The transcription factor STAT-1 couples macrophage synthesis of 25-hydroxycholesterol to the interferon antiviral response
- PMID: 23273843
- PMCID: PMC3556782
- DOI: 10.1016/j.immuni.2012.11.004
The transcription factor STAT-1 couples macrophage synthesis of 25-hydroxycholesterol to the interferon antiviral response
Abstract
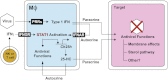
Recent studies suggest that the sterol metabolic network participates in the interferon (IFN) antiviral response. However, the molecular mechanisms linking IFN with the sterol network and the identity of sterol mediators remain unknown. Here we report a cellular antiviral role for macrophage production of 25-hydroxycholesterol (cholest-5-en-3β,25-diol, 25HC) as a component of the sterol metabolic network linked to the IFN response via Stat1. By utilizing quantitative metabolome profiling of all naturally occurring oxysterols upon infection or IFN-stimulation, we reveal 25HC as the only macrophage-synthesized and -secreted oxysterol. We show that 25HC can act at multiple levels as a potent paracrine inhibitor of viral infection for a broad range of viruses. We also demonstrate, using transcriptional regulatory-network analyses, genetic interventions and chromatin immunoprecipitation experiments that Stat1 directly coupled Ch25h regulation to IFN in macrophages. Our studies describe a physiological role for 25HC as a sterol-lipid effector of an innate immune pathway.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
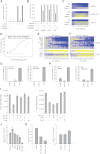
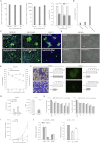
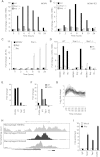
Comment in
-
Sterol-izing innate immunity.Immunity. 2013 Jan 24;38(1):3-5. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2013.01.002. Immunity. 2013. PMID: 23352217
Similar articles
-
25-Hydroxycholesterol Production by the Cholesterol-25-Hydroxylase Interferon-Stimulated Gene Restricts Mammalian Reovirus Infection.J Virol. 2018 Aug 29;92(18):e01047-18. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01047-18. Print 2018 Sep 15. J Virol. 2018. PMID: 29950420 Free PMC article.
-
Interferon-inducible cholesterol-25-hydroxylase broadly inhibits viral entry by production of 25-hydroxycholesterol.Immunity. 2013 Jan 24;38(1):92-105. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2012.11.005. Epub 2012 Dec 27. Immunity. 2013. PMID: 23273844 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid proteasomal elimination of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA reductase by interferon-γ in primary macrophages requires endogenous 25-hydroxycholesterol synthesis.Steroids. 2015 Jul;99(Pt B):219-29. doi: 10.1016/j.steroids.2015.02.022. Epub 2015 Mar 7. Steroids. 2015. PMID: 25759117 Free PMC article.
-
25-hydroxycholesterol: an integrator of antiviral ability and signaling.Front Immunol. 2023 Sep 13;14:1268104. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1268104. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37781400 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Armand-Frappier Outstanding Student Award--The emerging role of 25-hydroxycholesterol in innate immunity.Can J Microbiol. 2015 Aug;61(8):521-30. doi: 10.1139/cjm-2015-0292. Epub 2015 Jun 10. Can J Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 26182401 Review.
Cited by
-
Deciphering the modulation of gene expression by type I and II interferons combining 4sU-tagging, translational arrest and in silico promoter analysis.Nucleic Acids Res. 2013 Sep;41(17):8107-25. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt589. Epub 2013 Jul 5. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013. PMID: 23832230 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptome analysis based on RNA-seq of common innate immune responses of flounder cells to IHNV, VHSV, and HIRRV.PLoS One. 2020 Sep 28;15(9):e0239925. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0239925. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32986779 Free PMC article.
-
Diverse Immunoregulatory Roles of Oxysterols-The Oxidized Cholesterol Metabolites.Metabolites. 2020 Sep 28;10(10):384. doi: 10.3390/metabo10100384. Metabolites. 2020. PMID: 32998240 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immune Implications of Cholesterol-Containing Lipid Nanoparticles.ACS Nano. 2024 Oct 22;18(42):28480-28501. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.4c06369. Epub 2024 Oct 10. ACS Nano. 2024. PMID: 39388645 Review.
-
The Art of Viral Membrane Fusion and Penetration.Subcell Biochem. 2023;106:113-152. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-40086-5_4. Subcell Biochem. 2023. PMID: 38159225
References
-
- Adams C.M., Reitz J., De Brabander J.K., Feramisco J.D., Li L., Brown M.S., Goldstein J.L. Cholesterol and 25-hydroxycholesterol inhibit activation of SREBPs by different mechanisms, both involving SCAP and Insigs. J. Biol. Chem. 2004;279:52772–52780. - PubMed
-
- Amet T., Nonaka M., Dewan M.Z., Saitoh Y., Qi X., Ichinose S., Yamamoto N., Yamaoka S. Statin-induced inhibition of HIV-1 release from latently infected U1 cells reveals a critical role for protein prenylation in HIV-1 replication. Microbes Infect. 2008;10:471–480. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- BB/I0017351/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- BB/C5157712/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- BB/H0010181/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- BB/C511356/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- BB/H001018/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 HL067773/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- BB/C5113561/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- BB/C515771/2/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- BB/D019621/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- HL67773/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- WT066784/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- FS/05/022/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

