Vesicle-mediated export from the ER: COPII coat function and regulation
- PMID: 23419775
- PMCID: PMC3676692
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2013.02.003
Vesicle-mediated export from the ER: COPII coat function and regulation
Abstract
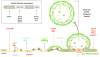
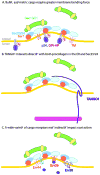
Vesicle trafficking from the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a vital cellular process in all eukaryotes responsible for moving secretory cargoes from the ER to the Golgi apparatus. To accomplish this feat, the cell employs a set of conserved cytoplasmic coat proteins - the coat protein II (COPII) complex - that recruit cargo into nascent buds and deform the ER membrane to drive vesicle formation. While our understanding of COPII coat mechanics has developed substantially since its discovery, we have only recently begun to appreciate the factors that regulate this complex and, in turn, ER-to-Golgi trafficking. Here, we describe these factors and their influences on COPII vesicle formation. Properties intrinsic to the GTP cycle of the coat, as well as coat structure, have critical implications for COPII vesicle trafficking. Extrinsic factors in the cytosol can modulate COPII activity through direct interaction with the coat or with scaffolding components, or by changing composition of the ER membrane. Further, lumenal and membrane-bound cargoes and cargo receptors can influence COPII-mediated trafficking in equally profound ways. Together, these factors work in concert to ensure proper cargo movement in this first step of the secretory pathway. This article is part of a Special Issue entitled: Functional and structural diversity of endoplasmic reticulum.
Keywords: CLSD; COPII; Cargo export; Cargo receptor; ER; ER exit sites; ERES; ERK; Endoplasmic reticulum; GAP; GEF; GPI-AP; GST; GTPase activating protein; MAPK; PH; PtdIns4P; TANGO1; TFG-1; TRK-fused gene 1; VSVG; Vesicle; bst; bypass-of-sec-thirteen; cTAGE5; coat protein II complex; cranio–lentinculo–sutural dysplasia; cutaneous T-cell lymphoma-associated antigen 5; endoplasmic reticulum; extracellular signal-regulated kinase; glutathione S-transferase; glycosylphophatidylinositol-anchored protein; guanine nucleotide exchange factor; mitogen activated protein kinase; phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate; pleckstrin homology; transport and Golgi organization 1; vesicular stomatitis virus G protein.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
COPII-mediated trafficking at the ER/ERGIC interface.Traffic. 2019 Jul;20(7):491-503. doi: 10.1111/tra.12654. Epub 2019 May 30. Traffic. 2019. PMID: 31059169 Free PMC article. Review.
-
COPII collar defines the boundary between ER and ER exit site and does not coat cargo containers.J Cell Biol. 2021 Jun 7;220(6):e201907224. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201907224. J Cell Biol. 2021. PMID: 33852719 Free PMC article.
-
TFG facilitates outer coat disassembly on COPII transport carriers to promote tethering and fusion with ER-Golgi intermediate compartments.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017 Sep 12;114(37):E7707-E7716. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1709120114. Epub 2017 Aug 29. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017. PMID: 28851831 Free PMC article.
-
COPII coat assembly and selective export from the endoplasmic reticulum.J Biochem. 2004 Dec;136(6):755-60. doi: 10.1093/jb/mvh184. J Biochem. 2004. PMID: 15671485 Review.
-
TFG regulates inner COPII coat recruitment to facilitate anterograde secretory protein transport.Mol Biol Cell. 2024 Aug 1;35(8):ar113. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E24-06-0282. Epub 2024 Jul 10. Mol Biol Cell. 2024. PMID: 38985515 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Host endoplasmic reticulum COPII proteins control cell-to-cell spread of the bacterial pathogen Listeria monocytogenes.Cell Microbiol. 2015 Jun;17(6):876-92. doi: 10.1111/cmi.12409. Epub 2015 Jan 26. Cell Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 25529574 Free PMC article.
-
An N-Terminal ER Export Signal Facilitates the Plasma Membrane Targeting of HCN1 Channels in Photoreceptors.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2015 Jun;56(6):3514-21. doi: 10.1167/iovs.15-16902. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2015. PMID: 26030105 Free PMC article.
-
GOLGI TRANSPORT 1B Regulates Protein Export from the Endoplasmic Reticulum in Rice Endosperm Cells.Plant Cell. 2016 Nov;28(11):2850-2865. doi: 10.1105/tpc.16.00717. Epub 2016 Nov 1. Plant Cell. 2016. PMID: 27803308 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of the unfolded protein response on ER protein export: a potential new mechanism to relieve ER stress.Cell Stress Chaperones. 2018 Sep;23(5):797-806. doi: 10.1007/s12192-018-0905-2. Epub 2018 May 5. Cell Stress Chaperones. 2018. PMID: 29730847 Free PMC article.
-
Tales of tails in transporters.Open Biol. 2019 Jun 28;9(6):190083. doi: 10.1098/rsob.190083. Epub 2019 Jun 19. Open Biol. 2019. PMID: 31213137 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Barlowe C, Orci L, Yeung T, Hosobuchi M, Hamamoto S, Salama N, Rexach MF, Ravazzola M, Amherdt M, Schekman R. COPII: a membrane coat formed by Sec proteins that drive vesicle budding from the endoplasmic reticulum. Cell. 1994;77:895–907. - PubMed
-
- Matsuoka K, Orci L, Amherdt M, Bednarek SY, Hamamoto S, Schekman R, Yeung T. COPII-coated vesicle formation reconstituted with purified coat proteins and chemically defined liposomes. Cell. 1998;93:263–275. - PubMed
-
- Antonny B, Madden D, Hamamoto S, Orci L, Schekman R. Dynamics of the COPII coat with GTP and stable analogues. Nature cell biology. 2001;3:531–537. - PubMed
-
- Ghaemmaghami S, Huh WK, Bower K, Howson RW, Belle A, Dephoure N, O’Shea EK, Weissman JS. Global analysis of protein expression in yeast. Nature. 2003;425:737–741. - PubMed
-
- Zanetti G, Pahuja KB, Studer S, Shim S, Schekman R. COPII and the regulation of protein sorting in mammals. Nat Cell Biol. 2012;14:20–28. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

