MicroRNA-182 regulates amygdala-dependent memory formation
- PMID: 23345246
- PMCID: PMC3711533
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2873-12.2013
MicroRNA-182 regulates amygdala-dependent memory formation
Abstract
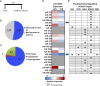
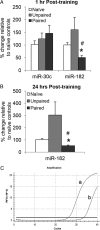
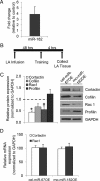
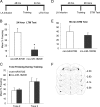
De novo protein synthesis supports long-lasting functional and structural plasticity and is a molecular requirement for new memory formation. Recent evidence has suggested that microRNAs may be involved in regulating the molecular mechanisms underlying neural plasticity. MicroRNAs are endogenous, noncoding RNAs capable of post-transcriptional repression of their mRNA targets. To explore the potential for microRNA-mediated regulation of amygdala-dependent memory formation, we performed expression profiling of microRNAs in the lateral amygdala of rats 1 h after auditory fear conditioning. Microarray analysis revealed that over half of all known microRNAs are endogenously expressed in the lateral amygdala, with 7 microRNAs upregulated and 32 downregulated by auditory fear training. Bioinformatic analysis identified several of the downregulated microRNAs as potential repressors of actin-regulating proteins known to be involved in plasticity and memory. Downregulation of one of these microRNAs by auditory fear conditioning, miR-182, was confirmed by quantitative real-time PCR. Overexpression of miR-182 within the lateral amygdala resulted in decreased expression of the protein but not mRNA of two synapse-enriched regulators of actin known to modulate structural plasticity, cortactin and Rac1. The overexpression of miR-182 also disrupted long-term but not short-term auditory fear memory. These data indicate that learning-induced suppression of miR-182, a microRNA previously uncharacterized in the brain, supports long-term memory formation in the amygdala and suggests it does so, at least in part, through the derepression of key actin-regulating proteins. These findings further indicate that microRNAs may represent a previously underappreciated mechanism for regulating protein synthesis during memory consolidation.
Figures

Similar articles
-
BAF53b, a Neuron-Specific Nucleosome Remodeling Factor, Is Induced after Learning and Facilitates Long-Term Memory Consolidation.J Neurosci. 2017 Mar 29;37(13):3686-3697. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3220-16.2017. Epub 2017 Mar 7. J Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28270570 Free PMC article.
-
Amygdala-dependent fear memory consolidation via miR-34a and Notch signaling.Neuron. 2014 Aug 20;83(4):906-18. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2014.07.019. Epub 2014 Aug 7. Neuron. 2014. PMID: 25123309 Free PMC article.
-
DNA methyltransferase activity is required for memory-related neural plasticity in the lateral amygdala.Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2014 Jan;107:93-100. doi: 10.1016/j.nlm.2013.11.008. Epub 2013 Nov 27. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2014. PMID: 24291571 Free PMC article.
-
Genes and mechanisms in the amygdala involved in the formation of fear memory.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2003 Apr;985:92-105. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2003.tb07074.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2003. PMID: 12724151 Review.
-
Fear memory and the amygdala: insights from a molecular perspective.Cell Tissue Res. 2002 Dec;310(3):271-7. doi: 10.1007/s00441-002-0656-2. Epub 2002 Nov 6. Cell Tissue Res. 2002. PMID: 12457225 Review.
Cited by
-
Suppression of neuronal CDK9/p53/VDAC signaling provides bioenergetic support and improves post-stroke neuropsychiatric outcomes.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2024 Sep 5;81(1):384. doi: 10.1007/s00018-024-05428-4. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2024. PMID: 39235466 Free PMC article.
-
Nonmuscle myosin IIB as a therapeutic target for the prevention of relapse to methamphetamine use.Mol Psychiatry. 2016 May;21(5):615-23. doi: 10.1038/mp.2015.103. Epub 2015 Aug 4. Mol Psychiatry. 2016. PMID: 26239291 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNAs in Learning and Memory and Their Impact on Alzheimer's Disease.Biomedicines. 2022 Aug 1;10(8):1856. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10081856. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 36009403 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interplay between TETs and microRNAs in the adult brain for memory formation.Sci Rep. 2018 Jan 26;8(1):1678. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-19806-z. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29374200 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-19b associates with Ago2 in the amygdala following chronic stress and regulates the adrenergic receptor beta 1.J Neurosci. 2014 Nov 5;34(45):15070-82. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0855-14.2014. J Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 25378171 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ashraf SI, Kunes S. A trace of silence: memory and microRNA at the synapse. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2006;16:535–539. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
