The multiple faces of proteinkinase R in antiviral defense
- PMID: 23314571
- PMCID: PMC3544753
- DOI: 10.4161/viru.23134
The multiple faces of proteinkinase R in antiviral defense
Abstract
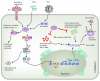
Various pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) have been implicated in the detection of viral RNA and subsequent interferon (IFN) gene expression, including the double-stranded RNA-dependent proteinkinase R (PKR). Now, a novel role of PKR has been unveiled, as it was shown that, upon the infection with certain viruses, PKR is crucial for the integrity of newly synthesized IFN mRNA, thereby generating an optimal host antiviral immune response. There is a need of future studies to investigate additional roles of PKR in innate immunity and the molecular understanding of this novel function of PKR.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Highly Pathogenic New World Arenavirus Infection Activates the Pattern Recognition Receptor Protein Kinase R without Attenuating Virus Replication in Human Cells.J Virol. 2017 Sep 27;91(20):e01090-17. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01090-17. Print 2017 Oct 15. J Virol. 2017. PMID: 28794024 Free PMC article.
-
The search for a PKR code-differential regulation of protein kinase R activity by diverse RNA and protein regulators.RNA. 2019 May;25(5):539-556. doi: 10.1261/rna.070169.118. Epub 2019 Feb 15. RNA. 2019. PMID: 30770398 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protein kinase regulated by dsRNA downregulates the interferon production in dengue virus- and dsRNA-stimulated human lung epithelial cells.PLoS One. 2013;8(1):e55108. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0055108. Epub 2013 Jan 25. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23372823 Free PMC article.
-
RNase L Amplifies Interferon Signaling by Inducing Protein Kinase R-Mediated Antiviral Stress Granules.J Virol. 2020 Jun 16;94(13):e00205-20. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00205-20. Print 2020 Jun 16. J Virol. 2020. PMID: 32295917 Free PMC article.
-
Viral proteins targeting host protein kinase R to evade an innate immune response: a mini review.Biotechnol Genet Eng Rev. 2018 Apr;34(1):33-59. doi: 10.1080/02648725.2018.1467151. Epub 2018 May 2. Biotechnol Genet Eng Rev. 2018. PMID: 29716441 Review.
Cited by
-
Synthesis and Translation of Viral mRNA in Reovirus-Infected Cells: Progress and Remaining Questions.Viruses. 2018 Nov 27;10(12):671. doi: 10.3390/v10120671. Viruses. 2018. PMID: 30486370 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The circRNA circVAMP3 restricts influenza A virus replication by interfering with NP and NS1 proteins.PLoS Pathog. 2023 Aug 21;19(8):e1011577. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1011577. eCollection 2023 Aug. PLoS Pathog. 2023. PMID: 37603540 Free PMC article.
-
Interferons and their receptors in birds: a comparison of gene structure, phylogenetic analysis, and cross modulation.Int J Mol Sci. 2014 Nov 14;15(11):21045-68. doi: 10.3390/ijms151121045. Int J Mol Sci. 2014. PMID: 25405736 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Avian Interferons and Their Antiviral Effectors.Front Immunol. 2017 Jan 31;8:49. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.00049. eCollection 2017. Front Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28197148 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Host Cell Restriction Factors of Paramyxoviruses and Pneumoviruses.Viruses. 2020 Dec 2;12(12):1381. doi: 10.3390/v12121381. Viruses. 2020. PMID: 33276587 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
