BMP4 increases canonical transient receptor potential protein expression by activating p38 MAPK and ERK1/2 signaling pathways in pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cells
- PMID: 23526217
- PMCID: PMC3824027
- DOI: 10.1165/rcmb.2012-0051OC
BMP4 increases canonical transient receptor potential protein expression by activating p38 MAPK and ERK1/2 signaling pathways in pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cells
Abstract
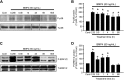
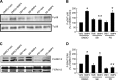
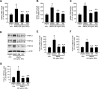
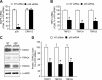
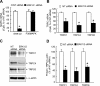
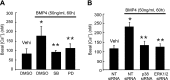
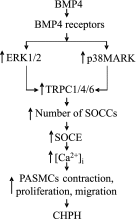
Abnormal bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) signaling has been implicated in the pathogenesis of pulmonary hypertension. We previously found that BMP4 elevated basal intracellular Ca(2+) ([Ca(2+)]i) concentrations in distal pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cells (PASMCs), attributable in large part to enhanced store-operated Ca(2+) entry through store-operated Ca(2+) channels (SOCCs). Moreover, BMP4 up-regulated the expression of canonical transient receptor potential (TRPC) proteins thought to compose SOCCs. The present study investigated the signaling pathways through which BMP4 regulates TRPC expression and basal [Ca(2+)]i in distal PASMCs. Real-time quantitative PCR was used for the measurement of mRNA, Western blotting was used for the measurement of protein, and fluorescent microscopic for [Ca(2+)]i was used to determine the involvement of p38 and extracellular regulated kinase (ERK)-1/2 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling in BMP4-induced TRPC expression and the elevation of [Ca(2+)]i in PASMCs. We found that the treatment of BMP4 led to the activation of both p38 MAPK and ERK1/2 in rat distal PASMCs. The induction of TRPC1, TRPC4, and TRPC6 expression, and the increases of [Ca(2+)]i caused by BMP4 in distal PASMCs, were inhibited by treatment with either SB203580 (10 μM), the selective inhibitor for p38 activation, or the specific p38 small interfering RNA (siRNA). Similarly, those responses induced by BMP4 were also abolished by treatment with PD98059 (5 μM), the selective inhibitor of ERK1/2, or by the knockdown of ERK1/2 using its specific siRNA. These results indicate that BMP4 participates in the regulation of Ca(2+) signaling in PASMCs by modulating TRPC channel expression via activating p38 and ERK1/2 MAPK pathways.
Figures
Similar articles
-
BMP4 increases the expression of TRPC and basal [Ca2+]i via the p38MAPK and ERK1/2 pathways independent of BMPRII in PASMCs.PLoS One. 2014 Dec 2;9(12):e112695. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0112695. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25461595 Free PMC article.
-
Hypoxia inducible factor-1-dependent up-regulation of BMP4 mediates hypoxia-induced increase of TRPC expression in PASMCs.Cardiovasc Res. 2015 Jul 1;107(1):108-18. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvv122. Epub 2015 Mar 30. Cardiovasc Res. 2015. PMID: 25824146 Free PMC article.
-
Bone morphogenetic protein 2 decreases TRPC expression, store-operated Ca(2+) entry, and basal [Ca(2+)]i in rat distal pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cells.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2013 May 1;304(9):C833-43. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00036.2012. Epub 2013 Feb 27. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2013. PMID: 23447035 Free PMC article.
-
The contribution of TRPC1 and STIM1 to capacitative Ca(2+) entry in pulmonary artery.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2010;661:123-35. doi: 10.1007/978-1-60761-500-2_8. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2010. PMID: 20204727 Review.
-
TRPC channels in smooth muscle cells.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2010 Jun 1;15(3):1023-39. doi: 10.2741/3660. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2010. PMID: 20515740 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Expression of canonical transient receptor potential channels in U-2 OS and MNNG-HOS osteosarcoma cell lines.Oncol Lett. 2021 Apr;21(4):307. doi: 10.3892/ol.2021.12568. Epub 2021 Feb 21. Oncol Lett. 2021. PMID: 33732383 Free PMC article.
-
Heart‑lung crosstalk in pulmonary arterial hypertension following myocardial infarction (Review).Int J Mol Med. 2020 Sep;46(3):913-924. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2020.4650. Epub 2020 Jun 18. Int J Mol Med. 2020. PMID: 32582962 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Notoginsenoside Rb1 inhibits activation of ERK and p38 MAPK pathways induced by hypoxia and hypercapnia.Exp Ther Med. 2016 Jun;11(6):2455-2461. doi: 10.3892/etm.2016.3217. Epub 2016 Apr 1. Exp Ther Med. 2016. PMID: 27313674 Free PMC article.
-
NADPH oxidases-do they play a role in TRPC regulation under hypoxia?Pflugers Arch. 2016 Jan;468(1):23-41. doi: 10.1007/s00424-015-1731-3. Epub 2015 Oct 1. Pflugers Arch. 2016. PMID: 26424109 Review.
-
Noggin inhibits hypoxia-induced proliferation by targeting store-operated calcium entry and transient receptor potential cation channels.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2015 Jun 1;308(11):C869-78. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00349.2014. Epub 2015 Mar 4. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2015. PMID: 25740156 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wang J, Weigand L, Lu W, Sylvester JT, Semenza GL, Shimoda LA. Hypoxia inducible factor 1 mediates hypoxia-induced TRPC expression and elevated intracellular Ca2+ in pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cells. Circ Res. 2006;98:1528–1537. - PubMed
-
- Lin MJ, Leung GP, Zhang WM, Yang XR, Yip KP, Tse CM, Sham JS. Chronic hypoxia-induced upregulation of store-operated and receptor-operated Ca2+ channels in pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cells: a novel mechanism of hypoxic pulmonary hypertension. Circ Res. 2004;95:496–505. - PubMed
-
- Shimoda LA, Wang J, Sylvester JT. Ca2+ channels and chronic hypoxia. Microcirculation. 2006;13:657–670. - PubMed
-
- Karaki H, Ozaki H, Hori M, Mitsui-Saito M, Amano K, Harada K, Miyamoto S, Nakazawa H, Won KJ, Sato K. Calcium movements, distribution, and functions in smooth muscle. Pharmacol Rev. 1997;49:157–230. - PubMed
-
- Shimoda LA, Sham JS, Shimoda TH, Sylvester JT. L-type Ca2+ channels, resting [Ca2+]i, and ET-1–induced responses in chronically hypoxic pulmonary myocytes. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2000;279:L884–L894. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

