Prognostic significance of the combined score of endothelial expression of nucleolin and CD31 in surgically resected non-small cell lung cancer
- PMID: 23382938
- PMCID: PMC3561357
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0054674
Prognostic significance of the combined score of endothelial expression of nucleolin and CD31 in surgically resected non-small cell lung cancer
Abstract
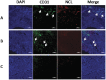
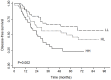
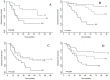
Nucleolin is implicated to play a role in angiogenesis, a vital process in tumor growth and metastasis. However, the presence and clinical relevance of nucleolin in human non small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) remains largely unknown. In this study, we explored the expression and prognostic implication of nucleolin in surgically resected NSCLC patients. A cohort of 146 NSCLC patients who underwent surgical resection was selected for tissue microarray. In this tissue microarray, nucleolin expression was measured by immunofluorescence. Staining for CD31, a marker of endothelial cells, was performed to mark blood vessels. A Cox proportional hazards model was used to assess the prognostic significance of nucleolin. Nucleolin expression was observed in 34.2% of all patients, and 64.1% in high CD31 expression patients. The disease-free survival (DFS) was significantly shorter in patients with high nucleolin (CD31(hi)NCL(hi)) compared to patients with low tumor blood vessels (CD31(lo)NCL(lo)) (5 ys of DFS 24% vs 64%, p = 0.002). Such a difference was demonstrated in the following stratified analyses: stage I (p<0.001), squamous cell carcinoma and adenosquamous cell carcinoma (p = 0.028), small tumor (<5 cm, p = 0.008), and surgery alone (p = 0.015). Multivariate analysis further revealed that nucleolin expression independently predicted for worse survival (p = 0.003). This study demonstrates that nucleolin is associated with the clinical outcomes in postoperative NSCLC patients. Thus, the expression levels of nucleolin may provide a new prognostic marker to identify patients at higher risk for treatment failure, especially in some subgroups.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prognostic significance of nuclear or cytoplasmic nucleolin expression in human non-small cell lung cancer and its relationship with DNA-PKcs.Tumour Biol. 2016 Aug;37(8):10349-56. doi: 10.1007/s13277-016-4920-6. Epub 2016 Feb 4. Tumour Biol. 2016. PMID: 26846099
-
LUNX mRNA-positive cells at different time points predict prognosis in patients with surgically resected nonsmall cell lung cancer.Transl Res. 2014 Jan;163(1):27-35. doi: 10.1016/j.trsl.2013.09.010. Epub 2013 Oct 10. Transl Res. 2014. PMID: 24120632
-
Prognostic significance of ERCC1, RRM1 and BRCA1 in surgically-treated patients with non-small cell lung cancer.Anticancer Res. 2012 Nov;32(11):5003-10. Anticancer Res. 2012. PMID: 23155271
-
Prognostic value of ERCC1 mRNA expression in non-small cell lung cancer, breast cancer, and gastric cancer in patients from Southern China.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014 Dec 1;7(12):8312-21. eCollection 2014. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014. PMID: 25674197 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Beyond biomarkers: Exploring the diverse potential of a novel phosphoprotein in lung cancer management.J Cell Mol Med. 2024 Sep;28(18):e70077. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.70077. J Cell Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 39304978 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Druggable Nucleolin Identifies Breast Tumours Associated with Poor Prognosis That Exhibit Different Biological Processes.Cancers (Basel). 2018 Oct 22;10(10):390. doi: 10.3390/cancers10100390. Cancers (Basel). 2018. PMID: 30360377 Free PMC article.
-
Nucleolin Aptamer N6L Reprograms the Translational Machinery and Acts Synergistically with mTORi to Inhibit Pancreatic Cancer Proliferation.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Oct 1;13(19):4957. doi: 10.3390/cancers13194957. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34638443 Free PMC article.
-
Increased level of nucleolin confers to aggressive tumor progression and poor prognosis in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma after hepatectomy.Diagn Pathol. 2014 Sep 18;9:175. doi: 10.1186/s13000-014-0175-y. Diagn Pathol. 2014. PMID: 25230759 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic significance of nuclear or cytoplasmic nucleolin expression in human non-small cell lung cancer and its relationship with DNA-PKcs.Tumour Biol. 2016 Aug;37(8):10349-56. doi: 10.1007/s13277-016-4920-6. Epub 2016 Feb 4. Tumour Biol. 2016. PMID: 26846099
-
Quantitative proteomics approach to screening of potential diagnostic and therapeutic targets for laryngeal carcinoma.PLoS One. 2014 Feb 27;9(2):e90181. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0090181. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24587265 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jemal A, Siegel R, Xu J, Ward E (2010) Cancer statistics, 2010. CA Cancer J Clin 60: 277–300. - PubMed
-
- van Rens MT, de la Riviere AB, Elbers HR, van Den Bosch JM (2000) Prognostic assessment of 2,361 patients who underwent pulmonary resection for non-small cell lung cancer, stage I, II, and IIIA. Chest 117: 374–379. - PubMed
-
- Mountain CF (1997) Revisions in the International System for Staging Lung Cancer. Chest 111: 1710–1717. - PubMed
-
- Folkman J (1995) Angiogenesis in cancer, vascular, rheumatoid and other disease. Nat Med 1: 27–31. - PubMed
-
- Hanahan D, Folkman J (1996) Patterns and emerging mechanisms of the angiogenic switch during tumorigenesis. Cell 86: 353–364. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

