Dissecting the role of the Atg12-Atg5-Atg16 complex during autophagosome formation
- PMID: 23321721
- PMCID: PMC3590266
- DOI: 10.4161/auto.22931
Dissecting the role of the Atg12-Atg5-Atg16 complex during autophagosome formation
Abstract
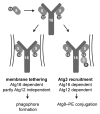
The activity of the conserved Atg12-Atg5-Atg16 complex is essential for autophagosome formation. However, little is known about its mechanism of action during this process. In our study we employed in vitro systems consisting of purified proteins and giant unilamellar vesicles (GUVs) or small liposomes to investigate membrane binding by the Atg12-Atg5-Atg16 complex and its interplay with the Atg8 conjugation system. We showed that Atg5 directly binds membranes and that this membrane binding is negatively regulated by Atg12 conjugation but activated by Atg16. Membrane binding by the Atg12-Atg5-Atg16 complex is required for efficient promotion of Atg8 lipidation. Additionally, we found that the Atg12-Atg5-Atg16 complex tethered vesicles in an Atg8-independent manner. In yeast, membrane binding by Atg5 is not required for its recruitment to the phagophore assembly site (PAS) but is essential for efficient promotion of autophagy and the cytoplasm-to-vacuole targeting (Cvt) pathway at a stage preceding Atg8 lipidation and autophagosome closure. Our findings provide new insights into the role of the Atg12-Atg5-Atg16 complex during autophagosome formation.
Keywords: Atg12; Atg16; Atg5; Atg8; autophagosome; cytoplasm-to-vacuole targeting; phagophore assembly site.
Figures
Comment on
- Romanov J, Walczak M, Ibiricu I, Schüchner S, Ogris E, Kraft C, et al. Mechanism and functions of membrane binding by the Atg5-Atg12/Atg16 complex during autophagosome formation. EMBO J. 2012;31:4304–17. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2012.278.
Similar articles
-
Mechanism and functions of membrane binding by the Atg5-Atg12/Atg16 complex during autophagosome formation.EMBO J. 2012 Nov 14;31(22):4304-17. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2012.278. Epub 2012 Oct 12. EMBO J. 2012. PMID: 23064152 Free PMC article.
-
The Atg12-Atg5 conjugate has a novel E3-like activity for protein lipidation in autophagy.J Biol Chem. 2007 Dec 28;282(52):37298-302. doi: 10.1074/jbc.C700195200. Epub 2007 Nov 6. J Biol Chem. 2007. PMID: 17986448
-
Membrane Binding and Homodimerization of Atg16 Via Two Distinct Protein Regions is Essential for Autophagy in Yeast.J Mol Biol. 2021 Mar 5;433(5):166809. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2021.166809. Epub 2021 Jan 21. J Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 33484718 Free PMC article.
-
Beyond Atg8 binding: The role of AIM/LIR motifs in autophagy.Autophagy. 2017 May 4;13(5):978-979. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2016.1277311. Epub 2017 Jan 25. Autophagy. 2017. PMID: 28121222 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Two ubiquitin-like conjugation systems that mediate membrane formation during autophagy.Essays Biochem. 2013;55:39-50. doi: 10.1042/bse0550039. Essays Biochem. 2013. PMID: 24070470 Review.
Cited by
-
A conserved MTMR lipid phosphatase increasingly suppresses autophagy in brain neurons during aging.Sci Rep. 2022 Dec 17;12(1):21817. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-24843-w. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36528685 Free PMC article.
-
PACAP-Sirtuin3 alleviates cognitive impairment through autophagy in Alzheimer's disease.Alzheimers Res Ther. 2023 Oct 27;15(1):184. doi: 10.1186/s13195-023-01334-2. Alzheimers Res Ther. 2023. PMID: 37891608 Free PMC article.
-
miR-30a-3p Regulates Autophagy in the Involution of Mice Mammary Glands.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Sep 20;24(18):14352. doi: 10.3390/ijms241814352. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37762652 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting Drug Chemo-Resistance in Cancer Using Natural Products.Biomedicines. 2021 Sep 29;9(10):1353. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9101353. Biomedicines. 2021. PMID: 34680470 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Dawn of Mitophagy: What Do We Know by Now?Curr Neuropharmacol. 2021;19(2):170-192. doi: 10.2174/1570159X18666200522202319. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2021. PMID: 32442087 Free PMC article. Review.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
