RETRACTED: Collagen prolyl hydroxylases are essential for breast cancer metastasis
- PMID: 23539444
- PMCID: PMC3674184
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-12-3963
RETRACTED: Collagen prolyl hydroxylases are essential for breast cancer metastasis
Retraction in
-
Retraction: Collagen Prolyl Hydroxylases Are Essential for Breast Cancer Metastasis.Cancer Res. 2024 Sep 4;84(17):2927. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-24-2214. Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 39228257 No abstract available.
Expression of concern in
-
Editor's Note: Collagen Prolyl Hydroxylases Are Essential for Breast Cancer Metastasis.Cancer Res. 2022 Mar 1;82(5):943. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-21-4312. Cancer Res. 2022. PMID: 35247897 No abstract available.
Abstract
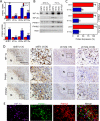
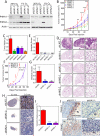
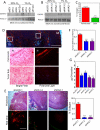
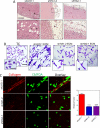
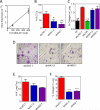
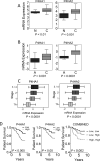
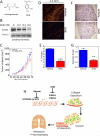
The presence of hypoxia and fibrosis within the primary tumor are two major risk factors for metastasis of human breast cancer. In this study, we demonstrate that hypoxia-inducible factor 1 activates the transcription of genes encoding collagen prolyl hydroxylases that are critical for collagen deposition by breast cancer cells. We show that expression of collagen prolyl hydroxylases promotes cancer cell alignment along collagen fibers, resulting in enhanced invasion and metastasis to lymph nodes and lungs. Finally, we establish the prognostic significance of collagen prolyl hydroxylase mRNA expression in human breast cancer biopsies and show that ethyl 3,4-dihydroxybenzoate, a prolyl hydroxylase inhibitor, decreases tumor fibrosis and metastasis in a mouse model of breast cancer.
©2013 AACR.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prolyl-4-hydroxylase α subunit 2 promotes breast cancer progression and metastasis by regulating collagen deposition.BMC Cancer. 2014 Jan 2;14:1. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-14-1. BMC Cancer. 2014. PMID: 24383403 Free PMC article.
-
Procollagen lysyl hydroxylase 2 is essential for hypoxia-induced breast cancer metastasis.Mol Cancer Res. 2013 May;11(5):456-66. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-12-0629. Epub 2013 Feb 1. Mol Cancer Res. 2013. Retraction in: Mol Cancer Res. 2023 Oct 2;21(10):1120. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-23-0654 PMID: 23378577 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 (HIF-1) promotes extracellular matrix remodeling under hypoxic conditions by inducing P4HA1, P4HA2, and PLOD2 expression in fibroblasts.J Biol Chem. 2013 Apr 12;288(15):10819-29. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.442939. Epub 2013 Feb 19. J Biol Chem. 2013. Retraction in: J Biol Chem. 2023 Sep;299(9):105144. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2023.105144 PMID: 23423382 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Collagen Prolyl Hydroxylases Are Bifunctional Growth Regulators in Melanoma.J Invest Dermatol. 2019 May;139(5):1118-1126. doi: 10.1016/j.jid.2018.10.038. Epub 2018 Nov 16. J Invest Dermatol. 2019. PMID: 30452903 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The hypoxia-inducible-factor hydroxylases bring fresh air into hypoxia signalling.EMBO Rep. 2006 Jan;7(1):41-5. doi: 10.1038/sj.embor.7400598. EMBO Rep. 2006. PMID: 16391536 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Restriction of drug transport by the tumor environment.Histochem Cell Biol. 2018 Dec;150(6):631-648. doi: 10.1007/s00418-018-1744-z. Epub 2018 Oct 25. Histochem Cell Biol. 2018. PMID: 30361778 Review.
-
The role of tumor microenvironment and exosomes in dormancy and relapse.Semin Cancer Biol. 2022 Jan;78:35-44. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2021.09.008. Epub 2021 Oct 30. Semin Cancer Biol. 2022. PMID: 34757184 Free PMC article. Review.
-
P4HA1: A single-gene surrogate of hypoxia signatures in oral squamous cell carcinoma patients.Clin Transl Radiat Oncol. 2017 Jun 27;5:6-11. doi: 10.1016/j.ctro.2017.05.002. eCollection 2017 Aug. Clin Transl Radiat Oncol. 2017. PMID: 29594211 Free PMC article.
-
Prolyl 4-hydroxylase 2 promotes B-cell lymphoma progression via hydroxylation of Carabin.Blood. 2018 Mar 22;131(12):1325-1336. doi: 10.1182/blood-2017-07-794875. Epub 2018 Feb 1. Blood. 2018. PMID: 29437589 Free PMC article.
-
Hypoxia and the extracellular matrix: drivers of tumour metastasis.Nat Rev Cancer. 2014 Jun;14(6):430-9. doi: 10.1038/nrc3726. Epub 2014 May 15. Nat Rev Cancer. 2014. PMID: 24827502 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Brahimi-Horn MC, Chiche J, Pouyssegur J. Hypoxia and cancer. J Mol Med. 2007;85:1301–7. - PubMed
-
- Dewhirst MW. Intermittent hypoxia furthers the rationale for hypoxia-inducible factor-1 targeting. Cancer Res. 2007;67:854–5. - PubMed
-
- Hiraga T, Kizaka-Kondoh S, Hirota K, Hiraoka M, Yoneda T. Hypoxia and hypoxia-inducible factor-1 expression enhance osteolytic bone metastases of breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2007;67:4157–63. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

