Bioprinting for stem cell research
- PMID: 23260439
- PMCID: PMC3534918
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tibtech.2012.10.005
Bioprinting for stem cell research
Abstract
Recently, there has been growing interest in applying bioprinting techniques to stem cell research. Several bioprinting methods have been developed utilizing acoustics, piezoelectricity, and lasers to deposit living cells onto receiving substrates. Using these technologies, spatially defined gradients of immobilized biomolecules can be engineered to direct stem cell differentiation into multiple subpopulations of different lineages. Stem cells can also be patterned in a high-throughput manner onto flexible implementation patches for tissue regeneration or onto substrates with the goal of accessing encapsulated stem cells of interest for genomic analysis. Here, we review recent achievements with bioprinting technologies in stem cell research, and identify future challenges and potential applications including tissue engineering and regenerative medicine, wound healing, and genomics.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
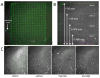
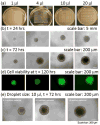
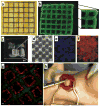
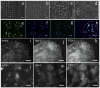

Similar articles
-
Stem cell bioprinting for applications in regenerative medicine.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2016 Nov;1383(1):115-124. doi: 10.1111/nyas.13266. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2016. PMID: 27870077 Review.
-
Three-dimensional bioprinting in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine.Biotechnol Lett. 2016 Feb;38(2):203-11. doi: 10.1007/s10529-015-1975-1. Epub 2015 Oct 14. Biotechnol Lett. 2016. PMID: 26466597 Review.
-
Three-dimensional bioprinting of stem-cell derived tissues for human regenerative medicine.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2018 Jul 5;373(1750):20170224. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2017.0224. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29786559 Free PMC article. Review.
-
3D bioprinting using stem cells.Pediatr Res. 2018 Jan;83(1-2):223-231. doi: 10.1038/pr.2017.252. Epub 2017 Nov 1. Pediatr Res. 2018. PMID: 28985202 Review.
-
Concise Review: Bioprinting of Stem Cells for Transplantable Tissue Fabrication.Stem Cells Transl Med. 2017 Oct;6(10):1940-1948. doi: 10.1002/sctm.17-0148. Epub 2017 Aug 24. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2017. PMID: 28836738 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Manipulating biological agents and cells in micro-scale volumes for applications in medicine.Chem Soc Rev. 2013 Jul 7;42(13):5788-808. doi: 10.1039/c3cs60042d. Chem Soc Rev. 2013. PMID: 23575660 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Highlights from the latest articles in advanced biomanufacturing at micro- and nano-scale.Nanomedicine (Lond). 2015 Feb;10(3):347-50. doi: 10.2217/nnm.14.210. Nanomedicine (Lond). 2015. PMID: 25707972 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Osteogenic Differentiation of Three-Dimensional Bioprinted Constructs Consisting of Human Adipose-Derived Stem Cells In Vitro and In Vivo.PLoS One. 2016 Jun 22;11(6):e0157214. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0157214. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27332814 Free PMC article.
-
Three-dimensional bioprinting using self-assembling scalable scaffold-free "tissue strands" as a new bioink.Sci Rep. 2016 Jun 27;6:28714. doi: 10.1038/srep28714. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27346373 Free PMC article.
-
Engineering an in vitro air-blood barrier by 3D bioprinting.Sci Rep. 2015 Jan 22;5:7974. doi: 10.1038/srep07974. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 25609567 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Derby B. Bioprinting: inkjet printing proteins and hybrid cell-containing materials and structures. Journal of Materials Chemistry. 2008;18:5717–5721.
-
- Demirci U, Montesano G. Single Cell Epitaxy by Acoustic Picoliter Droplets. Lab Chip. 2007;7:1139–1145. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

