Whole-genome sequencing in autism identifies hot spots for de novo germline mutation
- PMID: 23260136
- PMCID: PMC3712641
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2012.11.019
Whole-genome sequencing in autism identifies hot spots for de novo germline mutation
Abstract
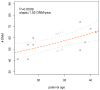
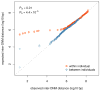
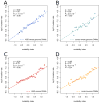
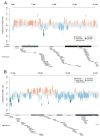
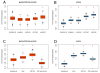
De novo mutation plays an important role in autism spectrum disorders (ASDs). Notably, pathogenic copy number variants (CNVs) are characterized by high mutation rates. We hypothesize that hypermutability is a property of ASD genes and may also include nucleotide-substitution hot spots. We investigated global patterns of germline mutation by whole-genome sequencing of monozygotic twins concordant for ASD and their parents. Mutation rates varied widely throughout the genome (by 100-fold) and could be explained by intrinsic characteristics of DNA sequence and chromatin structure. Dense clusters of mutations within individual genomes were attributable to compound mutation or gene conversion. Hypermutability was a characteristic of genes involved in ASD and other diseases. In addition, genes impacted by mutations in this study were associated with ASD in independent exome-sequencing data sets. Our findings suggest that regional hypermutation is a significant factor shaping patterns of genetic variation and disease risk in humans.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
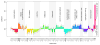

Comment in
-
Loaded dice for human genome mutation.Cell. 2012 Dec 21;151(7):1399-400. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2012.12.002. Cell. 2012. PMID: 23260131
Similar articles
-
De novo structural mutation rates and gamete-of-origin biases revealed through genome sequencing of 2,396 families.Am J Hum Genet. 2021 Apr 1;108(4):597-607. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2021.02.012. Epub 2021 Mar 5. Am J Hum Genet. 2021. PMID: 33675682 Free PMC article.
-
Parental influence on human germline de novo mutations in 1,548 trios from Iceland.Nature. 2017 Sep 28;549(7673):519-522. doi: 10.1038/nature24018. Epub 2017 Sep 20. Nature. 2017. PMID: 28959963
-
Strong association of de novo copy number mutations with autism.Science. 2007 Apr 20;316(5823):445-9. doi: 10.1126/science.1138659. Epub 2007 Mar 15. Science. 2007. PMID: 17363630 Free PMC article.
-
The genetics of autism.Pediatrics. 2004 May;113(5):e472-86. doi: 10.1542/peds.113.5.e472. Pediatrics. 2004. PMID: 15121991 Review.
-
From the periphery to centre stage: de novo single nucleotide variants play a key role in human genetic disease.J Med Genet. 2013 Apr;50(4):203-11. doi: 10.1136/jmedgenet-2013-101519. Epub 2013 Feb 9. J Med Genet. 2013. PMID: 23396985 Review.
Cited by
-
Properties and rates of germline mutations in humans.Trends Genet. 2013 Oct;29(10):575-84. doi: 10.1016/j.tig.2013.04.005. Epub 2013 May 16. Trends Genet. 2013. PMID: 23684843 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Parental mosaicism for apparent de novo genetic variants: Scope, detection, and counseling challenges.Prenat Diagn. 2022 Jun;42(7):811-821. doi: 10.1002/pd.6144. Epub 2022 Apr 14. Prenat Diagn. 2022. PMID: 35394072 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Adhesion-GPCR BAI1 Promotes Excitatory Synaptogenesis by Coordinating Bidirectional Trans-synaptic Signaling.J Neurosci. 2018 Sep 26;38(39):8388-8406. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3461-17.2018. Epub 2018 Aug 17. J Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 30120207 Free PMC article.
-
Genetics and epigenetics of autism spectrum disorder-current evidence in the field.J Appl Genet. 2019 Feb;60(1):37-47. doi: 10.1007/s13353-018-00480-w. Epub 2019 Jan 10. J Appl Genet. 2019. PMID: 30627967 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The adhesion-GPCR BAI1 shapes dendritic arbors via Bcr-mediated RhoA activation causing late growth arrest.Elife. 2019 Aug 28;8:e47566. doi: 10.7554/eLife.47566. Elife. 2019. PMID: 31461398 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Amiel J, Rio M, de Pontual L, Redon R, Malan V, Boddaert N, Plouin P, Carter NP, Lyonnet S, Munnich A, et al. Mutations in TCF4, encoding a class I basic helix-loop-helix transcription factor, are responsible for Pitt-Hopkins syndrome, a severe epileptic encephalopathy associated with autonomic dysfunction. Am J Hum Genet. 2007;80:988–993. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Berkel S, Marshall CR, Weiss B, Howe J, Roeth R, Moog U, Endris V, Roberts W, Szatmari P, Pinto D, et al. Mutations in the SHANK2 synaptic scaffolding gene in autism spectrum disorder and mental retardation. Nat Genet. 2010;42:489–491. - PubMed
-
- Chen JM, Cooper DN, Chuzhanova N, Ferec C, Patrinos GP. Gene conversion: mechanisms, evolution and human disease. Nat Rev Genet. 2007;8:762–775. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

