Occupying chromatin: Polycomb mechanisms for getting to genomic targets, stopping transcriptional traffic, and staying put
- PMID: 23473600
- PMCID: PMC3628831
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2013.02.013
Occupying chromatin: Polycomb mechanisms for getting to genomic targets, stopping transcriptional traffic, and staying put
Abstract
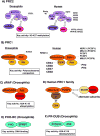
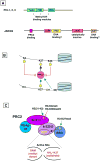
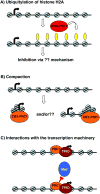
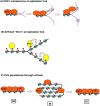
Chromatin modification by Polycomb proteins provides an essential strategy for gene silencing in higher eukaryotes. Polycomb repressive complexes (PRCs) silence key developmental regulators and are centrally integrated in the transcriptional circuitry of stem cells. PRC2 trimethylates histone H3 on lysine 27 (H3K27me3), and PRC1-type complexes ubiquitylate histone H2A and compact polynucleosomes. How PRCs are deployed to select and silence genomic targets is the subject of intense investigation. We review advances on targeting, modulation, and functions of PRC1 and PRC2 and progress on defining the transcriptional steps they impact. Recent findings emphasize PRC1 targeting independent of H3K27me3, nonenzymatic PRC1-mediated compaction, and connections between PRCs and noncoding RNAs. Systematic analyses of Polycomb complexes and associated histone modifications during DNA replication and mitosis have also emerged. The stage is now set to reveal fundamental epigenetic mechanisms that determine how Polycomb target genes are silenced and how Polycomb silence is preserved through cell-cycle progression.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Polycomb Gene Silencing Mechanisms: PRC2 Chromatin Targeting, H3K27me3 'Readout', and Phase Separation-Based Compaction.Trends Genet. 2021 Jun;37(6):547-565. doi: 10.1016/j.tig.2020.12.006. Epub 2021 Jan 22. Trends Genet. 2021. PMID: 33494958 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Polycomb-mediated histone modifications and gene regulation.Biochem Soc Trans. 2024 Feb 28;52(1):151-161. doi: 10.1042/BST20230336. Biochem Soc Trans. 2024. PMID: 38288743 Review.
-
Interdependence of PRC1 and PRC2 for recruitment to Polycomb Response Elements.Nucleic Acids Res. 2016 Dec 1;44(21):10132-10149. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw701. Epub 2016 Aug 23. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016. PMID: 27557709 Free PMC article.
-
RYBP stimulates PRC1 to shape chromatin-based communication between Polycomb repressive complexes.Elife. 2016 Oct 5;5:e18591. doi: 10.7554/eLife.18591. Elife. 2016. PMID: 27705745 Free PMC article.
-
H2A monoubiquitination in Arabidopsis thaliana is generally independent of LHP1 and PRC2 activity.Genome Biol. 2017 Apr 12;18(1):69. doi: 10.1186/s13059-017-1197-z. Genome Biol. 2017. PMID: 28403905 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
MicroRNA-31 is a transcriptional target of histone deacetylase inhibitors and a regulator of cellular senescence.J Biol Chem. 2015 Apr 17;290(16):10555-67. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.624361. Epub 2015 Mar 3. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 25737447 Free PMC article.
-
EZH2 regulates neuroepithelium structure and neuroblast proliferation by repressing p21.Open Biol. 2016 Apr;6(4):150227. doi: 10.1098/rsob.150227. Epub 2016 Apr 20. Open Biol. 2016. PMID: 27248655 Free PMC article.
-
Maintaining cell identity: PRC2-mediated regulation of transcription and cancer.Nat Rev Cancer. 2016 Dec;16(12):803-810. doi: 10.1038/nrc.2016.83. Epub 2016 Sep 23. Nat Rev Cancer. 2016. PMID: 27658528 Review.
-
Regulation of Polyhomeotic Condensates by Intrinsically Disordered Sequences That Affect Chromatin Binding.Epigenomes. 2022 Nov 3;6(4):40. doi: 10.3390/epigenomes6040040. Epigenomes. 2022. PMID: 36412795 Free PMC article.
-
Allosteric regulation of histone lysine methyltransferases: from context-specific regulation to selective drugs.Biochem Soc Trans. 2021 Apr 30;49(2):591-607. doi: 10.1042/BST20200238. Biochem Soc Trans. 2021. PMID: 33769454 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Beisel C, Paro R. Silencing chromatin: comparing modes and mechanisms. Nat Rev Genet. 2011;12:123–135. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

