Effects of SGLT2 inhibition in human kidney proximal tubular cells--renoprotection in diabetic nephropathy?
- PMID: 23390498
- PMCID: PMC3563635
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0054442
Effects of SGLT2 inhibition in human kidney proximal tubular cells--renoprotection in diabetic nephropathy?
Abstract
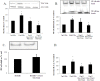
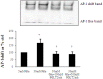
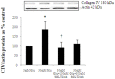
Sodium/glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors are oral hypoglycemic agents used to treat patients with diabetes mellitus. SGLT2 inhibitors block reabsorption of filtered glucose by inhibiting SGLT2, the primary glucose transporter in the proximal tubular cell (PTC), leading to glycosuria and lowering of serum glucose. We examined the renoprotective effects of the SGLT2 inhibitor empagliflozin to determine whether blocking glucose entry into the kidney PTCs reduced the inflammatory and fibrotic responses of the cell to high glucose. We used an in vitro model of human PTCs. HK2 cells (human kidney PTC line) were exposed to control 5 mM, high glucose (HG) 30 mM or the profibrotic cytokine transforming growth factor beta (TGFβ1; 0.5 ng/ml) in the presence and absence of empagliflozin for up to 72 h. SGLT1 and 2 expression and various inflammatory/fibrotic markers were assessed. A chromatin immunoprecipitation assay was used to determine the binding of phosphorylated smad3 to the promoter region of the SGLT2 gene. Our data showed that TGFβ1 but not HG increased SGLT2 expression and this occurred via phosphorylated smad3. HG induced expression of Toll-like receptor-4, increased nuclear deoxyribonucleic acid binding for nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) and activator protein 1, induced collagen IV expression as well as interleukin-6 secretion all of which were attenuated with empagliflozin. Empagliflozin did not reduce high mobility group box protein 1 induced NF-κB suggesting that its effect is specifically related to a reduction in glycotoxicity. SGLT1 and GLUT2 expression was not significantly altered with HG or empagliflozin. In conclusion, empagliflozin reduces HG induced inflammatory and fibrotic markers by blocking glucose transport and did not induce a compensatory increase in SGLT1/GLUT2 expression. Although HG itself does not regulate SGLT2 expression in our model, TGFβ increases SGLT2 expression through phosphorylated smad3.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Inhibition of kidney proximal tubular glucose reabsorption does not prevent against diabetic nephropathy in type 1 diabetic eNOS knockout mice.PLoS One. 2014 Nov 4;9(11):e108994. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0108994. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25369239 Free PMC article.
-
High glucose-induced Smad3 linker phosphorylation and CCN2 expression are inhibited by dapagliflozin in a diabetic tubule epithelial cell model.Biosci Rep. 2021 Jun 25;41(6):BSR20203947. doi: 10.1042/BSR20203947. Biosci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34003249 Free PMC article.
-
SGLT2 inhibitor empagliflozin reduces renal growth and albuminuria in proportion to hyperglycemia and prevents glomerular hyperfiltration in diabetic Akita mice.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2014 Jan;306(2):F194-204. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00520.2013. Epub 2013 Nov 13. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2014. PMID: 24226524 Free PMC article.
-
Sodium glucose cotransporter 2 and the diabetic kidney.Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2013 Jan;22(1):113-9. doi: 10.1097/MNH.0b013e32835a17ae. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2013. PMID: 23042029 Review.
-
SGLT2 Inhibition in the Diabetic Kidney-From Mechanisms to Clinical Outcome.Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2017 Apr 3;12(4):700-710. doi: 10.2215/CJN.06080616. Epub 2017 Mar 2. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2017. PMID: 28254770 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Anti-inflammatory potential of Empagliflozin.Inflammopharmacology. 2021 Apr;29(2):573-576. doi: 10.1007/s10787-021-00797-9. Epub 2021 Mar 17. Inflammopharmacology. 2021. PMID: 33728540 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Empagliflozin improves post-infarction cardiac remodeling through GTP enzyme cyclohydrolase 1 and irrespective of diabetes status.Sci Rep. 2020 Aug 11;10(1):13553. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-70454-8. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32782412 Free PMC article.
-
SGLT2 Inhibitors in Chronic Kidney Disease: From Mechanisms to Clinical Practice.Biomedicines. 2022 Oct 1;10(10):2458. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10102458. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 36289720 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Experimental study on the effect of chlorhexidine gluconate (CG)-induced atrial fibrillation on renal water and sodium metabolism.Sci Rep. 2023 Mar 10;13(1):4016. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-30783-w. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 36899056 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of SGLT2 inhibitors on haematocrit and haemoglobin levels and the associated cardiorenal benefits in T2DM patients: A meta-analysis.J Cell Mol Med. 2022 Jan;26(2):540-547. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.17115. Epub 2021 Dec 8. J Cell Mol Med. 2022. PMID: 34878225 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ghosh RK, Ghosh SM, Chawla S, Jasdanwala SA (2011) SGLT2 Inhibitors: A New Emerging Therapeutic Class in the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. J Clin Pharmacol. - PubMed
-
- Johnson DW, Saunders HJ, Brew BK, Poronnik P, Cook DI, et al. (1998) TGF-beta 1 dissociates human proximal tubule cell growth and Na(+)-H+ exchange activity. Kidney Int 53: 1601–1607. - PubMed
-
- Panchapakesan U, Pollock CA, Chen XM (2004) The effect of high glucose and PPAR-gamma agonists on PPAR-gamma expression and function in HK-2 cells. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 287: F528–534. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

