Chiral discrimination and writhe-dependent relaxation mechanism of human topoisomerase IIα
- PMID: 23508957
- PMCID: PMC3650406
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M112.444745
Chiral discrimination and writhe-dependent relaxation mechanism of human topoisomerase IIα
Abstract
Background: Human topoisomerase IIα unlinks catenated chromosomes and preferentially relaxes positive supercoils.
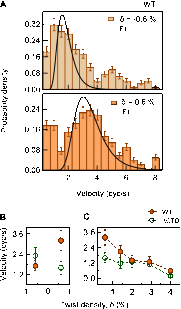
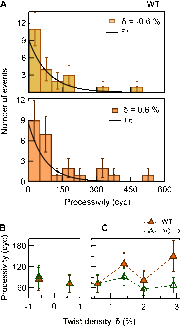
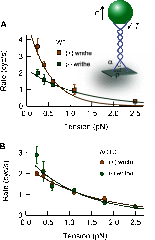
Results: Supercoil chirality, twist density, and tension determine topoisomerase IIα relaxation rate and processivity.
Conclusion: Strand passage rate is determined by the efficiency of transfer segment capture that is modulated by the topoisomerase C-terminal domains.
Significance: Single-molecule measurements reveal the mechanism of chiral discrimination and tension dependence of supercoil relaxation by human topoisomerase IIα. Type IIA topoisomerases (Topo IIA) are essential enzymes that relax DNA supercoils and remove links joining replicated chromosomes. Human topoisomerase IIα (htopo IIα), one of two human isoforms, preferentially relaxes positive supercoils, a feature shared with Escherichia coli topoisomerase IV (Topo IV). The mechanistic basis of this chiral discrimination remains unresolved. To address this important issue, we measured the relaxation of individual supercoiled and "braided" DNA molecules by htopo IIα using a magnetic tweezers-based single-molecule assay. Our study confirmed the chiral discrimination activity of htopo IIα and revealed that the strand passage rate depends on DNA twist, tension on the DNA, and the C-terminal domain (CTD). Similar to Topo IV, chiral discrimination by htopo IIα results from chiral interactions of the CTDs with DNA writhe. In contrast to Topo IV, however, these interactions lead to chiral differences in relaxation rate rather than processivity. Increasing tension or twist disrupts the CTD-DNA interactions with a subsequent loss of chiral discrimination. Together, these results suggest that transfer segment (T-segment) capture is the rate-limiting step in the strand passage cycle. We propose a model for T-segment capture that provides a mechanistic basis for chiral discrimination and provides a coherent explanation for the effects of DNA twist and tension on eukaryotic type IIA topoisomerases.
Keywords: Biophysics; Chiral Discrimination; DNA Replication; DNA Topoisomerase; DNA Topology; Magnetic Tweezers; Single Molecule Biophysics.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Bimodal recognition of DNA geometry by human topoisomerase II alpha: preferential relaxation of positively supercoiled DNA requires elements in the C-terminal domain.Biochemistry. 2008 Dec 16;47(50):13169-78. doi: 10.1021/bi800453h. Biochemistry. 2008. PMID: 19053267 Free PMC article.
-
Human topoisomerase IIalpha rapidly relaxes positively supercoiled DNA: implications for enzyme action ahead of replication forks.J Biol Chem. 2005 Nov 25;280(47):39337-45. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M503320200. Epub 2005 Sep 27. J Biol Chem. 2005. PMID: 16188892
-
Mechanisms of chiral discrimination by topoisomerase IV.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009 Apr 28;106(17):6986-91. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0900574106. Epub 2009 Apr 9. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009. PMID: 19359479 Free PMC article.
-
What makes a type IIA topoisomerase a gyrase or a Topo IV?Nucleic Acids Res. 2021 Jun 21;49(11):6027-6042. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkab270. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021. PMID: 33905522 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[DNA supercoiling and topoisomerases in Escherichia coli].Rev Latinoam Microbiol. 1995 Jul-Sep;37(3):291-304. Rev Latinoam Microbiol. 1995. PMID: 8850348 Review. Spanish.
Cited by
-
Increased negative supercoiling of mtDNA in TOP1mt knockout mice and presence of topoisomerases IIα and IIβ in vertebrate mitochondria.Nucleic Acids Res. 2014 Jun;42(11):7259-67. doi: 10.1093/nar/gku384. Epub 2014 May 6. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014. PMID: 24803675 Free PMC article.
-
Etoposide promotes DNA loop trapping and barrier formation by topoisomerase II.Nat Chem Biol. 2023 May;19(5):641-650. doi: 10.1038/s41589-022-01235-9. Epub 2023 Jan 30. Nat Chem Biol. 2023. PMID: 36717711 Free PMC article.
-
Telling Your Right Hand from Your Left: The Effects of DNA Supercoil Handedness on the Actions of Type II Topoisomerases.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jul 7;24(13):11199. doi: 10.3390/ijms241311199. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37446377 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Impact of the C-Terminal Region on the Interaction of Topoisomerase II Alpha with Mitotic Chromatin.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Mar 12;20(5):1238. doi: 10.3390/ijms20051238. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30871006 Free PMC article.
-
Basis for the discrimination of supercoil handedness during DNA cleavage by human and bacterial type II topoisomerases.Nucleic Acids Res. 2023 May 8;51(8):3888-3902. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkad190. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023. PMID: 36999602 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Champoux J. J. (2001) DNA topoisomerases: structure, function, and mechanism. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 70, 369–413 - PubMed
-
- Forterre P., Gribaldo S., Gadelle D., Serre M.-C. (2007) Origin and evolution of DNA topoisomerases. Biochimie 89, 427–446 - PubMed
-
- Schoeffler A. J., Berger J. M. (2008) DNA topoisomerases: harnessing and constraining energy to govern chromosome topology. Q. Rev. Biophys. 41, 41–101 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

