The enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli effector protein NleF binds mammalian Tmp21
- PMID: 23434013
- PMCID: PMC3640833
- DOI: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2013.01.028
The enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli effector protein NleF binds mammalian Tmp21
Abstract
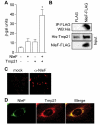
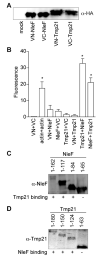
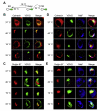
The human pathogens enterohemorrhagic and enteropathogenic Escherichia coli (EHEC and EPEC), as well as the mouse pathogen Citrobacter rodentium encode type III secretion system (T3SS) effector proteins to promote their survival in the infected host. The mechanisms of action and the host targets of T3SS effectors are under active investigation because of their importance to bacterial virulence. The non-locus of enterocyte effacement (LEE)-encoded protein F, NleF, contributes to E. coli and C. rodentium colonization of piglets and mice, respectively. Here we sought to characterize the host binding partners of NleF. Using a yeast two-hybrid screen, we identified Tmp21, a type-I integral membrane protein and COPI-vesicle receptor involved in trans-Golgi network function, as an NleF-binding partner. We confirmed this interaction using immunoprecipitation and bimolecular fluorescence complementation (BiFC). We expressed a temperature-sensitive vesicular stomatitis virus glycoprotein (tsVSVG) to monitor protein trafficking and determined that NleF slows the intracellular trafficking of tsVSVG from the endoplasmic reticulum to the Golgi.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Characterization of the NleF effector protein from attaching and effacing bacterial pathogens.FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2008 Apr;281(1):98-107. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.2008.01088.x. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2008. PMID: 18279332 Free PMC article.
-
Distinct Roles of the Antiapoptotic Effectors NleB and NleF from Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli.Infect Immun. 2017 Mar 23;85(4):e01071-16. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01071-16. Print 2017 Apr. Infect Immun. 2017. PMID: 28138023 Free PMC article.
-
Type Three Secretion System in Attaching and Effacing Pathogens.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2016 Oct 21;6:129. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2016.00129. eCollection 2016. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27818950 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The inhibition of COPII trafficking is important for intestinal epithelial tight junction disruption during enteropathogenic Escherichia coli and Citrobacter rodentium infection.Microbes Infect. 2013 Sep-Oct;15(10-11):738-44. doi: 10.1016/j.micinf.2013.05.001. Epub 2013 Jun 6. Microbes Infect. 2013. PMID: 23747681
-
Salmonella, E. coli, and Citrobacter Type III Secretion System Effector Proteins that Alter Host Innate Immunity.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2019;1111:205-218. doi: 10.1007/5584_2018_289. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2019. PMID: 30411307 Review.
Cited by
-
Bacteria fighting back: how pathogens target and subvert the host innate immune system.Mol Cell. 2014 Apr 24;54(2):321-8. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2014.03.010. Mol Cell. 2014. PMID: 24766896 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diffusely Adherent Escherichia coli Strains Isolated from Healthy Carriers Suppress Cytokine Secretions of Epithelial Cells Stimulated by Inflammatory Substances.Infect Immun. 2018 Dec 19;87(1):e00683-18. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00683-18. Print 2019 Jan. Infect Immun. 2018. PMID: 30323026 Free PMC article.
-
The type III secretion effector NleF of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli activates NF-κB early during infection.Infect Immun. 2014 Nov;82(11):4878-88. doi: 10.1128/IAI.02131-14. Epub 2014 Sep 2. Infect Immun. 2014. PMID: 25183730 Free PMC article.
-
The EHEC-host interactome reveals novel targets for the translocated intimin receptor.Sci Rep. 2014 Dec 18;4:7531. doi: 10.1038/srep07531. Sci Rep. 2014. PMID: 25519916 Free PMC article.
-
A Genome-Wide Haploid Genetic Screen Identifies Heparan Sulfate-Associated Genes and the Macropinocytosis Modulator TMED10 as Factors Supporting Vaccinia Virus Infection.J Virol. 2019 Jun 14;93(13):e02160-18. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02160-18. Print 2019 Jul 1. J Virol. 2019. PMID: 30996093 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Blum R, Lepier A. The luminal domain of p23 (Tmp21) plays a critical role in p23 cell surface trafficking. Traffic. 2008;9:1530–1550. - PubMed
-
- Blum R, Pfeiffer F, Feick P, Nastainczyk W, Kohler B, Schafer KH, Schulz I. Intracellular localization and in vivo trafficking of p24A and p23. J. Cell Sci. 1999;112(Pt 4):537–548. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

