Artificial liver support system combined with liver transplantation in the treatment of patients with acute-on-chronic liver failure
- PMID: 23516546
- PMCID: PMC3597613
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0058738
Artificial liver support system combined with liver transplantation in the treatment of patients with acute-on-chronic liver failure
Retraction in
-
Retraction: Artificial Liver Support System Combined with Liver Transplantation in the Treatment of Patients with Acute-on-Chronic Liver Failure.PLoS One. 2019 Aug 27;14(8):e0221917. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0221917. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31454401 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: The search for a strategy to provide temporary liver support and salvage the patients with acute-on-chronic liver failure (ACLF) remains an important issue. This study was designed to evaluate the experience in artificial liver support system (ALSS) combined with liver transplantation (LT) in the treatment of ACLF.
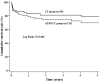
Methodology/principal findings: One hundred and seventy one patients with HBV related ACLF undergoing LT between January 2001 and December 2009 were included. Of the 171 patients, 115 received 247 sessions of plasma exchange-centered ALSS treatment prior to LT (ALSS-LT group) and the other 56 received emergency LT (LT group). The MELD score were 31±6 and 30±7 in ALSS-LT group and LT group. ALSS treatment resulted in improvement of liver function and better tolerance to LT. The average level of serum total bilirubin before LT was lower than that before the first time of ALSS treatment. The median waiting time for a donor liver was 12 days (2-226 days) from the first run of ALSS treatment to LT. Compared to LT group, the beneficial influences of ALSS on intraoperative blood loss and endotracheal intubation time were also observed in ALSS-LT group. The 1-year and 5-year survival rates in the ALSS-LT group and LT group were 79.2% and 83%, 69.7% and 78.6%.
Conclusions/significance: Plasma exchange-centered ALSS is beneficial in salvaging patients with ACLF when a donor liver is not available. The consequential LT is the fundamental treatment modality to rescue these patients and lead to a similar survival rate as those patients receiving emergency transplantation.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
A non-bioartificial liver support system combined with transplantation in HBV-related acute-on-chronic liver failure.Sci Rep. 2021 Feb 3;11(1):2975. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-82719-x. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33536531 Free PMC article.
-
Artificial Liver Support System Improves Short-Term Outcomes of Patients with HBV-Associated Acute-on-Chronic Liver Failure: A Propensity Score Analysis.Biomed Res Int. 2019 Nov 29;2019:3757149. doi: 10.1155/2019/3757149. eCollection 2019. Biomed Res Int. 2019. PMID: 31871940 Free PMC article.
-
A multi-subgroup predictive model based on clinical parameters and laboratory biomarkers to predict in-hospital outcomes of plasma exchange-centered artificial liver treatment in patients with hepatitis B virus-related acute-on-chronic liver failure.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023 Mar 21;13:1107351. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2023.1107351. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37026054 Free PMC article.
-
Survival Benefits With Artificial Liver Support System for Acute-on-Chronic Liver Failure: A Time Series-Based Meta-Analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2016 Jan;95(3):e2506. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000002506. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016. PMID: 26817889 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Artificial liver support system in China: a review over the last 30 years.Ther Apher Dial. 2006 Apr;10(2):160-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1744-9987.2006.00358.x. Ther Apher Dial. 2006. PMID: 16684218 Review.
Cited by
-
The Clinical Efficacy of Double Plasma Molecular Absorption System Combined with Plasma Exchange in the Treatment of Acute-on-Chronic Liver Failure: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.J Healthc Eng. 2022 Mar 25;2022:3139929. doi: 10.1155/2022/3139929. eCollection 2022. J Healthc Eng. 2022. PMID: 35368957 Free PMC article.
-
A prognostic score for patients with acute-on-chronic liver failure treated with plasma exchange-centered artificial liver support system.Sci Rep. 2021 Jan 14;11(1):1469. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-81019-8. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33446902 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Six month abstinence rule for liver transplantation in severe alcoholic liver disease patients.World J Gastroenterol. 2015 Apr 14;21(14):4423-6. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i14.4423. World J Gastroenterol. 2015. PMID: 25892898 Free PMC article.
-
A prognostic model for hepatitis B acute-on-chronic liver failure patients treated using a plasma exchange-centered liver support system.J Clin Apher. 2020 Apr;35(2):94-103. doi: 10.1002/jca.21762. Epub 2019 Nov 26. J Clin Apher. 2020. PMID: 31769901 Free PMC article.
-
Acute-on-chronic liver failure: Pathogenesis, prognostic factors and management.World J Gastroenterol. 2015 Nov 14;21(42):12125-40. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i42.12125. World J Gastroenterol. 2015. PMID: 26576097 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Santoro A, Mancini E, Buttiglieri S, Krause A, Yakubovich M, et al. (2004) Extracorporeal support of liver function (II Part). Int J Artif Organs 27: 176–185. - PubMed
-
- Li LJ, Zhang YM, Liu XL, Du WB, Huang JR, et al. (2006) Artificial liver support system in China: a review over the last 30 years. Ther Apher Dial 10: 160–167. - PubMed
-
- Wiesner R, Edwards E, Freeman R, Harper A, Kim R, et al. (2003) Model for end-stage liver disease (MELD) and allocation of donor livers. Gastroenterology 124: 91–96. - PubMed
-
- Lu AW, Zheng SS, Wu MP, Shen Y, Yang RW (2008) Reevaluation of the effect of lamivudine therapy preoperative to prevent HBV recurrence after liver transplantation. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int 7: 357–361. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical