Excitatory amino acid transporter 5 is widely expressed in peripheral tissues
- PMID: 23549460
- PMCID: PMC3683608
- DOI: 10.4081/ejh.2013.e11
Excitatory amino acid transporter 5 is widely expressed in peripheral tissues
Abstract
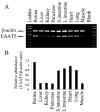
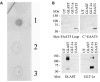
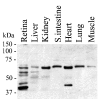
It is routinely stated in the literature that Excitatory Amino Acid Transporter 5 (EAAT5) is a retina-specific glutamate transporter. EAAT5 is expressed by retinal photoreceptors and bipolar cells, where it serves as a slow transporter and as an inhibitory glutamate receptor, the latter role is due to the gating of a large chloride conductance. The dogma of an exclusively retinal distribution has arisen because Northern blot analyses have previously shown only modest hybridisation in non-retinal tissues. Others have re-interpreted this as indicating that EAAT5 was only present in retinal tissues. However, this view appears to be erroneous; recent evidence demonstrating abundant expression of EAAT5 in rat testis prompted us to re-examine this dogma. A new antibody was developed to an intracellular loop region of rat EAAT5. This new tool, in concert with RT-PCR and sequencing, demonstrated that EAAT5 is widely distributed at the mRNA and protein levels in many non-nervous tissues including liver, kidney, intestine, heart, lung, and skeletal muscle. We conclude that EAAT5 is a widely distributed protein. Whether it functions in all locations as a glutamate transporter, or mainly as a glutamate-gated chloride conductance, remains to be determined.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interests: the authors declare no conflict of interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Human brain neurons express a novel splice variant of excitatory amino acid transporter 5 (hEAAT5v).J Comp Neurol. 2020 Dec 1;528(17):3134-3142. doi: 10.1002/cne.24907. Epub 2020 Apr 3. J Comp Neurol. 2020. PMID: 32173860
-
Alternate splicing and expression of the glutamate transporter EAAT5 in the rat retina.Gene. 2012 Sep 15;506(2):283-8. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2012.07.010. Epub 2012 Jul 20. Gene. 2012. PMID: 22820393
-
Excitatory amino acid transporter 5, a retinal glutamate transporter coupled to a chloride conductance.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997 Apr 15;94(8):4155-60. doi: 10.1073/pnas.94.8.4155. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997. PMID: 9108121 Free PMC article.
-
A novel splice variant of the Excitatory Amino Acid Transporter 5: Cloning, immunolocalization and functional characterization of hEAAT5v in human retina.Neurochem Int. 2016 Oct 28:S0197-0186(16)30404-1. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2016.10.013. Online ahead of print. Neurochem Int. 2016. PMID: 27984169
-
EAAT5 Glutamate Transporter-Mediated Inhibition in the Vertebrate Retina.Front Cell Neurosci. 2021 May 6;15:662859. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2021.662859. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34025361 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Glutamatergic system components as potential biomarkers and therapeutic targets in cancer in non-neural organs.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Nov 15;13:1029210. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.1029210. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36457557 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Localization of excitatory amino acid transporters EAAT1 and EAAT2 in human postmortem cortex: a light and electron microscopic study.Neuroscience. 2014 Sep 26;277:522-40. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2014.07.019. Epub 2014 Jul 24. Neuroscience. 2014. PMID: 25064059 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptional Regulation of Glutamate Transporters: From Extracellular Signals to Transcription Factors.Adv Pharmacol. 2016;76:103-45. doi: 10.1016/bs.apha.2016.01.004. Epub 2016 Mar 24. Adv Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27288076 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Histochemistry in biology and medicine: a message from the citing journals.Eur J Histochem. 2015 Dec 23;59(4):2610. doi: 10.4081/ejh.2015.2610. Eur J Histochem. 2015. PMID: 26708189 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Excitatory Amino Acid Transporter EAAT5 Improves Temporal Resolution in the Retina.eNeuro. 2021 Dec 10;8(6):ENEURO.0406-21.2021. doi: 10.1523/ENEURO.0406-21.2021. Print 2021 Nov-Dec. eNeuro. 2021. PMID: 34772693 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Danbolt NC. Glutamate uptake. Prog Neurobiol. 2001;65:1–105. - PubMed
-
- Lee A, Pow DV. Astrocytes: glutamate transport and alternate splicing of transporters. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2010;42:1901–6. - PubMed
-
- Pow DV, Barnett NL. Developmental expression of excitatory amino acid transporter 5: a photoreceptor and bipolar cell glutamate transporter in rat retina. Neurosci Lett. 2000;280:21–4. - PubMed
-
- Lee A, Anderson AR, Barnett NL, Stevens MG, Pow DV. Alternate splicing and expression of the glutamate transporter EAAT5 in the rat retina. Gene. 2012;506:283–8. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

