The eIF2α kinases: their structures and functions
- PMID: 23354059
- PMCID: PMC11113696
- DOI: 10.1007/s00018-012-1252-6
The eIF2α kinases: their structures and functions
Abstract
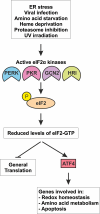
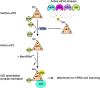
Cell signaling in response to an array of diverse stress stimuli converges on the phosphorylation of the α-subunit of eukaryotic initiation factor 2 (eIF2). Phosphorylation of eIF2α on serine 51 results in a severe decline in de novo protein synthesis and is an important strategy in the cell's armory against stressful insults including viral infection, the accumulation of misfolded proteins, and starvation. The phosphorylation of eIF2α is carried out by a family of four kinases, PERK (PKR-like ER kinase), PKR (protein kinase double-stranded RNA-dependent), GCN2 (general control non-derepressible-2), and HRI (heme-regulated inhibitor). Each primarily responds to a distinct type of stress or stresses. Thus, while significant sequence similarity exists between the eIF2α kinases in their kinase domains, underlying their common role in phosphorylating eIF2α, additional unique features determine the regulation of these four proteins, that is, what signals activate them. This review will describe the structure of each eIF2α kinase and discuss how this is linked to their activation and function. In parallel to the general translational attenuation elicited by eIF2α kinase activation the translation of stress-induced mRNAs, most notably activating transcription factor 4 (ATF4) is enhanced and these set in motion cascades of gene expression constituting the integrated stress response (ISR), which seek to remediate stress and restore homeostasis. Depending on the cellular context and concurrent signaling pathways active, however, translational attenuation can also facilitate apoptosis. Accordingly, the role of the kinases in determining cell fate will also be discussed.
Figures

Similar articles
-
p58IPK is an inhibitor of the eIF2α kinase GCN2 and its localization and expression underpin protein synthesis and ER processing capacity.Biochem J. 2015 Jan 15;465(2):213-25. doi: 10.1042/BJ20140852. Biochem J. 2015. PMID: 25329545
-
Translational control during endoplasmic reticulum stress beyond phosphorylation of the translation initiation factor eIF2α.J Biol Chem. 2014 May 2;289(18):12593-611. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.543215. Epub 2014 Mar 19. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24648524 Free PMC article.
-
Pathogenesis and promising therapeutics of Alzheimer disease through eIF2α pathway and correspondent kinases.Metab Brain Dis. 2020 Dec;35(8):1241-1250. doi: 10.1007/s11011-020-00600-8. Epub 2020 Jul 17. Metab Brain Dis. 2020. PMID: 32681467 Review.
-
eIF2alpha kinases GCN2 and PERK modulate transcription and translation of distinct sets of mRNAs in mouse liver.Physiol Genomics. 2009 Aug 7;38(3):328-41. doi: 10.1152/physiolgenomics.90396.2008. Epub 2009 Jun 9. Physiol Genomics. 2009. PMID: 19509078 Free PMC article.
-
Coping with stress: eIF2 kinases and translational control.Biochem Soc Trans. 2006 Feb;34(Pt 1):7-11. doi: 10.1042/BST20060007. Biochem Soc Trans. 2006. PMID: 16246168 Review.
Cited by
-
Quantification of eIF2α Phosphorylation Associated with Mitotic Catastrophe by Immunofluorescence Microscopy.Methods Mol Biol. 2021;2267:217-226. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-1217-0_15. Methods Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 33786795
-
Duck Hepatitis A Virus Type 1 Induces eIF2α Phosphorylation-Dependent Cellular Translation Shutoff via PERK/GCN2.Front Microbiol. 2021 Apr 12;12:624540. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.624540. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33912143 Free PMC article.
-
SnoRNAs: Exploring Their Implication in Human Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jun 29;25(13):7202. doi: 10.3390/ijms25137202. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39000310 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mammalian integrated stress responses in stressed organelles and their functions.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2024 Jun;45(6):1095-1114. doi: 10.1038/s41401-023-01225-0. Epub 2024 Jan 24. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2024. PMID: 38267546 Review.
-
Host WD repeat-containing protein 5 inhibits protein kinase R-mediated integrated stress response during measles virus infection.J Virol. 2024 Sep 17;98(9):e0102024. doi: 10.1128/jvi.01020-24. Epub 2024 Aug 28. J Virol. 2024. PMID: 39194235 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abraham N, Stojdl DF, Duncan PI, Methot N, Ishii T, Dube M, Vanderhyden BC, Atkins HL, Gray DA, McBurney MW, Koromilas AE, Brown EG, Sonenberg N, Bell JC. Characterization of transgenic mice with targeted disruption of the catalytic domain of the double-stranded RNA-dependent protein kinase, PKR. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:5953–5962. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.9.5953. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Acharya P, Chen JJ, Correia MA. Hepatic heme-regulated inhibitor (HRI) eukaryotic initiation factor 2alpha kinase: a protagonist of heme-mediated translational control of CYP2B enzymes and a modulator of basal endoplasmic reticulum stress tone. Mol Pharmacol. 2010;77:575–592. doi: 10.1124/mol.109.061259. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Acharya P, Engel JC, Correia MA. Hepatic CYP3A suppression by high concentrations of proteasomal inhibitors: a consequence of endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress induction, activation of RNA-dependent protein kinase-like ER-bound eukaryotic initiation factor 2alpha (eIF2alpha)-kinase (PERK) and general control nonderepressible-2 eIF2alpha kinase (GCN2), and global translational shutoff. Mol Pharmacol. 2009;76:503–515. doi: 10.1124/mol.109.056002. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

