Protein export by the mycobacterial SecA2 system is determined by the preprotein mature domain
- PMID: 23204463
- PMCID: PMC3562099
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.02032-12
Protein export by the mycobacterial SecA2 system is determined by the preprotein mature domain
Abstract
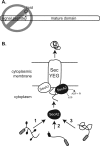
At the core of the bacterial general secretion (Sec) pathway is the SecA ATPase, which powers translocation of unfolded preproteins containing Sec signal sequences through the SecYEG membrane channel. Mycobacteria have two nonredundant SecA homologs: SecA1 and SecA2. While the essential SecA1 handles "housekeeping" export, the nonessential SecA2 exports a subset of proteins and is required for Mycobacterium tuberculosis virulence. Currently, it is not understood how SecA2 contributes to Sec export in mycobacteria. In this study, we focused on identifying the features of two SecA2 substrates that target them to SecA2 for export, the Ms1704 and Ms1712 lipoproteins of the model organism Mycobacterium smegmatis. We found that the mature domains of Ms1704 and Ms1712, not the N-terminal signal sequences, confer SecA2-dependent export. We also demonstrated that the lipid modification and the extreme N terminus of the mature protein do not impart the requirement for SecA2 in export. We further showed that the Ms1704 mature domain can be efficiently exported by the twin-arginine translocation (Tat) pathway. Because the Tat system exports only folded proteins, this result implies that SecA2 substrates can fold in the cytoplasm and suggests a putative role of SecA2 in enabling export of such proteins. Thus, the mycobacterial SecA2 system may represent another way that bacteria solve the problem of exporting proteins that can fold in the cytoplasm.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Suppressor analysis reveals a role for SecY in the SecA2-dependent protein export pathway of Mycobacteria.J Bacteriol. 2013 Oct;195(19):4456-65. doi: 10.1128/JB.00630-13. Epub 2013 Aug 2. J Bacteriol. 2013. PMID: 23913320 Free PMC article.
-
Two nonredundant SecA homologues function in mycobacteria.J Bacteriol. 2001 Dec;183(24):6979-90. doi: 10.1128/JB.183.24.6979-6990.2001. J Bacteriol. 2001. PMID: 11717254 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of two Mycobacterium smegmatis lipoproteins exported by a SecA2-dependent pathway.J Bacteriol. 2007 Jul;189(14):5090-100. doi: 10.1128/JB.00163-07. Epub 2007 May 11. J Bacteriol. 2007. PMID: 17496088 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging themes in SecA2-mediated protein export.Nat Rev Microbiol. 2012 Nov;10(11):779-89. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro2874. Epub 2012 Sep 24. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 23000954 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Sec Pathways and Exportomes of Mycobacterium tuberculosis.Microbiol Spectr. 2017 Apr;5(2). doi: 10.1128/microbiolspec.TBTB2-0013-2016. Microbiol Spectr. 2017. PMID: 28387178 Review.
Cited by
-
Characterization of the Protective Immune Responses Conferred by Recombinant BCG Overexpressing Components of Mycobacterium tuberculosis Sec Protein Export System.Vaccines (Basel). 2022 Jun 14;10(6):945. doi: 10.3390/vaccines10060945. Vaccines (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35746553 Free PMC article.
-
Structural Similarities and Differences between Two Functionally Distinct SecA Proteins, Mycobacterium tuberculosis SecA1 and SecA2.J Bacteriol. 2015 Dec 14;198(4):720-30. doi: 10.1128/JB.00696-15. J Bacteriol. 2015. PMID: 26668263 Free PMC article.
-
Understanding HIV-Mycobacteria synergism through comparative proteomics of intra-phagosomal mycobacteria during mono- and HIV co-infection.Sci Rep. 2016 Feb 26;6:22060. doi: 10.1038/srep22060. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 26916387 Free PMC article.
-
Suppressor analysis reveals a role for SecY in the SecA2-dependent protein export pathway of Mycobacteria.J Bacteriol. 2013 Oct;195(19):4456-65. doi: 10.1128/JB.00630-13. Epub 2013 Aug 2. J Bacteriol. 2013. PMID: 23913320 Free PMC article.
-
Bacillus anthracis SlaQ Promotes S-Layer Protein Assembly.J Bacteriol. 2015 Oct;197(19):3216-27. doi: 10.1128/JB.00492-15. Epub 2015 Jul 27. J Bacteriol. 2015. PMID: 26216847 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Palmer T, Berks BC. 2012. The twin-arginine translocation (Tat) protein export pathway. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 10:483–496 - PubMed
-
- Brundage L, Hendrick JP, Schiebel E, Driessen AJ, Wickner W. 1990. The purified E. coli integral membrane protein SecY/E is sufficient for reconstitution of SecA-dependent precursor protein translocation. Cell 62:649–657 - PubMed
-
- von Heijne G. 1990. The signal peptide. J. Membr. Biol. 115:195–201 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

