Susceptibility loci associated with specific and shared subtypes of lymphoid malignancies
- PMID: 23349640
- PMCID: PMC3547842
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1003220
Susceptibility loci associated with specific and shared subtypes of lymphoid malignancies
Abstract
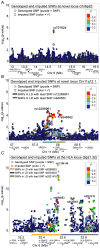
The genetics of lymphoma susceptibility reflect the marked heterogeneity of diseases that comprise this broad phenotype. However, multiple subtypes of lymphoma are observed in some families, suggesting shared pathways of genetic predisposition to these pathologically distinct entities. Using a two-stage GWAS, we tested 530,583 SNPs in 944 cases of lymphoma, including 282 familial cases, and 4,044 public shared controls, followed by genotyping of 50 SNPs in 1,245 cases and 2,596 controls. A novel region on 11q12.1 showed association with combined lymphoma (LYM) subtypes. SNPs in this region included rs12289961 near LPXN, (P(LYM) = 3.89×10(-8), OR = 1.29) and rs948562 (P(LYM) = 5.85×10(-7), OR = 1.29). A SNP in a novel non-HLA region on 6p23 (rs707824, P(NHL) = 5.72×10(-7)) was suggestive of an association conferring susceptibility to lymphoma. Four SNPs, all in a previously reported HLA region, 6p21.32, showed genome-wide significant associations with follicular lymphoma. The most significant association with follicular lymphoma was for rs4530903 (P(FL) = 2.69×10(-12), OR = 1.93). Three novel SNPs near the HLA locus, rs9268853, rs2647046, and rs2621416, demonstrated additional variation contributing toward genetic susceptibility to FL associated with this region. Genes implicated by GWAS were also found to be cis-eQTLs in lymphoblastoid cell lines; candidate genes in these regions have been implicated in hematopoiesis and immune function. These results, showing novel susceptibility regions and allelic heterogeneity, point to the existence of pathways of susceptibility to both shared as well as specific subtypes of lymphoid malignancy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

Similar articles
-
GWAS of follicular lymphoma reveals allelic heterogeneity at 6p21.32 and suggests shared genetic susceptibility with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma.PLoS Genet. 2011 Apr;7(4):e1001378. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1001378. Epub 2011 Apr 21. PLoS Genet. 2011. PMID: 21533074 Free PMC article.
-
A meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies of follicular lymphoma.BMC Genomics. 2012 Oct 1;13:516. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-13-516. BMC Genomics. 2012. PMID: 23025665 Free PMC article.
-
A two-stage evaluation of genetic variation in immune and inflammation genes with risk of non-Hodgkin lymphoma identifies new susceptibility locus in 6p21.3 region.Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2012 Oct;21(10):1799-806. doi: 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-12-0696. Epub 2012 Aug 21. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2012. PMID: 22911334 Free PMC article.
-
Tracking the Genetic Susceptibility Background of B-Cell Non-Hodgkin's Lymphomas from Genome-Wide Association Studies.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Dec 24;22(1):122. doi: 10.3390/ijms22010122. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33374413 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Shared genetic etiology underlying Alzheimer's disease and type 2 diabetes.Mol Aspects Med. 2015 Jun-Oct;43-44:66-76. doi: 10.1016/j.mam.2015.06.006. Epub 2015 Jun 23. Mol Aspects Med. 2015. PMID: 26116273 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Human leukocyte antigens and epstein-barr virus-associated nasopharyngeal carcinoma: old associations offer new clues into the role of immunity in infection-associated cancers.Front Oncol. 2013 Dec 9;3:299. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2013.00299. Front Oncol. 2013. PMID: 24367763 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanistic and Clinical Evidence Supports a Key Role for Cell Division Cycle Associated 5 (CDCA5) as an Independent Predictor of Outcome in Invasive Breast Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Nov 17;14(22):5643. doi: 10.3390/cancers14225643. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36428736 Free PMC article.
-
Immunomodulatory germline variation associated with the development of multiple primary melanoma (MPM).Sci Rep. 2019 Jul 15;9(1):10173. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-46665-z. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31308438 Free PMC article.
-
Sequencing at lymphoid neoplasm susceptibility loci maps six myeloma risk genes.Hum Mol Genet. 2021 Jun 9;30(12):1142-1153. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddab066. Hum Mol Genet. 2021. PMID: 33751038 Free PMC article.
-
Ultra Low-Coverage Whole-Genome Sequencing as an Alternative to Genotyping Arrays in Genome-Wide Association Studies.Front Genet. 2022 Feb 15;12:790445. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.790445. eCollection 2021. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 35251117 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pileri SA, Milani M, Fraternali-Orcioni G, Sabattini E (1998) From the REAL classification to the upcoming WHO scheme: A step toward universal categorization of lymphoma entities? Ann Oncol 9: 607–612. - PubMed
-
- Zintzaras E, Voulgarelis M, Moutsopoulos HM (2005) The risk of lymphoma development in autoimmune diseases: a meta-analysis. Arch Intern Med 165: 2337–2344. - PubMed
-
- Siddiqui R, Onel K, Facio F, Offit K (2004) The genetics of familial lymphomas. Curr Oncol Rep 6: 380–387. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

