Aldo-keto reductase family 1 member C3 (AKR1C3) is a biomarker and therapeutic target for castration-resistant prostate cancer
- PMID: 23196782
- PMCID: PMC3563708
- DOI: 10.2119/molmed.2012.00296
Aldo-keto reductase family 1 member C3 (AKR1C3) is a biomarker and therapeutic target for castration-resistant prostate cancer
Abstract
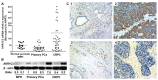
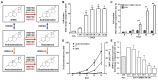
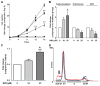
Current endocrine treatment for advanced prostate cancer does not result in a complete ablation of adrenal androgens. Adrenal androgens can be metabolized by prostate cancer cells, which is one of the mechanisms associated with progression to castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC). Aldo-keto reductase family 1 member C3 (AKR1C3) is a steroidogenic enzyme that plays a crucial role in the conversion of adrenal androgen dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) into high-affinity ligands for the androgen receptor (testosterone [T] and dihydrotestosterone [DHT]). The aim of this study was to examine whether AKR1C3 could be used as a marker and therapeutic target for CRPC. AKR1C3 mRNA and protein levels were upregulated in CRPC tissue, compared with benign prostate and primary prostate cancer tissue. High AKR1C3 levels were found only in a subset of CRPC patients. AKR1C3 can be used as a biomarker for active intratumoral steroidogenesis and can be measured in biopsy or transurethral resection of the prostate specimens. DuCaP (a CRPC cell line that has high AKR1C3 expression levels) used and converted DHEA under hormone-depleted conditions into T and DHT. The DHEA-induced growth of DuCaP could be antagonized by indomethacine, an inhibitor of AKR1C3. This study indicates that AKR1C3 can be considered a therapeutic target in a subgroup of patients with high AKR1C3 expression.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Overexpression of aldo-keto reductase 1C3 (AKR1C3) in LNCaP cells diverts androgen metabolism towards testosterone resulting in resistance to the 5α-reductase inhibitor finasteride.J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2012 May;130(1-2):7-15. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2011.12.012. Epub 2012 Jan 12. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2012. PMID: 22265960 Free PMC article.
-
Development of potent and selective indomethacin analogues for the inhibition of AKR1C3 (Type 5 17β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase/prostaglandin F synthase) in castrate-resistant prostate cancer.J Med Chem. 2013 Mar 28;56(6):2429-46. doi: 10.1021/jm3017656. Epub 2013 Mar 13. J Med Chem. 2013. PMID: 23432095 Free PMC article.
-
Steroidogenic enzymes and stem cell markers are upregulated during androgen deprivation in prostate cancer.Mol Med. 2011;17(7-8):657-64. doi: 10.2119/molmed.2010.00143. Epub 2011 Feb 22. Mol Med. 2011. PMID: 21365123 Free PMC article.
-
The DHEA-sulfate depot following P450c17 inhibition supports the case for AKR1C3 inhibition in high risk localized and advanced castration resistant prostate cancer.Chem Biol Interact. 2015 Jun 5;234:332-8. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2014.12.012. Epub 2014 Dec 13. Chem Biol Interact. 2015. PMID: 25514466 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibitors of type 5 17β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase (AKR1C3): overview and structural insights.J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2011 May;125(1-2):95-104. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2010.11.004. Epub 2010 Nov 16. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2011. PMID: 21087665 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Computational modeling studies reveal the origin of the binding preference of 3-(3,4-di hydroisoquinolin-2(1H)-ylsulfonyl)benzoic acids for AKR1C3 over its isoforms.Protein Sci. 2022 Dec;31(12):e4499. doi: 10.1002/pro.4499. Protein Sci. 2022. PMID: 36335585 Free PMC article.
-
The Potential Preventive and Therapeutic Roles of NSAIDs in Prostate Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Nov 16;15(22):5435. doi: 10.3390/cancers15225435. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38001694 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Aldo-keto reductases: Role in cancer development and theranostics.Oncol Res. 2024 Jul 17;32(8):1287-1308. doi: 10.32604/or.2024.049918. eCollection 2024. Oncol Res. 2024. PMID: 39055885 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of adrenal derived androgens in castration resistant prostate cancer.J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2020 Mar;197:105506. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2019.105506. Epub 2019 Oct 28. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2020. PMID: 31672619 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structural and Functional Biology of Aldo-Keto Reductase Steroid-Transforming Enzymes.Endocr Rev. 2019 Apr 1;40(2):447-475. doi: 10.1210/er.2018-00089. Endocr Rev. 2019. PMID: 30137266 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lee DJ, et al. Novel therapeutics for the management of castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC) BJU Int. 2012;109:968–85. - PubMed
-
- Tsao CK, Galsky MD, Small AC, Yee T, Oh WK. Targeting the androgen receptor signalling axis in castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC) BJU Int. 2012;110:1580–8. - PubMed
-
- Mottet N, et al. EAU guidelines on prostate cancer. Part II: Treatment of advanced, relapsing, and castration-resistant prostate cancer. Eur Urol. 2011;59:572–83. - PubMed
-
- Nishiyama T, Hashimoto Y, Takahashi K. The influence of androgen deprivation therapy on dihydrotestosterone levels in the prostatic tissue of patients with prostate cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2004;10:7121–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

