CCN proteins: A centralized communication network
- PMID: 23420091
- PMCID: PMC3709049
- DOI: 10.1007/s12079-013-0193-7
CCN proteins: A centralized communication network
Abstract
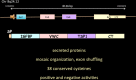
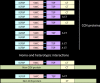
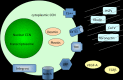
The CCN family of proteins includes six members presently known as CCN1, CCN2, CCN3, CCN4, CCN5 and CCN6. These proteins were originally designated CYR61, CTGF, NOV, and WISP-1, WISP-2, WISP-3. Although these proteins share a significant amount of structural features and a partial identity with other large families of regulatory proteins, they exhibit different biological functions. A critical examination of the progress made over the past two decades, since the first CCN proteins were discovered brings me to the conclusion that most of our present knowledge regarding the functions of these proteins was predicted very early after their discovery. In an effort to point out some of the gaps that prevent us to reach a comprehensive view of the functional interactions between CCN proteins, it is necessary to reconsider carefully data that was already published and put aside, either because the scientific community was not ready to accept them, or because they were not fitting with the « consensus » when they were published. This review article points to avenues that were not attracting the attention that they deserved. However, it is quite obvious that the six members of this unique family of tetra-modular proteins must act in concert, either simultaneously or sequentially, on the same sites or at different times in the life of living organisms. A better understanding of the spatio-temporal regulation of CCN proteins expression requires considering the family as such, not as a set of single proteins related only by their name. As proposed in this review, there is enough convincing pieces of evidence, at the present time, in favor of these proteins playing a role in the coordination of multiple signaling pathways, and constituting a Centralized Communication Network. Deciphering the hierarchy of regulatory circuits involved in this complex system is an important challenge for the near future. In this article, I would like to briefly review the concept of a CCN family of proteins and critically examine the progress made over the past 10 years in the understanding of their biological functions and involvement in both normal and pathological processes.
Figures


Similar articles
-
CCN family of proteins: critical modulators of the tumor cell microenvironment.J Cell Commun Signal. 2016 Sep;10(3):229-240. doi: 10.1007/s12079-016-0346-6. Epub 2016 Aug 12. J Cell Commun Signal. 2016. PMID: 27517291 Free PMC article.
-
The CCN family of proteins: a 25th anniversary picture.J Cell Commun Signal. 2016 Sep;10(3):177-190. doi: 10.1007/s12079-016-0340-z. Epub 2016 Aug 31. J Cell Commun Signal. 2016. PMID: 27581423 Free PMC article.
-
Alternative splicing of CCN mRNAs .... it has been upon us.J Cell Commun Signal. 2009 Jun;3(2):153-7. doi: 10.1007/s12079-009-0051-9. Epub 2009 Apr 28. J Cell Commun Signal. 2009. PMID: 19399643 Free PMC article.
-
Biological characteristics of CCN proteins in tumor development.J BUON. 2016 Nov-Dec;21(6):1359-1367. J BUON. 2016. PMID: 28039692 Review.
-
The CCN proteins: important signaling mediators in stem cell differentiation and tumorigenesis.Histol Histopathol. 2010 Jun;25(6):795-806. doi: 10.14670/HH-25.795. Histol Histopathol. 2010. PMID: 20376786 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
7th international workshop on the CCN family of genes: Nice to be in nice.J Cell Commun Signal. 2013 Aug;7(3):165-7. doi: 10.1007/s12079-013-0209-3. Epub 2013 Jul 6. J Cell Commun Signal. 2013. PMID: 23832607 Free PMC article.
-
CYR61 overexpression associated with the development and poor prognosis of ovarian carcinoma.Med Oncol. 2014 Aug;31(8):117. doi: 10.1007/s12032-014-0117-2. Epub 2014 Jul 22. Med Oncol. 2014. PMID: 25048722
-
Matricellular proteins in immunometabolism and tissue homeostasis.BMB Rep. 2024 Sep;57(9):400-416. doi: 10.5483/BMBRep.2023-0156. BMB Rep. 2024. PMID: 38919018 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cysteine-rich protein 61 (CCN1) and connective tissue growth factor (CCN2) at the crosshairs of ocular neovascular and fibrovascular disease therapy.J Cell Commun Signal. 2013 Dec;7(4):253-63. doi: 10.1007/s12079-013-0206-6. Epub 2013 Jun 7. J Cell Commun Signal. 2013. PMID: 23740088 Free PMC article.
-
CCN family of proteins: critical modulators of the tumor cell microenvironment.J Cell Commun Signal. 2016 Sep;10(3):229-240. doi: 10.1007/s12079-016-0346-6. Epub 2016 Aug 12. J Cell Commun Signal. 2016. PMID: 27517291 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ball DK, Surveyor GA, Diehl JR, Steffen CL, Uzumcu M, Mirando MA, Brigstock DR. Characterization of 16- to 20-kilodalton (kDa) connective tissue growth factors (CTGFs) and demonstration of proteolytic activity for 38-kDa CTGF in pig uterine luminal flushings. Biol Reprod. 1998;59(4):828–835. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod59.4.828. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

