The role of auxin-cytokinin antagonism in plant-pathogen interactions
- PMID: 23209407
- PMCID: PMC3510258
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003026
The role of auxin-cytokinin antagonism in plant-pathogen interactions
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
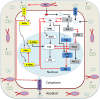
Figures
Similar articles
-
Assessment of Cytokinin-Induced Immunity Through Quantification of Hyaloperonospora arabidopsidis Infection in Arabidopsis thaliana.Methods Mol Biol. 2017;1569:113-126. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-6831-2_9. Methods Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 28265992
-
Integration of boolean models on hormonal interactions and prospects of cytokinin-auxin crosstalk in plant immunity.Plant Signal Behav. 2013 Apr;8(4):e23890. doi: 10.4161/psb.23890. Epub 2013 Feb 20. Plant Signal Behav. 2013. PMID: 23425857 Free PMC article.
-
Abscisic Acid-Cytokinin Antagonism Modulates Resistance Against Pseudomonas syringae in Tobacco.Phytopathology. 2014 Dec;104(12):1283-8. doi: 10.1094/PHYTO-03-14-0076-R. Phytopathology. 2014. PMID: 24941328
-
Auxin crosstalk to plant immune networks: a plant-pathogen interaction perspective.Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2015;16(5):389-94. doi: 10.2174/1389203716666150330124911. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2015. PMID: 25824384 Review.
-
Making sense of hormone crosstalk during plant immune responses.Cell Host Microbe. 2008 Jun 12;3(6):348-51. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2008.05.009. Cell Host Microbe. 2008. PMID: 18541211 Review.
Cited by
-
Growth-defense tradeoffs in plants: a balancing act to optimize fitness.Mol Plant. 2014 Aug;7(8):1267-1287. doi: 10.1093/mp/ssu049. Epub 2014 Apr 27. Mol Plant. 2014. PMID: 24777989 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Involvement of potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) MKK6 in response to potato virus Y.PLoS One. 2014 Aug 11;9(8):e104553. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0104553. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25111695 Free PMC article.
-
Bacillus aryabhattai SRB02 tolerates oxidative and nitrosative stress and promotes the growth of soybean by modulating the production of phytohormones.PLoS One. 2017 Mar 10;12(3):e0173203. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0173203. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28282395 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative transcriptome profiling of resistant and susceptible foxtail millet responses to Sclerospora graminicola infection.BMC Plant Biol. 2022 Dec 6;22(1):567. doi: 10.1186/s12870-022-03963-5. BMC Plant Biol. 2022. PMID: 36471245 Free PMC article.
-
Cytokinins.Arabidopsis Book. 2014 Jan 2;12:e0168. doi: 10.1199/tab.0168. eCollection 2014 Jan 2. Arabidopsis Book. 2014. PMID: 24465173 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Skoog F, Miller CO (1957) Chemical regulation of growth and organ formation in plant tissues cultured in vitro. Symp Soc Exp Biol 54: 118–130. - PubMed
-
- Dello Ioio R, Nakamura K, Moubayidin L, Perilli S, Taniguchi M, et al. (2008) A genetic framework for the control of cell division and differentiation in the root meristem. Science 322: 1380–1384. - PubMed
-
- Shimizu-Sato S, Tanaka M, Mori H (2009) Auxin-cytokinin interactions in the control of shoot branching. Plant Mol Biol 69: 429–435. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

