Multiple sensors ensure guide strand selection in human RNAi pathways
- PMID: 23531496
- PMCID: PMC3677279
- DOI: 10.1261/rna.037424.112
Multiple sensors ensure guide strand selection in human RNAi pathways
Abstract
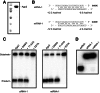
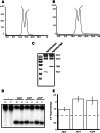
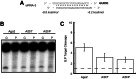
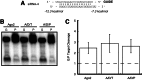
Small RNAs guide RNA-induced silencing complexes (RISCs) to bind to cognate mRNA transcripts and trigger silencing of protein expression during RNA interference (RNAi) in eukaryotes. A fundamental aspect of this process is the asymmetric loading of one strand of a short interfering RNA (siRNA) or microRNA (miRNA) duplex onto RISCs for correct target recognition. Here, we use a reconstituted system to determine the extent to which the core components of the human RNAi machinery contribute to RNA guide strand selection. We show that Argonaute2 (Ago2), the endonuclease that binds directly to siRNAs and miRNAs within RISC, has intrinsic but substrate-dependent RNA strand selection capability. This activity can be enhanced substantially when Ago2 is in complex with the endonuclease Dicer and the double-stranded RNA-binding proteins (dsRBPs)-trans-activation response (TAR) RNA-binding protein (TRBP) or protein activator of PKR (PACT). The extent to which human Dicer/dsRBP complexes contribute to strand selection is dictated by specific duplex parameters such as thermodynamics, 5' nucleotide identity, and structure. Surprisingly, our results also suggest that strand selection for some miRNAs is enhanced by PACT-containing complexes but not by those containing TRBP. Furthermore, overall mRNA targeting by miRNAs is disfavored for complexes containing TRBP but not PACT. These findings demonstrate that multiple proteins collaborate to ensure optimal strand selection in humans and reveal the possibility of delineating RNAi pathways based on the presence of TRBP or PACT.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Differential roles of human Dicer-binding proteins TRBP and PACT in small RNA processing.Nucleic Acids Res. 2013 Jul;41(13):6568-76. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt361. Epub 2013 May 9. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013. PMID: 23661684 Free PMC article.
-
The role of PACT in the RNA silencing pathway.EMBO J. 2006 Feb 8;25(3):522-32. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600942. Epub 2006 Jan 19. EMBO J. 2006. PMID: 16424907 Free PMC article.
-
Distinguishable in vitro binding mode of monomeric TRBP and dimeric PACT with siRNA.PLoS One. 2013 May 2;8(5):e63434. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0063434. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23658827 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of mammalian transcription and splicing by Nuclear RNAi.Nucleic Acids Res. 2016 Jan 29;44(2):524-37. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv1305. Epub 2015 Nov 26. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016. PMID: 26612865 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intracellular localization and routing of miRNA and RNAi pathway components.Curr Top Med Chem. 2012;12(2):79-88. doi: 10.2174/156802612798919132. Curr Top Med Chem. 2012. PMID: 22196276 Review.
Cited by
-
One locus, several functional RNAs-emerging roles of the mechanisms responsible for the sequence variability of microRNAs.Biol Futur. 2023 Jun;74(1-2):17-28. doi: 10.1007/s42977-023-00154-7. Epub 2023 Feb 27. Biol Futur. 2023. PMID: 36847925 Review.
-
Use of Mature miRNA Strand Selection in miRNAs Families in Cervical Cancer Development.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Feb 14;18(2):407. doi: 10.3390/ijms18020407. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28216603 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structural Foundations of RNA Silencing by Argonaute.J Mol Biol. 2017 Aug 18;429(17):2619-2639. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2017.07.018. Epub 2017 Jul 27. J Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 28757069 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Small-RNA asymmetry is directly driven by mammalian Argonautes.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2015 Jul;22(7):512-21. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.3050. Epub 2015 Jun 22. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2015. PMID: 26098316
-
Dicer-TRBP complex formation ensures accurate mammalian microRNA biogenesis.Mol Cell. 2015 Feb 5;57(3):397-407. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2014.11.030. Epub 2014 Dec 31. Mol Cell. 2015. PMID: 25557550 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
