The expression of interleukin-32 is activated by human cytomegalovirus infection and down regulated by hcmv-miR-UL112-1
- PMID: 23402302
- PMCID: PMC3598236
- DOI: 10.1186/1743-422X-10-51
The expression of interleukin-32 is activated by human cytomegalovirus infection and down regulated by hcmv-miR-UL112-1
Abstract
Background: Interleukin-32 (IL-32) is an important factor in innate and adaptive immune responses, which activates the p38MAPK, NF-kappa B and AP-1 signaling pathways. Recent reports have highlighted that IL-32 is regulated during viral infection in humans.
Methods: Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISA) were carried out to detect IL-32 levels in serum samples. Detailed kinetics of the transcription of IL-32 mRNA and expression of IL-32 protein during human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) infection were determined by semi-quantitative RT-PCR and western blot, respectively. The expression levels of hcmv-miR-UL112-1 were detected using TaqMan® miRNA assays during a time course of 96 hours. The effects of hcmv-miR-UL112-1 on IL-32 expression were demonstrated by luciferase assay and western blot, respectively.
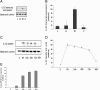
Results: Serum levels of IL-32 in HCMV-IgM positive patients (indicating an active HCMV infection) were significantly higher than those in HCMV-IgM negative controls. HCMV infection activated cellular IL-32 transcription mainly in the immediately early (IE) phase and elevated IL-32 protein levels between 6 and 72 hours post infection (hpi) in the human embryonic lung fibroblast cell line, MRC-5. The expression of hcmv-miR-UL112-1 was detected at 24 hpi and increased gradually as the HCMV-infection process was prolonged. In addition, it was demonstrated that hcmv-miR-UL112-1 targets a sequence in the IL-32 3'-UTR. The protein level of IL-32 in HEK293 cells could be functionally down-regulated by transfected hcmv-miR-UL112-1.
Conclusions: IL-32 expression was induced by active HCMV infection and could be functionally down-regulated by ectopically expressed hcmv-miR-UL112-1. Our data may indicate a new strategy of immune evasion by HCMV through post-transcriptional regulation.
Figures

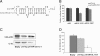
Similar articles
-
Human Cytomegalovirus miR-UL112-3p Targets TLR2 and Modulates the TLR2/IRAK1/NFκB Signaling Pathway.PLoS Pathog. 2015 May 8;11(5):e1004881. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1004881. eCollection 2015 May. PLoS Pathog. 2015. PMID: 25955717 Free PMC article.
-
Human Cytomegalovirus MicroRNAs miR-US5-1 and miR-UL112-3p Block Proinflammatory Cytokine Production in Response to NF-κB-Activating Factors through Direct Downregulation of IKKα and IKKβ.mBio. 2017 Mar 7;8(2):e00109-17. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00109-17. mBio. 2017. PMID: 28270578 Free PMC article.
-
Hcmv-miR-UL112 attenuates NK cell activity by inhibition type I interferon secretion.Immunol Lett. 2015 Feb;163(2):151-6. doi: 10.1016/j.imlet.2014.12.003. Epub 2014 Dec 18. Immunol Lett. 2015. PMID: 25530545
-
[Interrelationship between human cytomegalovirus infection and chemokine].Nihon Rinsho. 1998 Jan;56(1):69-74. Nihon Rinsho. 1998. PMID: 9465667 Review. Japanese.
-
Human cytomegalovirus encoded microRNAs: hitting targets.Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2015;13(12):1469-79. doi: 10.1586/14787210.2015.1106939. Epub 2015 Oct 28. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2015. PMID: 26509290 Review.
Cited by
-
The role of microRNAs in respiratory viral infection: friend or foe?Rev Med Virol. 2016 Nov;26(6):389-407. doi: 10.1002/rmv.1894. Epub 2016 Jul 4. Rev Med Virol. 2016. PMID: 27373545 Free PMC article. Review.
-
microRNA, a Subtle Indicator of Human Cytomegalovirus against Host Immune Cells.Vaccines (Basel). 2022 Jan 19;10(2):144. doi: 10.3390/vaccines10020144. Vaccines (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35214602 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Viral miRNA regulation of host gene expression.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2023 Sep 15;146:2-19. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2022.11.007. Epub 2022 Nov 30. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2023. PMID: 36463091 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of microRNAs in the Pathogenesis of Herpesvirus Infection.Viruses. 2016 Jun 2;8(6):156. doi: 10.3390/v8060156. Viruses. 2016. PMID: 27271654 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human Cytomegalovirus miR-US25-1 Targets the GTPase RhoA To Inhibit CD34+ Hematopoietic Progenitor Cell Proliferation To Maintain the Latent Viral Genome.mBio. 2021 Apr 6;12(2):e00621-21. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00621-21. mBio. 2021. PMID: 33824207 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kim SH, Han SY, Azam T, Yoon DY, Dinarello CA. Interleukin-32: a cytokine and inducer of TNFalpha. Immunity. 2005;22:131–142. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

