Multiparametric analysis of cell-free DNA in melanoma patients
- PMID: 23209607
- PMCID: PMC3507877
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0049843
Multiparametric analysis of cell-free DNA in melanoma patients
Abstract
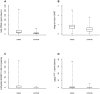
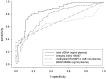
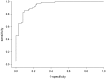
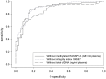
Cell-free DNA in blood (cfDNA) represents a promising biomarker for cancer diagnosis. Total cfDNA concentration showed a scarce discriminatory power between patients and controls. A higher specificity in cancer diagnosis can be achieved by detecting tumor specific alterations in cfDNA, such as DNA integrity, genetic and epigenetic modifications.The aim of the present study was to identify a sequential multi-marker panel in cfDNA able to increase the predictive capability in the diagnosis of cutaneous melanoma in comparison with each single marker alone. To this purpose, we tested total cfDNA concentration, cfDNA integrity, BRAF(V600E) mutation and RASSF1A promoter methylation associated to cfDNA in a series of 76 melanoma patients and 63 healthy controls. The chosen biomarkers were assayed in cfDNA samples by qPCR. Comparison of biomarkers distribution in cases and controls was performed by a logistic regression model in both univariate and multivariate analysis. The predictive capability of each logistic model was investigated by means of the area under the ROC curve (AUC). To aid the reader to interpret the value of the AUC, values between 0.6 and 0.7, between 0.71 and 0.8 and greater than 0.8 were considered as indicating a weak predictive, satisfactory and good predictive capacity, respectively. The AUC value for each biomarker (univariate logistic model) was weak/satisfactory ranging between 0.64 (BRAF(V600E)) to 0.85 (total cfDNA). A good overall predictive capability for the final logistic model was found with an AUC of 0.95. The highest predictive capability was given by total cfDNA (AUC:0.86) followed by integrity index 180/67 (AUC:0.90) and methylated RASSF1A (AUC:0.89).An approach based on the simultaneous determination of three biomarkers (total cfDNA, integrity index 180/67 and methylated RASSF1A) could improve the diagnostic performance in melanoma.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Tumor-Related Methylated Cell-Free DNA and Circulating Tumor Cells in Melanoma.Front Mol Biosci. 2016 Jan 8;2:76. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2015.00076. eCollection 2015. Front Mol Biosci. 2016. PMID: 26779490 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating cell-free DNA in plasma of melanoma patients: qualitative and quantitative considerations.Clin Chim Acta. 2011 Nov 20;412(23-24):2141-5. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2011.07.027. Epub 2011 Aug 3. Clin Chim Acta. 2011. PMID: 21839068
-
Quantitative analysis of the BRAF V600E mutation in circulating tumor-derived DNA in melanoma patients using competitive allele-specific TaqMan PCR.Int J Clin Oncol. 2016 Oct;21(5):981-988. doi: 10.1007/s10147-016-0976-y. Epub 2016 Apr 4. Int J Clin Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27041702
-
Liquid biopsy utility for the surveillance of cutaneous malignant melanoma patients.Mol Oncol. 2016 Mar;10(3):450-63. doi: 10.1016/j.molonc.2015.12.008. Epub 2015 Dec 17. Mol Oncol. 2016. PMID: 26778792 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diagnostic Capacity of RASSF1A Promoter Methylation as a Biomarker in Tissue, Brushing, and Blood Samples of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma.EBioMedicine. 2017 Apr;18:32-40. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2017.03.038. Epub 2017 Apr 2. EBioMedicine. 2017. PMID: 28396012 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Machine Learning Algorithm to Predict Worsening of Flexion Range of Motion After Total Knee Arthroplasty.Arthroplast Today. 2022 Aug 19;17:66-73. doi: 10.1016/j.artd.2022.07.011. eCollection 2022 Oct. Arthroplast Today. 2022. PMID: 36042941 Free PMC article.
-
Liquid biopsies: genotyping circulating tumor DNA.J Clin Oncol. 2014 Feb 20;32(6):579-86. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2012.45.2011. Epub 2014 Jan 21. J Clin Oncol. 2014. PMID: 24449238 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Applicability of liquid biopsies to represent the mutational profile of tumor tissue from different cancer entities.Oncogene. 2021 Aug;40(33):5204-5212. doi: 10.1038/s41388-021-01928-w. Epub 2021 Jul 6. Oncogene. 2021. PMID: 34230613 Free PMC article.
-
Liquid biopsy for early stage lung cancer.J Thorac Dis. 2018 Apr;10(Suppl 7):S876-S881. doi: 10.21037/jtd.2018.04.26. J Thorac Dis. 2018. PMID: 29780634 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cell-free circulating tumor DNA in cancer.Chin J Cancer. 2016 Apr 7;35:36. doi: 10.1186/s40880-016-0092-4. Chin J Cancer. 2016. PMID: 27056366 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hodgson DR, Wellings R, Orr MC, McCormack R, Malone M, et al. (2010) Circulating tumour-derived predictive biomarkers in oncology. Drug Discov Today 15: 98–101. - PubMed
-
- Fleischhacker M, Schmidt B (2007) Circulating nucleic acids (CNAs) and cancer-a survey. Biochim Biophys Acta 1775: 181–232. - PubMed
-
- Jung K, Fleischhacker M, Rabien A (2010) Cell-free DNA in the blood as a solid tumor biomarker–a critical appraisal of the literature. Clin Chim Acta 411: 1611–24. - PubMed
-
- Wang BG, Huang HY, Chen YC, Bristow RE, Kassauei K, et al. (2003) Increased plasma DNA integrity in cancer patients. Cancer Res 63: 3966–8. - PubMed
-
- Umetani N, Giuliano AE, Hiramatsu SH, Amersi F, Nakagawa T, et al. (2006) Prediction of breast tumor progression by integrity of free circulating DNA in serum. J Clin Oncol 24: 4270–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

