Quantification of 5-methylcytosine and 5-hydroxymethylcytosine in genomic DNA from hepatocellular carcinoma tissues by capillary hydrophilic-interaction liquid chromatography/quadrupole TOF mass spectrometry
- PMID: 23344498
- PMCID: PMC3773166
- DOI: 10.1373/clinchem.2012.193938
Quantification of 5-methylcytosine and 5-hydroxymethylcytosine in genomic DNA from hepatocellular carcinoma tissues by capillary hydrophilic-interaction liquid chromatography/quadrupole TOF mass spectrometry
Abstract
Background: 5-Methylcytosine (5-mC) is an important epigenetic modification involved in development and is frequently altered in cancer. 5-mC can be enzymatically converted to 5-hydroxymethylcytosine (5-hmC). 5-hmC modifications are known to be prevalent in DNA of embryonic stem cells and neurons, but the distribution of 5-hmC in human liver tumor and matched control tissues has not been rigorously explored.
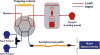
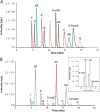
Methods: We developed an online trapping/capillary hydrophilic-interaction liquid chromatography (cHILIC)/in-source fragmentation/tandem mass spectrometry system for quantifying 5-mC and 5-hmC in genomic DNA from hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) tumor tissues and relevant tumor adjacent tissues. A polymer-based hydrophilic monolithic column was prepared and used for the separation of 12 nucleosides by cHILIC coupled with an online trapping system. Limits of detection and quantification, recovery, and imprecision of the method were determined.
Results: Limits of detection for 5-mC and 5-hmC were 0.06 and 0.19 fmol, respectively. The imprecision and recovery of the method were determined, with the relative SDs and relative errors being <14.9% and 15.8%, respectively. HCC tumor tissues had a 4- to 5-fold lower 5-hmC content compared to tumor-adjacent tissues. In addition, 5-hmC content highly correlated with tumor stage (tumor-nodes-metastasis, P = 0.0002; Barcelona Clinic liver cancer, P = 0.0003).
Conclusions: The marked depletion of 5-hmC may have profound effects on epigenetic regulation in HCC and could be a potential biomarker for the early detection and prognosis of HCC.
© 2013 American Association for Clinical Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
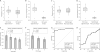
Similar articles
-
Sensitive and simultaneous determination of 5-methylcytosine and its oxidation products in genomic DNA by chemical derivatization coupled with liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry analysis.Anal Chem. 2015 Mar 17;87(6):3445-52. doi: 10.1021/ac504786r. Epub 2015 Feb 24. Anal Chem. 2015. PMID: 25675106
-
Hydrophilic material for the selective enrichment of 5-hydroxymethylcytosine and its liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry detection.Anal Chem. 2013 Jun 18;85(12):6129-35. doi: 10.1021/ac4010869. Epub 2013 May 28. Anal Chem. 2013. PMID: 23678980
-
Quantification of the sixth DNA base 5-hydroxymethylcytosine in colorectal cancer tissue and C-26 cell line.Bioanalysis. 2013 Apr;5(7):839-45. doi: 10.4155/bio.13.28. Bioanalysis. 2013. PMID: 23534428
-
5-methylcytosine and its derivatives.Adv Clin Chem. 2014;67:151-87. doi: 10.1016/bs.acc.2014.09.003. Epub 2014 Nov 4. Adv Clin Chem. 2014. PMID: 25735861 Review.
-
5-Hydroxymethylcytosine, the sixth base of the genome.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2011 Jul 11;50(29):6460-8. doi: 10.1002/anie.201101547. Epub 2011 Jun 17. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2011. PMID: 21688365 Review.
Cited by
-
Associations of ChREBP and Global DNA Methylation with Genetic and Environmental Factors in Chinese Healthy Adults.PLoS One. 2016 Jun 9;11(6):e0157128. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0157128. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27281235 Free PMC article.
-
Association of global DNA hypomethylation with clinicopathological variables in colonic tumors of Iraqi patients.Saudi J Gastroenterol. 2016 Mar-Apr;22(2):139-47. doi: 10.4103/1319-3767.178525. Saudi J Gastroenterol. 2016. PMID: 26997221 Free PMC article.
-
Selective inhibition of CTCF binding by iAs directs TET-mediated reprogramming of 5-hydroxymethylation patterns in iAs-transformed cells.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2018 Jan 1;338:124-133. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2017.11.015. Epub 2017 Nov 22. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29175454 Free PMC article.
-
The hypomethylating agent Decitabine causes a paradoxical increase in 5-hydroxymethylcytosine in human leukemia cells.Sci Rep. 2015 Apr 22;5:9281. doi: 10.1038/srep09281. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 25901663 Free PMC article.
-
Bisulfite-free and single-nucleotide resolution sequencing of DNA epigenetic modification of 5-hydroxymethylcytosine using engineered deaminase.Chem Sci. 2022 May 26;13(23):7046-7056. doi: 10.1039/d2sc01052f. eCollection 2022 Jun 15. Chem Sci. 2022. PMID: 35774177 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Esteller M. Cancer epigenomics: DNA methylomes and histone-modification maps. Nat Rev Genet. 2007;8:286–98. - PubMed
-
- Rottach A, Leonhardt H, Spada F. DNA methylation-mediated epigenetic control. J Cell Biochem. 2009;108:43–51. - PubMed
-
- Robertson KD. DNA methylation and human disease. Nat Rev Genet. 2005;6:597–610. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

