Relief of feedback inhibition of HER3 transcription by RAF and MEK inhibitors attenuates their antitumor effects in BRAF-mutant thyroid carcinomas
- PMID: 23365119
- PMCID: PMC3651738
- DOI: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-12-0531
Relief of feedback inhibition of HER3 transcription by RAF and MEK inhibitors attenuates their antitumor effects in BRAF-mutant thyroid carcinomas
Abstract
The RAF inhibitor vemurafenib (PLX4032) increases survival in patients with BRAF-mutant metastatic melanoma, but has limited efficacy in patients with colorectal cancers. Thyroid cancer cells are also comparatively refractory to RAF inhibitors. In contrast to melanomas, inhibition of mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling by PLX4032 is transient in thyroid and colorectal cancer cells. The rebound in extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) in thyroid cells is accompanied by increased HER3 signaling caused by induction of ERBB3 (HER3) transcription through decreased promoter occupancy by the transcriptional repressors C-terminal binding protein 1 and 2 and by autocrine secretion of neuregulin-1 (NRG1). The HER kinase inhibitor lapatinib prevents MAPK rebound and sensitizes BRAF-mutant thyroid cancer cells to RAF or MAP-ERK kinase inhibitors. This provides a rationale for combining ERK pathway antagonists with inhibitors of feedback-reactivated HER signaling in this disease. The determinants of primary resistance to MAPK inhibitors vary between cancer types, due to preferential upregulation of specific receptor tyrosine kinases, and the abundance of their respective ligands.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
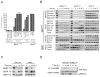
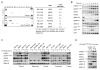
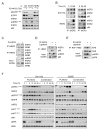
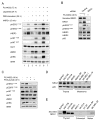
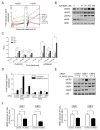
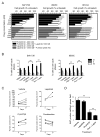
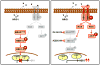
Comment on
-
Deja Vu: EGF receptors drive resistance to BRAF inhibitors.Cancer Discov. 2013 May;3(5):487-90. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-13-0131. Cancer Discov. 2013. PMID: 23658295 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
Pin1 inhibitor API-1 sensitizes BRAF-mutant thyroid cancers to BRAF inhibitors by attenuating HER3-mediated feedback activation of MAPK/ERK and PI3K/AKT pathways.Int J Biol Macromol. 2023 Sep 1;248:125867. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.125867. Epub 2023 Jul 18. Int J Biol Macromol. 2023. PMID: 37473892
-
The RAF inhibitor PLX4032 inhibits ERK signaling and tumor cell proliferation in a V600E BRAF-selective manner.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 Aug 17;107(33):14903-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1008990107. Epub 2010 Jul 28. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010. PMID: 20668238 Free PMC article.
-
EGFR-mediated re-activation of MAPK signaling contributes to insensitivity of BRAF mutant colorectal cancers to RAF inhibition with vemurafenib.Cancer Discov. 2012 Mar;2(3):227-35. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-11-0341. Epub 2012 Jan 16. Cancer Discov. 2012. PMID: 22448344 Free PMC article.
-
Resistance to MEK inhibitors: should we co-target upstream?Sci Signal. 2011 Mar 29;4(166):pe16. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.2001948. Sci Signal. 2011. PMID: 21447797 Review.
-
Targeting oncogenic Raf protein-serine/threonine kinases in human cancers.Pharmacol Res. 2018 Sep;135:239-258. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2018.08.013. Epub 2018 Aug 15. Pharmacol Res. 2018. PMID: 30118796 Review.
Cited by
-
Pan-HER inhibitors overcome lorlatinib resistance caused by NRG1/HER3 activation in ALK-rearranged lung cancer.Cancer Sci. 2023 Jan;114(1):164-173. doi: 10.1111/cas.15579. Epub 2022 Sep 21. Cancer Sci. 2023. PMID: 36086904 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of angiogenic switch, cachexia and inflammation factors at the crossroad in undifferentiated thyroid carcinoma with BRAF(V600E).Cancer Lett. 2016 Oct 1;380(2):577-585. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2015.07.012. Epub 2015 Jul 17. Cancer Lett. 2016. PMID: 26189429 Free PMC article.
-
New Horizons: Emerging Therapies and Targets in Thyroid Cancer.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2021 Jan 1;106(1):e382-e388. doi: 10.1210/clinem/dgaa687. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2021. PMID: 32977343 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An update on redifferentiation strategies for radioactive iodine-refractory differentiated thyroid carcinoma.Endocrine. 2025 Jan;87(1):1-10. doi: 10.1007/s12020-024-04018-5. Epub 2024 Sep 4. Endocrine. 2025. PMID: 39231920 Review.
-
Deja Vu: EGF receptors drive resistance to BRAF inhibitors.Cancer Discov. 2013 May;3(5):487-90. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-13-0131. Cancer Discov. 2013. PMID: 23658295 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Davies H, Bignell GR, Cox C, Stephens P, Edkins S, Clegg S, et al. Mutations of the BRAF gene in human cancer. Nature. 2002;417:949–54. - PubMed
-
- Kimura ET, Nikiforova MN, Zhu Z, Knauf JA, Nikiforov YE, Fagin JA. High prevalence of BRAF mutations in thyroid cancer: genetic evidence for constitutive activation of the RET/PTC-RAS-BRAF signaling pathway in papillary thyroid carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2003;63:1454–7. - PubMed
-
- Xing M. BRAF mutation in papillary thyroid cancer: pathogenic role, molecular bases, and clinical implications. Endocr Rev. 2007;28:742–62. - PubMed
-
- Yang H, Higgins B, Kolinsky K, Packman K, Go Z, Iyer R, et al. RG7204 (PLX4032), a selective BRAFV600E inhibitor, displays potent antitumor activity in preclinical melanoma models. Cancer Res. 2010;70:5518–27. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

