Oxysterol-binding protein family I is the target of minor enviroxime-like compounds
- PMID: 23365445
- PMCID: PMC3624399
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.03546-12
Oxysterol-binding protein family I is the target of minor enviroxime-like compounds
Abstract
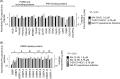
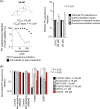
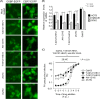
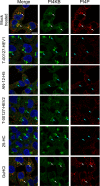
Enviroxime is an antipicornavirus compound that targets host phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase III beta (PI4KB) activity for its antipicornavirus activity. To date, several antipoliovirus (PV) compounds similar to enviroxime that are associated with a common resistance mutation in viral protein 3A (a G5318A [3A-Ala70Thr] mutation in PV) have been identified. Most of these compounds have a direct inhibitory effect on PI4KB activity, as well as enviroxime (designated major enviroxime-like compounds). However, one of the compounds, AN-12-H5, showed no inhibitory effect on PI4KB and was considered to belong to another group of enviroxime-like compounds (designated minor enviroxime-like compounds). In the present study, we performed a small interfering RNA (siRNA) sensitization assay targeting PI4KB-related genes and identified oxysterol-binding protein (OSBP) as a target of minor enviroxime-like compounds. Knockdown of OSBP and OSBP2 increased the anti-PV activities of AN-12-H5 and a newly identified minor enviroxime-like compound, T-00127-HEV2, and also to T-00127-HEV1 to a minor extent, in the cells. A ligand of OSBP, 25-hydroxycholesterol (25-HC), acted as a minor enviroxime-like compound. Minor enviroxime-like compounds induced relocalization of OSBP to the Golgi apparatus in cells. Treatment of the cells with major or minor enviroxime-like compounds suppressed the expression of genes (HMGCS1 and SQLE) in the SREBP/SCAP regulatory pathway and diminished endogenous phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate (PI4P) at the Golgi apparatus. Our results suggested that minor enviroxime-like compounds are phenotypically identical to 25-HC and that major and minor enviroxime-like compounds suppress the production and/or accumulation of PI4P in PV-infected cells by targeting PI4KB and OSBP family I activities, respectively.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase III beta is a target of enviroxime-like compounds for antipoliovirus activity.J Virol. 2011 Mar;85(5):2364-72. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02249-10. Epub 2010 Dec 22. J Virol. 2011. PMID: 21177810 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanism of Poliovirus Resistance to Host Phosphatidylinositol-4 Kinase III β Inhibitor.ACS Infect Dis. 2016 Feb 12;2(2):140-8. doi: 10.1021/acsinfecdis.5b00122. Epub 2015 Dec 16. ACS Infect Dis. 2016. PMID: 27624965
-
Phosphatidylinositol-4 kinase III beta and oxysterol-binding protein accumulate unesterified cholesterol on poliovirus-induced membrane structure.Microbiol Immunol. 2014 Apr;58(4):239-56. doi: 10.1111/1348-0421.12144. Microbiol Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24527995
-
[Exploration for anti-enterovirus compounds and analysis on the mechanism of its inhibitory effect on virus infection].Uirusu. 2013;63(1):93-102. doi: 10.2222/jsv.63.93. Uirusu. 2013. PMID: 24769585 Review. Japanese.
-
Oxysterol-binding proteins: sterol and phosphoinositide sensors coordinating transport, signaling and metabolism.Prog Lipid Res. 2013 Oct;52(4):529-38. doi: 10.1016/j.plipres.2013.06.004. Epub 2013 Jul 2. Prog Lipid Res. 2013. PMID: 23830809 Review.
Cited by
-
Antiviral Actions of 25-Hydroxycholesterol in Fish Vary With the Virus-Host Combination.Front Immunol. 2021 Feb 24;12:581786. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.581786. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33717065 Free PMC article.
-
The Oxysterol 25-Hydroxycholesterol Inhibits Replication of Murine Norovirus.Viruses. 2019 Jan 24;11(2):97. doi: 10.3390/v11020097. Viruses. 2019. PMID: 30682775 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Lipid Transfer Proteins (LTPs) in the Viral Life Cycle.Front Microbiol. 2021 Jun 23;12:673509. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.673509. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34248884 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Return of the Neurotropic Enteroviruses: Co-Opting Cellular Pathways for Infection.Viruses. 2021 Jan 22;13(2):166. doi: 10.3390/v13020166. Viruses. 2021. PMID: 33499355 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Experimental Antiviral Therapeutic Studies for Human Rhinovirus Infections.J Exp Pharmacol. 2021 Jul 9;13:645-659. doi: 10.2147/JEP.S255211. eCollection 2021. J Exp Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34276229 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bodian D. 1949. Histopathologic basis of clinical findings in poliomyelitis. Am. J. Med. 6:563–578 - PubMed
-
- Couderc T, Christodoulou C, Kopecka H, Marsden S, Taffs LF, Crainic R, Horaud F. 1989. Molecular pathogenesis of neural lesions induced by poliovirus type 1. J. Gen. Virol. 70:2907–2918 - PubMed
-
- Sabin AB. 1965. Oral poliovirus vaccine. History of its development and prospects for eradication of poliomyelitis. JAMA 194:872–876 - PubMed
-
- Collett MS, Neyts J, Modlin JF. 2008. A case for developing antiviral drugs against polio. Antiviral Res. 79:179–187 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

