Widespread long noncoding RNAs as endogenous target mimics for microRNAs in plants
- PMID: 23429259
- PMCID: PMC3613462
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.113.215962
Widespread long noncoding RNAs as endogenous target mimics for microRNAs in plants
Abstract
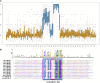
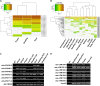
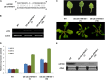
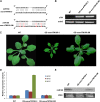
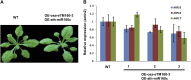
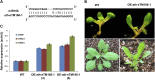
Target mimicry is a recently identified regulatory mechanism for microRNA (miRNA) functions in plants in which the decoy RNAs bind to miRNAs via complementary sequences and therefore block the interaction between miRNAs and their authentic targets. Both endogenous decoy RNAs (miRNA target mimics) and engineered artificial RNAs can induce target mimicry effects. Yet until now, only the Induced by Phosphate Starvation1 RNA has been proven to be a functional endogenous microRNA target mimic (eTM). In this work, we developed a computational method and systematically identified intergenic or noncoding gene-originated eTMs for 20 conserved miRNAs in Arabidopsis (Arabidopsis thaliana) and rice (Oryza sativa). The predicted miRNA binding sites were well conserved among eTMs of the same miRNA, whereas sequences outside of the binding sites varied a lot. We proved that the eTMs of miR160 and miR166 are functional target mimics and identified their roles in the regulation of plant development. The effectiveness of eTMs for three other miRNAs was also confirmed by transient agroinfiltration assay.
Figures
Similar articles
-
PeTMbase: A Database of Plant Endogenous Target Mimics (eTMs).PLoS One. 2016 Dec 9;11(12):e0167698. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0167698. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27936097 Free PMC article.
-
Target mimics: an embedded layer of microRNA-involved gene regulatory networks in plants.BMC Genomics. 2012 May 21;13:197. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-13-197. BMC Genomics. 2012. PMID: 22613869 Free PMC article.
-
A transcriptome-wide study on the microRNA- and the Argonaute 1-enriched small RNA-mediated regulatory networks involved in plant leaf senescence.Plant Biol (Stuttg). 2016 Mar;18(2):197-205. doi: 10.1111/plb.12373. Epub 2015 Aug 4. Plant Biol (Stuttg). 2016. PMID: 26206233
-
Functions of long intergenic non-coding (linc) RNAs in plants.J Plant Res. 2017 Jan;130(1):67-73. doi: 10.1007/s10265-016-0894-0. Epub 2016 Dec 20. J Plant Res. 2017. PMID: 27999969 Review.
-
Long Non-Coding RNAs as Endogenous Target Mimics and Exploration of Their Role in Low Nutrient Stress Tolerance in Plants.Genes (Basel). 2018 Sep 14;9(9):459. doi: 10.3390/genes9090459. Genes (Basel). 2018. PMID: 30223541 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Cucumber STACHYOSE SYNTHASE is regulated by its cis-antisense RNA asCsSTS to balance source-sink carbon partitioning.Plant Cell. 2023 Jan 2;35(1):435-452. doi: 10.1093/plcell/koac317. Plant Cell. 2023. PMID: 36342214 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide identification of potato long intergenic noncoding RNAs responsive to Pectobacterium carotovorum subspecies brasiliense infection.BMC Genomics. 2016 Aug 11;17(1):614. doi: 10.1186/s12864-016-2967-9. BMC Genomics. 2016. PMID: 27515663 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide identification and functional analysis of circRNAs in Zea mays.PLoS One. 2018 Dec 11;13(12):e0202375. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0202375. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30533052 Free PMC article.
-
Functional analysis of the eTM-miR171-SCL6 module regulating somatic embryogenesis in Lilium pumilum DC. Fisch.Hortic Res. 2022 Feb 19;9:uhac045. doi: 10.1093/hr/uhac045. Online ahead of print. Hortic Res. 2022. PMID: 35184179 Free PMC article.
-
Role of long non-coding RNA in regulatory network response to Candidatus Liberibacter asiaticus in citrus.Front Plant Sci. 2023 Feb 20;14:1090711. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1090711. eCollection 2023. Front Plant Sci. 2023. PMID: 36890903 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Axtell MJ, Bowman JL. (2008) Evolution of plant microRNAs and their targets. Trends Plant Sci 13: 343–349 - PubMed
-
- Clough SJ, Bent AF. (1998) Floral dip: a simplified method for Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 16: 735–743 - PubMed
-
- Franco-Zorrilla JM, Valli A, Todesco M, Mateos I, Puga MI, Rubio-Somoza I, Leyva A, Weigel D, García JA, Paz-Ares J. (2007) Target mimicry provides a new mechanism for regulation of microRNA activity. Nat Genet 39: 1033–1037 - PubMed
-
- He XF, Fang YY, Feng L, Guo HS. (2008) Characterization of conserved and novel microRNAs and their targets, including a TuMV-induced TIR-NBS-LRR class R gene-derived novel miRNA in Brassica. FEBS Lett 582: 2445–2452 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

