A mechanism of resistance to gefitinib mediated by cellular reprogramming and the acquisition of an FGF2-FGFR1 autocrine growth loop
- PMID: 23552882
- PMCID: PMC3641357
- DOI: 10.1038/oncsis.2013.4
A mechanism of resistance to gefitinib mediated by cellular reprogramming and the acquisition of an FGF2-FGFR1 autocrine growth loop
Abstract
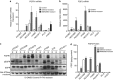
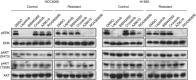
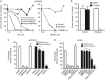
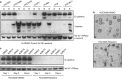
Despite initial and often dramatic responses of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)-addicted lung tumors to the EGFR-specific tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs), gefitinib and erlotinib, nearly all develop resistance and relapse. To explore novel mechanisms mediating acquired resistance, we employed non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) cell lines bearing activating mutations in EGFR and rendered them resistant to EGFR-specific TKIs through chronic adaptation in tissue culture. In addition to previously observed resistance mechanisms including EGFR-T790M 'gate-keeper' mutations and MET amplification, a subset of the seven chronically adapted NSCLC cell lines including HCC4006, HCC2279 and H1650 cells exhibited marked induction of fibroblast growth factor (FGF) 2 and FGF receptor 1 (FGFR1) mRNA and protein. Also, adaptation to EGFR-specific TKIs was accompanied by an epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT) as assessed by changes in CDH1, VIM, ZEB1 and ZEB2 expression and altered growth properties in Matrigel. In adapted cell lines exhibiting increased FGF2 and FGFR1 expression, measures of growth and signaling, but not EMT, were blocked by FGFR-specific TKIs, an FGF-ligand trap and FGFR1 silencing with RNAi. In parental HCC4006 cells, cell growth was strongly inhibited by gefitinib, although drug-resistant clones progress within 10 days. Combined treatment with gefitinib and AZD4547, an FGFR-specific TKI, prevented the outgrowth of drug-resistant clones. Thus, induction of FGF2 and FGFR1 following chronic adaptation to EGFR-specific TKIs provides a novel autocrine receptor tyrosine kinase-driven bypass pathway in a subset of lung cancer cell lines that are initially sensitive to EGFR-specific TKIs. The findings support FGFR-specific TKIs as potentially valuable additions to existing targeted therapeutic strategies with EGFR-specific TKIs to prevent or delay acquired resistance in EGFR-driven NSCLC.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Activation of the FGF2-FGFR1 autocrine pathway: a novel mechanism of acquired resistance to gefitinib in NSCLC.Mol Cancer Res. 2013 Jul;11(7):759-67. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-12-0652. Epub 2013 Mar 27. Mol Cancer Res. 2013. PMID: 23536707
-
ZEB1 Mediates Acquired Resistance to the Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor-Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer.PLoS One. 2016 Jan 20;11(1):e0147344. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0147344. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 26789630 Free PMC article.
-
Cause-and-Effect relationship between FGFR1 expression and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in EGFR-mutated non-small cell lung cancer cells.Lung Cancer. 2019 Jun;132:132-140. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2019.04.023. Epub 2019 Apr 18. Lung Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31097086
-
Acquired resistance to epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors in non-small-cell lung cancers dependent on the epidermal growth factor receptor pathway.Clin Lung Cancer. 2009 Jul;10(4):281-9. doi: 10.3816/CLC.2009.n.039. Clin Lung Cancer. 2009. PMID: 19632948 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Erlotinib or gefitinib for the treatment of relapsed platinum pretreated non-small cell lung cancer and ovarian cancer: a systematic review.Drug Resist Updat. 2011 Jun;14(3):177-90. doi: 10.1016/j.drup.2011.02.004. Epub 2011 Mar 24. Drug Resist Updat. 2011. PMID: 21435938 Review.
Cited by
-
Tackling Drug Resistance in EGFR Exon 20 Insertion Mutant Lung Cancer.Pharmgenomics Pers Med. 2021 Mar 9;14:301-317. doi: 10.2147/PGPM.S242045. eCollection 2021. Pharmgenomics Pers Med. 2021. PMID: 33727854 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multiple receptor tyrosine kinase activation attenuates therapeutic efficacy of the fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 inhibitor AZD4547 in FGFR2 amplified gastric cancer.Oncotarget. 2015 Feb 10;6(4):2009-22. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.2987. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 25576915 Free PMC article.
-
Abstracts from the European Respiratory Society Annual Conference 2018 on Thoracic Oncology.J Thorac Dis. 2018 Sep;10(Suppl 25):S3020-S3023. doi: 10.21037/jtd.2018.08.121. J Thorac Dis. 2018. PMID: 30310693 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
MicroRNA-147 induces a mesenchymal-to-epithelial transition (MET) and reverses EGFR inhibitor resistance.PLoS One. 2014 Jan 15;9(1):e84597. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0084597. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24454732 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic aberrations in the FGFR pathway: opportunities for targeted therapies in solid tumors.Ann Oncol. 2014 Mar;25(3):552-563. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdt419. Epub 2013 Nov 20. Ann Oncol. 2014. PMID: 24265351 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- American Cancer Society . Cancer Facts & Figures. American Cancer Society, Atlanta, GA, USA; 2012.
-
- Schiller JH, Harrington D, Belani CP, Langer C, Sandler A, Krook J, et al. Comparison of four chemotherapy regimens for advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2002;346:92–98. - PubMed
-
- Hirsch FR, Varella-Garcia M, Bunn PA, Di Maria MV, Veve R, Bremmes RM, et al. Epidermal growth factor receptor in non-small-cell lung carcinomas: correlation between gene copy number and protein expression and impact on prognosis. J Clin Oncol. 2003;21:3798–3807. - PubMed
-
- da Cunha Santos G, Shepherd FA, Tsao MS. EGFR mutations and lung cancer. Ann Rev Pathol. 2011;6:49–69. - PubMed
-
- Engelman JA, Janne PA. Mechanisms of acquired resistance to epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors in non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2008;14:2895–2899. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

