Opioid agonist treatments and heroin overdose deaths in Baltimore, Maryland, 1995-2009
- PMID: 23488511
- PMCID: PMC3670653
- DOI: 10.2105/AJPH.2012.301049
Opioid agonist treatments and heroin overdose deaths in Baltimore, Maryland, 1995-2009
Abstract
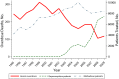
Objectives: We examined the association between the expansion of methadone and buprenorphine treatment and the prevalence of heroin overdose deaths in Baltimore, Maryland from 1995 to 2009.
Methods: We conducted a longitudinal time series analysis of archival data using linear regression with the Newey-West method to correct SEs for heteroscedasticity and autocorrelation, adjusting for average heroin purity.
Results: Overdose deaths attributed to heroin ranged from a high of 312 in 1999 to a low of 106 in 2008. While mean heroin purity rose sharply (1995-1999), the increasing number of patients treated with methadone was not associated with a change in the number of overdose deaths, but starting in 2000 expansion of opioid agonist treatment was associated with a decline in overdose deaths. Adjusting for heroin purity and the number of methadone patients, there was a statistically significant inverse relationship between heroin overdose deaths and patients treated with buprenorphine (P = .002).
Conclusions: Increased access to opioid agonist treatment was associated with a reduction in heroin overdose deaths. Implementing policies that support evidence-based medication treatment of opiate dependence may decrease heroin overdose deaths.
Figures
Comment in
-
Schwartz et al. respond.Am J Public Health. 2013 Aug;103(8):e2-3. doi: 10.2105/AJPH.2013.301428. Epub 2013 Jun 13. Am J Public Health. 2013. PMID: 23763406 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Efforts to reduce overdose deaths.Am J Public Health. 2013 Aug;103(8):e1-2. doi: 10.2105/AJPH.2013.301410. Epub 2013 Jun 13. Am J Public Health. 2013. PMID: 23763429 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Efforts to reduce overdose deaths.Am J Public Health. 2013 Aug;103(8):e1-2. doi: 10.2105/AJPH.2013.301410. Epub 2013 Jun 13. Am J Public Health. 2013. PMID: 23763429 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Schwartz et al. respond.Am J Public Health. 2013 Aug;103(8):e2-3. doi: 10.2105/AJPH.2013.301428. Epub 2013 Jun 13. Am J Public Health. 2013. PMID: 23763406 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Opioid agonist treatment and fatal overdose risk in a state-wide US population receiving opioid use disorder services.Addiction. 2020 Sep;115(9):1683-1694. doi: 10.1111/add.14991. Epub 2020 Feb 24. Addiction. 2020. PMID: 32096302 Free PMC article.
-
Mortality risk during and after opioid substitution treatment: systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort studies.BMJ. 2017 Apr 26;357:j1550. doi: 10.1136/bmj.j1550. BMJ. 2017. PMID: 28446428 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pharmacologic Treatment of Opioid Use Disorder: a Review of Pharmacotherapy, Adjuncts, and Toxicity.J Med Toxicol. 2018 Dec;14(4):306-322. doi: 10.1007/s13181-018-0685-1. Epub 2018 Oct 30. J Med Toxicol. 2018. PMID: 30377951 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Disparities in Opioid Use Disorder Treatment Admissions.J Health Econ Outcomes Res. 2020 Jun 22;7(1):85-93. doi: 10.36469/jheor.2020.13266. eCollection 2020. J Health Econ Outcomes Res. 2020. PMID: 32685601 Free PMC article.
-
Motivations for opioid and stimulant use among drug using black sexual minority men: A life course perspective.Drug Alcohol Depend. 2020 Oct 1;215:108224. doi: 10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2020.108224. Epub 2020 Aug 6. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2020. PMID: 32777690 Free PMC article.
-
Substance use disorders and avoidable mortality after prison.Lancet Psychiatry. 2015 May;2(5):369-370. doi: 10.1016/S2215-0366(15)00125-X. Lancet Psychiatry. 2015. PMID: 26069881 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Prior Experience with Non-Prescribed Buprenorphine: Role in Treatment Entry and Retention.J Subst Abuse Treat. 2015 Oct;57:57-62. doi: 10.1016/j.jsat.2015.04.010. Epub 2015 May 7. J Subst Abuse Treat. 2015. PMID: 25980599 Free PMC article.
-
Heroin Use, HIV-Risk, and Criminal Behavior in Baltimore: Findings from Clinical Research.J Addict Dis. 2015;34(2-3):151-61. doi: 10.1080/10550887.2015.1059222. J Addict Dis. 2015. PMID: 26079104 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hickman M, Carrivick S, Paterson Set al.London audit of drug-related overdose deaths: characteristics and typology, and implications for prevention and monitoring. Addiction. 2007;102(2):317–323 - PubMed
-
- Preti A, Miotto P, De Coppi M. Deaths by unintentional illicit drug overdose in Italy, 1984–2000. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2002;66(3):275–282 - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization Substitution Maintenance Therapy in the Management of Opioid Dependence and HIV/AIDS Prevention. Vienna: United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime; 2004
-
- Darke S, Duflou J, Torok M. A reduction in blood morphine concentrations amongst heroin overdose fatalities associated with a sustained reduction in street heroin purity. Forensic Sci Int. 2010;198(1–3):118–120 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical