A systematic mammalian genetic interaction map reveals pathways underlying ricin susceptibility
- PMID: 23394947
- PMCID: PMC3652613
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2013.01.030
A systematic mammalian genetic interaction map reveals pathways underlying ricin susceptibility
Abstract
Genetic interaction (GI) maps, comprising pairwise measures of how strongly the function of one gene depends on the presence of a second, have enabled the systematic exploration of gene function in microorganisms. Here, we present a two-stage strategy to construct high-density GI maps in mammalian cells. First, we use ultracomplex pooled shRNA libraries (25 shRNAs/gene) to identify high-confidence hit genes for a given phenotype and effective shRNAs. We then construct double-shRNA libraries from these to systematically measure GIs between hits. A GI map focused on ricin susceptibility broadly recapitulates known pathways and provides many unexpected insights. These include a noncanonical role for COPI, a previously uncharacterized protein complex affecting toxin clearance, a specialized role for the ribosomal protein RPS25, and functionally distinct mammalian TRAPP complexes. The ability to rapidly generate mammalian GI maps provides a potentially transformative tool for defining gene function and designing combination therapies based on synergistic pairs.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
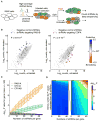
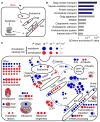
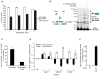
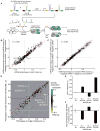
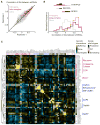
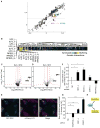
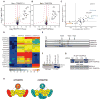
Comment in
-
Genetic screening: Interaction maps for mammals.Nat Rev Genet. 2013 Apr;14(4):240. doi: 10.1038/nrg3451. Epub 2013 Feb 19. Nat Rev Genet. 2013. PMID: 23419280 No abstract available.
-
Genetics: Mammalian genes interacting.Nat Methods. 2013 Apr;10(4):281. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.2424. Nat Methods. 2013. PMID: 23653921 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Integrated platform for genome-wide screening and construction of high-density genetic interaction maps in mammalian cells.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013 Jun 18;110(25):E2317-26. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1307002110. Epub 2013 Jun 5. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013. PMID: 23739767 Free PMC article.
-
Evidence that the transport of ricin to the cytoplasm is independent of both Rab6A and COPI.J Cell Sci. 2003 Sep 1;116(Pt 17):3503-10. doi: 10.1242/jcs.00641. Epub 2003 Jul 15. J Cell Sci. 2003. PMID: 12865434
-
Functional genomics platform for pooled screening and generation of mammalian genetic interaction maps.Nat Protoc. 2014 Aug;9(8):1825-47. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2014.103. Epub 2014 Jul 3. Nat Protoc. 2014. PMID: 24992097 Free PMC article.
-
Ricin: the endoplasmic reticulum connection.Toxicon. 2004 Oct;44(5):469-72. doi: 10.1016/j.toxicon.2004.07.002. Toxicon. 2004. PMID: 15450920 Review.
-
Transport between ER and Golgi.Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2000 Aug;12(4):445-9. doi: 10.1016/s0955-0674(00)00115-0. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2000. PMID: 10873822 Review.
Cited by
-
Scaling up the systematic hunt for mammalian genetic interactions.Nat Methods. 2013 May;10(5):397-9. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.2449. Nat Methods. 2013. PMID: 23629415 No abstract available.
-
CRISPR-mediated modular RNA-guided regulation of transcription in eukaryotes.Cell. 2013 Jul 18;154(2):442-51. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2013.06.044. Epub 2013 Jul 11. Cell. 2013. PMID: 23849981 Free PMC article.
-
Cell density-induced changes in lipid composition and intracellular trafficking.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2014 Mar;71(6):1097-116. doi: 10.1007/s00018-013-1441-y. Epub 2013 Aug 7. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2014. PMID: 23921715 Free PMC article.
-
A tapt1 knock-out zebrafish line with aberrant lens development and impaired vision models human early-onset cataract.Hum Genet. 2023 Mar;142(3):457-476. doi: 10.1007/s00439-022-02518-w. Epub 2023 Jan 25. Hum Genet. 2023. PMID: 36697720
-
Mapping a diversity of genetic interactions in yeast.Curr Opin Syst Biol. 2017 Dec;6:14-21. doi: 10.1016/j.coisb.2017.08.002. Epub 2017 Aug 12. Curr Opin Syst Biol. 2017. PMID: 30505984 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

