Microfluidic Synthesis of Highly Potent Limit-size Lipid Nanoparticles for In Vivo Delivery of siRNA
- PMID: 23344179
- PMCID: PMC3442367
- DOI: 10.1038/mtna.2012.28
Microfluidic Synthesis of Highly Potent Limit-size Lipid Nanoparticles for In Vivo Delivery of siRNA
Abstract
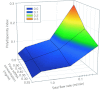
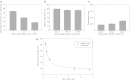
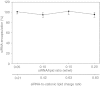
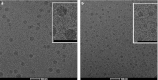
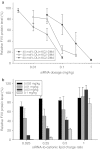
Lipid nanoparticles (LNP) are the leading systems for in vivo delivery of small interfering RNA (siRNA) for therapeutic applications. Formulation of LNP siRNA systems requires rapid mixing of solutions containing cationic lipid with solutions containing siRNA. Current formulation procedures employ macroscopic mixing processes to produce systems 70-nm diameter or larger that have variable siRNA encapsulation efficiency, homogeneity, and reproducibility. Here, we show that microfluidic mixing techniques, which permit millisecond mixing at the nanoliter scale, can reproducibly generate limit size LNP siRNA systems 20 nm and larger with essentially complete encapsulation of siRNA over a wide range of conditions with polydispersity indexes as low as 0.02. Optimized LNP siRNA systems produced by microfluidic mixing achieved 50% target gene silencing in hepatocytes at a dose level of 10 µg/kg siRNA in mice. We anticipate that microfluidic mixing, a precisely controlled and readily scalable technique, will become the preferred method for formulation of LNP siRNA delivery systems.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Microfluidic Mixing: A General Method for Encapsulating Macromolecules in Lipid Nanoparticle Systems.J Phys Chem B. 2015 Jul 16;119(28):8698-706. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcb.5b02891. Epub 2015 Jul 7. J Phys Chem B. 2015. PMID: 26087393
-
Characterization of Lipid Nanoparticles Containing Ionizable Cationic Lipids Using Design-of-Experiments Approach.Langmuir. 2021 Jan 26;37(3):1120-1128. doi: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.0c03039. Epub 2021 Jan 13. Langmuir. 2021. PMID: 33439022
-
Lipid Nanoparticles Containing siRNA Synthesized by Microfluidic Mixing Exhibit an Electron-Dense Nanostructured Core.J Phys Chem C Nanomater Interfaces. 2012 Aug 30;116(34):18440-18450. doi: 10.1021/jp303267y. Epub 2012 Jul 18. J Phys Chem C Nanomater Interfaces. 2012. PMID: 22962627 Free PMC article.
-
Lipid Nanoparticle Technology for Clinical Translation of siRNA Therapeutics.Acc Chem Res. 2019 Sep 17;52(9):2435-2444. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.9b00368. Epub 2019 Aug 9. Acc Chem Res. 2019. PMID: 31397996 Review.
-
Lipid Nanoparticle Systems for Enabling Gene Therapies.Mol Ther. 2017 Jul 5;25(7):1467-1475. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2017.03.013. Epub 2017 Apr 13. Mol Ther. 2017. PMID: 28412170 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Lipid nanoparticle technology for therapeutic gene regulation in the liver.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2020;159:344-363. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2020.06.026. Epub 2020 Jul 2. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2020. PMID: 32622021 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lipid nanoparticles for delivery of RNA therapeutics: Current status and the role of in vivo imaging.Theranostics. 2022 Oct 24;12(17):7509-7531. doi: 10.7150/thno.77259. eCollection 2022. Theranostics. 2022. PMID: 36438494 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Micro and nanoscale technologies in oral drug delivery.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2020;157:37-62. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2020.07.012. Epub 2020 Jul 22. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2020. PMID: 32707147 Free PMC article. Review.
-
3D-printed microfluidic device for high-throughput production of lipid nanoparticles incorporating SARS-CoV-2 spike protein mRNA.Lab Chip. 2024 Jan 17;24(2):162-170. doi: 10.1039/d3lc00520h. Lab Chip. 2024. PMID: 38165143 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Advances in Drug Delivery System Fabricated by Microfluidics for Disease Therapy.Bioengineering (Basel). 2022 Oct 29;9(11):625. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering9110625. Bioengineering (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36354536 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

