroblasts. J Cell Biol. 1993;122:103–111. doi:10.1083/jcb.122.1.103. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Petrov VV, Fagard RH, Lijnen PJ. Transforming growth factor-beta(1) induces angiotensin-converting enzyme synthesis in rat cardiac fibroblasts during their differentiation to myofibroblasts. J Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone Syst. 2000;1:342–352. doi:10.3317/jraas.2000.064. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

