Tissue-specific direct targets of Caenorhabditis elegans Rb/E2F dictate distinct somatic and germline programs
- PMID: 23347407
- PMCID: PMC4053757
- DOI: 10.1186/gb-2013-14-1-r5
Tissue-specific direct targets of Caenorhabditis elegans Rb/E2F dictate distinct somatic and germline programs
Abstract
Background: The tumor suppressor Rb/E2F regulates gene expression to control differentiation in multiple tissues during development, although how it directs tissue-specific gene regulation in vivo is poorly understood.
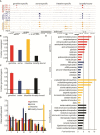
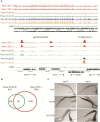
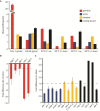
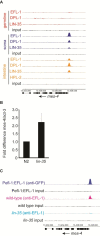
Results: We determined the genome-wide binding profiles for Caenorhabditis elegans Rb/E2F-like components in the germline, in the intestine and broadly throughout the soma, and uncovered highly tissue-specific binding patterns and target genes. Chromatin association by LIN-35, the C. elegans ortholog of Rb, is impaired in the germline but robust in the soma, a characteristic that might govern differential effects on gene expression in the two cell types. In the intestine, LIN-35 and the heterochromatin protein HPL-2, the ortholog of Hp1, coordinately bind at many sites lacking E2F. Finally, selected direct target genes contribute to the soma-to-germline transformation of lin-35 mutants, including mes-4, a soma-specific target that promotes H3K36 methylation, and csr-1, a germline-specific target that functions in a 22G small RNA pathway.
Conclusions: In sum, identification of tissue-specific binding profiles and effector target genes reveals important insights into the mechanisms by which Rb/E2F controls distinct cell fates in vivo.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Caenorhabditis elegans Heterochromatin protein 1 (HPL-2) links developmental plasticity, longevity and lipid metabolism.Genome Biol. 2011 Dec 20;12(12):R123. doi: 10.1186/gb-2011-12-12-r123. Genome Biol. 2011. PMID: 22185090 Free PMC article.
-
Repression of germline RNAi pathways in somatic cells by retinoblastoma pathway chromatin complexes.PLoS Genet. 2012;8(3):e1002542. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002542. Epub 2012 Mar 8. PLoS Genet. 2012. PMID: 22412383 Free PMC article.
-
Promotion of oogenesis and embryogenesis in the C. elegans gonad by EFL-1/DPL-1 (E2F) does not require LIN-35 (pRB).Development. 2006 Aug;133(16):3147-57. doi: 10.1242/dev.02490. Epub 2006 Jul 19. Development. 2006. PMID: 16854972
-
Chromatin regulation during C. elegans germline development.Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2003 Oct;13(5):455-62. doi: 10.1016/s0959-437x(03)00109-6. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2003. PMID: 14550409 Review.
-
Insulin and germline proliferation in Caenorhabditis elegans.Vitam Horm. 2011;87:61-77. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-386015-6.00024-X. Vitam Horm. 2011. PMID: 22127237 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A parental transcriptional response to microsporidia infection induces inherited immunity in offspring.Sci Adv. 2021 May 5;7(19):eabf3114. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abf3114. Print 2021 May. Sci Adv. 2021. PMID: 33952520 Free PMC article.
-
A universal transcriptomic signature of age reveals the temporal scaling of Caenorhabditis elegans aging trajectories.Sci Rep. 2019 May 14;9(1):7368. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-43075-z. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31089188 Free PMC article.
-
LIN-35 is necessary in both the soma and germline for preserving fertility in Caenorhabditis elegans under moderate temperature stress.PLoS One. 2023 Jun 9;18(6):e0286926. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0286926. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 37294778 Free PMC article.
-
Loss of the Caenorhabditis elegans pocket protein LIN-35 reveals MuvB's innate function as the repressor of DREAM target genes.PLoS Genet. 2017 Nov 1;13(11):e1007088. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1007088. eCollection 2017 Nov. PLoS Genet. 2017. PMID: 29091720 Free PMC article.
-
Wnt Signaling Drives Ectopic Gene Expression and Larval Arrest in the Absence of the Caenorhabditis elegans DREAM Repressor Complex.G3 (Bethesda). 2020 Feb 6;10(2):863-874. doi: 10.1534/g3.119.400850. G3 (Bethesda). 2020. PMID: 31843805 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

